Sleep techniques in intrusion refer to methods attackers use to evade detection by security systems. One common example is the "polite sleep" technique, where malicious processes insert deliberate delays between their actions. This tactic reduces the chances of triggering real-time monitoring alerts by mimicking normal system behavior and spreading out suspicious activities over extended periods. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) must account for sleep techniques to accurately identify threats. Data analysis of network traffic and process behavior often reveals irregular timing patterns indicative of sleep tactics. Security solutions leverage behavioral analytics and extended observation windows to detect intrusions that use sleep techniques, improving the overall effectiveness of threat mitigation.
Table of Comparison
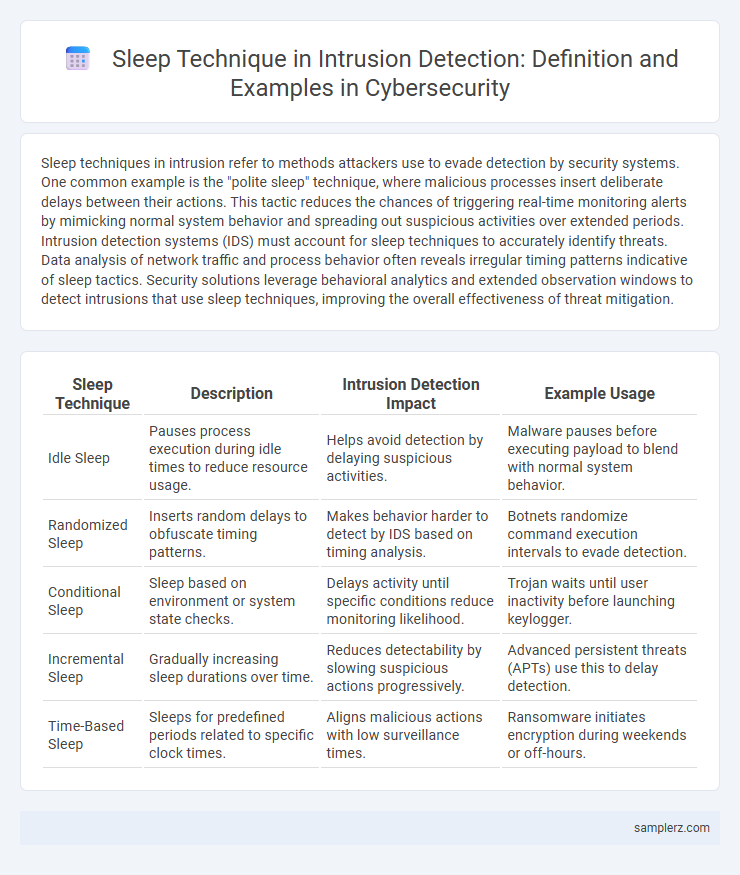
| Sleep Technique | Description | Intrusion Detection Impact | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Idle Sleep | Pauses process execution during idle times to reduce resource usage. | Helps avoid detection by delaying suspicious activities. | Malware pauses before executing payload to blend with normal system behavior. |
| Randomized Sleep | Inserts random delays to obfuscate timing patterns. | Makes behavior harder to detect by IDS based on timing analysis. | Botnets randomize command execution intervals to evade detection. |
| Conditional Sleep | Sleep based on environment or system state checks. | Delays activity until specific conditions reduce monitoring likelihood. | Trojan waits until user inactivity before launching keylogger. |
| Incremental Sleep | Gradually increasing sleep durations over time. | Reduces detectability by slowing suspicious actions progressively. | Advanced persistent threats (APTs) use this to delay detection. |
| Time-Based Sleep | Sleeps for predefined periods related to specific clock times. | Aligns malicious actions with low surveillance times. | Ransomware initiates encryption during weekends or off-hours. |
Understanding Sleep Techniques in Intrusion Attacks
Sleep techniques in intrusion attacks exploit system idle states by inserting deliberate delays to evade detection by time-based security measures. Attackers use these methods to slow down the execution of malicious payloads, avoiding pattern recognition by intrusion detection systems (IDS) that monitor high-frequency activity. Understanding these techniques helps security analysts design more robust detection algorithms that account for temporal evasion strategies in cyber threats.
Common Sleep Methods Used by Attackers
Common sleep methods used by attackers include the use of timed delays or sleep commands embedded within malware scripts to evade detection by security scanners. Techniques such as "sleep()" functions in programming languages like Python or PowerShell intentionally pause execution, allowing malicious activities to bypass behavioral analysis during these inactive periods. Attackers often vary sleep durations to disrupt anomaly detection systems and prolong persistence within compromised networks.
Real-World Examples of Sleep Technique Exploitation
Attackers have exploited the sleep technique in intrusion scenarios by delaying command execution to bypass security monitoring systems, as seen in the 2020 SolarWinds breach where malware paused operations to avoid detection during scheduled scans. In ransomware attacks, adversaries have used sleep commands to synchronize encrypted file access, minimizing suspicious activity logs and delaying incident response efforts. These real-world cases highlight the need for advanced anomaly detection that can identify unusual process suspensions indicative of sleep technique exploitation.
How Malware Uses Sleep Techniques to Evade Detection
Malware employs sleep techniques by deliberately pausing its malicious activities for specific time intervals or until triggered by certain events, thereby avoiding real-time detection by security systems. This method exploits system timers and sleep functions to remain dormant, reducing network activity and evading behavioral analysis tools focused on anomalous patterns. By using varying sleep durations, sophisticated malware bypasses heuristic scans and time-based monitoring, prolonging its undetected presence within the target environment.
Sleep-Based Evasion in Advanced Persistent Threats (APT)
Sleep-based evasion techniques in Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) involve attackers deliberately pausing malicious activities to avoid detection by security systems. These tactics exploit system sleep modes or inject delays between actions to bypass behavioral analysis and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools. By leveraging prolonged inactivity or timed sleeps, APT actors maintain persistence while minimizing their digital footprint within targeted networks.
Case Study: Sleep Function Abuse in Recent Intrusions
Sleep function abuse in recent intrusions exemplifies how attackers exploit delay techniques to evade detection in cybersecurity environments. Attackers inject sleep commands in malware to postpone malicious actions, bypassing time-based analysis and sandbox detection systems. This tactic complicates real-time monitoring and emphasizes the need for advanced behavior-based threat detection.
Detecting Suspicious Sleep Patterns in Network Traffic
Detecting suspicious sleep patterns in network traffic involves analyzing unusual delays or periodic idle times in communication streams that may indicate stealthy intrusion attempts. Advanced intrusion detection systems employ machine learning algorithms to identify these irregular sleep intervals, distinguishing between normal latency and maliciously induced pauses designed to evade detection. Monitoring such patterns enhances early detection of covert attacks like slow-rate denial-of-service or data exfiltration through timing channels.
Mitigation Strategies Against Sleep Technique Attacks
Mitigation strategies against sleep technique attacks include implementing anomaly detection systems that monitor unusual delay patterns in network traffic and applying strict timeout policies to prevent indefinite resource waiting. Network segmentation and regular security audits help limit the attack surface and detect potential exploitation of sleep mechanisms. Employing rate limiting and adaptive defense algorithms further reduces the effectiveness of sleep-based intrusion tactics.
Sleep Obfuscation and Its Impact on Security Monitoring
Sleep obfuscation techniques manipulate system sleep intervals to evade detection by security monitoring tools, delaying or hiding malicious activities within these quiet periods. By inserting stealth sleep commands, attackers reduce their operational footprint, making it challenging for intrusion detection systems (IDS) to correlate suspicious behavior with real-time events. Effective security monitoring requires advanced anomaly detection algorithms capable of recognizing irregular sleep patterns and delayed event signatures to mitigate the impact of sleep obfuscation on threat detection.
Future Trends: Evolution of Sleep Techniques in Cyber Intrusions
Emerging sleep techniques in cyber intrusions leverage AI-driven modulation to mimic legitimate system pauses, enhancing stealth in advanced persistent threats (APTs). Quantum computing integration is poised to revolutionize these methods by enabling near-instantaneous adaptation and evasion of traditional detection algorithms. Future trends indicate a shift towards bio-inspired sleep patterns, utilizing neural network mimicry to further obscure malicious intrusions within complex environments.
example of sleep technique in intrusion Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com