Shoulder surfing is a common security threat where an attacker physically observes a victim's sensitive information, such as passwords or PINs, by looking over their shoulder. This technique often occurs in public spaces like ATMs, coffee shops, or open office environments where users enter confidential data on their devices. By capturing this information through direct observation, attackers can gain unauthorized access to personal accounts or corporate systems. In information security, shoulder surfing can be mitigated through the use of privacy screens on monitors and mobile devices, which limit viewing angles and prevent unauthorized people from seeing displayed data. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) further reduces the risk by requiring additional verification steps beyond just a password. Employee training on situational awareness and secure input habits is critical to strengthen defenses against shoulder surfing attacks.
Table of Comparison
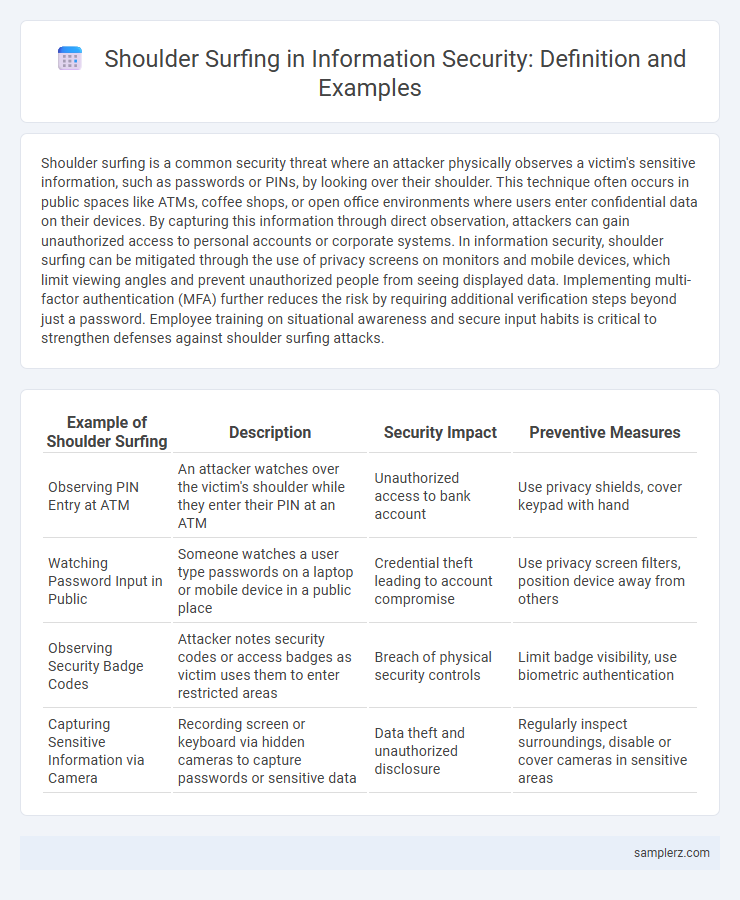
| Example of Shoulder Surfing | Description | Security Impact | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Observing PIN Entry at ATM | An attacker watches over the victim's shoulder while they enter their PIN at an ATM | Unauthorized access to bank account | Use privacy shields, cover keypad with hand |
| Watching Password Input in Public | Someone watches a user type passwords on a laptop or mobile device in a public place | Credential theft leading to account compromise | Use privacy screen filters, position device away from others |
| Observing Security Badge Codes | Attacker notes security codes or access badges as victim uses them to enter restricted areas | Breach of physical security controls | Limit badge visibility, use biometric authentication |
| Capturing Sensitive Information via Camera | Recording screen or keyboard via hidden cameras to capture passwords or sensitive data | Data theft and unauthorized disclosure | Regularly inspect surroundings, disable or cover cameras in sensitive areas |
Common Scenarios of Shoulder Surfing in Daily Life
Common scenarios of shoulder surfing in daily life include observing individuals entering passwords at ATMs, typing login credentials on laptops in public places, and accessing sensitive information on smartphones in crowded environments. Attackers often exploit busy areas such as coffee shops, public transport, and office spaces with open layouts to discreetly gather confidential data. Using binoculars or hidden cameras further facilitates unauthorized data capture in these everyday situations.
Real-World Incidents Involving Shoulder Surfing
Real-world incidents involving shoulder surfing include cybercriminals observing employees enter passwords at ATMs or public kiosks, leading to unauthorized account access and financial theft. In one documented case, attackers used binoculars from a nearby building to capture login credentials of remote workers on outdoor balconies, resulting in compromised corporate networks. These threats emphasize the importance of secure input methods and privacy screens in preventing sensitive data exposure in public spaces.
ATM PIN Theft: A Classic Shoulder Surfing Example
ATM PIN theft is a common example of shoulder surfing in information security, where attackers discreetly observe victims entering their PINs at cash machines. These criminals often use close physical proximity or hidden cameras to capture sensitive numerical inputs. Preventing such attacks involves shielding the keypad with your hand and remaining vigilant of suspicious individuals nearby.
Shoulder Surfing in Public Transportation Settings
Shoulder surfing in public transportation settings occurs when attackers discreetly observe individuals accessing sensitive information on smartphones or laptops during commutes. This type of attack exploits crowded environments such as buses, trains, or subways where privacy is limited and distractions are common. Awareness and physical barriers, like privacy screen protectors, help mitigate risks of unauthorized data exposure in these scenarios.
Office Environment: Risks of Shoulder Surfing Among Colleagues
In an office environment, shoulder surfing poses significant risks as employees may unknowingly expose sensitive information like passwords or confidential emails when working in close proximity. Colleagues or visitors can easily glimpse over shoulders during login processes or while reviewing private documents, leading to potential data breaches. Implementing privacy screens and promoting awareness about secure workspace practices are essential to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
Online Banking and Shoulder Surfing Vulnerabilities
Shoulder surfing in online banking occurs when attackers visually capture sensitive information, such as login credentials and account numbers, by watching over a user's shoulder or recording screens covertly. Vulnerabilities include unsecured public Wi-Fi environments and lack of privacy screens, which increase the risk of unauthorized access to financial data. Mitigating these risks involves implementing multi-factor authentication and educating users on the dangers of entering sensitive information in exposed locations.
Mobile Device Exposure: Shoulder Surfing in Cafés
Mobile device exposure to shoulder surfing in cafes poses a significant risk to information security, as attackers can easily observe passwords, PINs, or sensitive communications over the user's shoulder. Public Wi-Fi networks commonly found in cafes can compound vulnerabilities by enabling interception of data once credentials are compromised. Implementing screen privacy filters and two-factor authentication helps mitigate the threats associated with shoulder surfing in such environments.
Social Engineering Attacks Leveraging Shoulder Surfing
Shoulder surfing in information security involves attackers observing or recording sensitive information such as passwords, PINs, or security codes by looking over a victim's shoulder in public or crowded spaces. Social engineering attacks leveraging shoulder surfing exploit human behavior and environmental vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access without technical hacking. Common scenarios include attackers using cameras or binoculars to capture login credentials at ATMs, open office spaces, or public Wi-Fi hotspots.
Security Breaches Through Shoulder Surfing at Conferences
Security breaches through shoulder surfing at conferences occur when attackers discreetly observe attendees entering sensitive information like passwords or access codes on laptops and mobile devices. Conference environments often expose individuals to heightened risks due to crowded spaces and limited privacy, facilitating unauthorized data capture. Implementing privacy screens and awareness training significantly reduces the likelihood of confidential information being intercepted in these settings.
Protecting Sensitive Information from Shoulder Surfing Threats
Shoulder surfing occurs when an attacker visually captures sensitive information such as passwords, PINs, or confidential data by observing over a person's shoulder in public or unsecured environments. To protect against this threat, organizations should implement privacy screens on devices, enforce strict clean desk policies, and educate employees on the risks of entering sensitive information in open areas. Using multi-factor authentication and biometric verification further mitigates the impact of compromised credentials from shoulder surfing incidents.
example of shoulder surfing in information security Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com