A sandbox in endpoint security is an isolated environment where suspicious files or programs are executed to monitor their behavior without risking the host system. This technique helps detect malware by analyzing actions such as unauthorized file modifications or network connections in a controlled setting. Sandboxing is a critical component in advanced threat protection tools used by enterprises to prevent endpoint breaches. Endpoint security solutions like CrowdStrike Falcon and Symantec Endpoint Protection utilize sandbox technology to enhance malware detection capabilities. These platforms gather detailed telemetry data during sandbox execution, enabling rapid identification of zero-day threats and polymorphic malware. By integrating sandbox analysis, organizations strengthen their defense posture against sophisticated cyberattacks targeting endpoint devices.
Table of Comparison
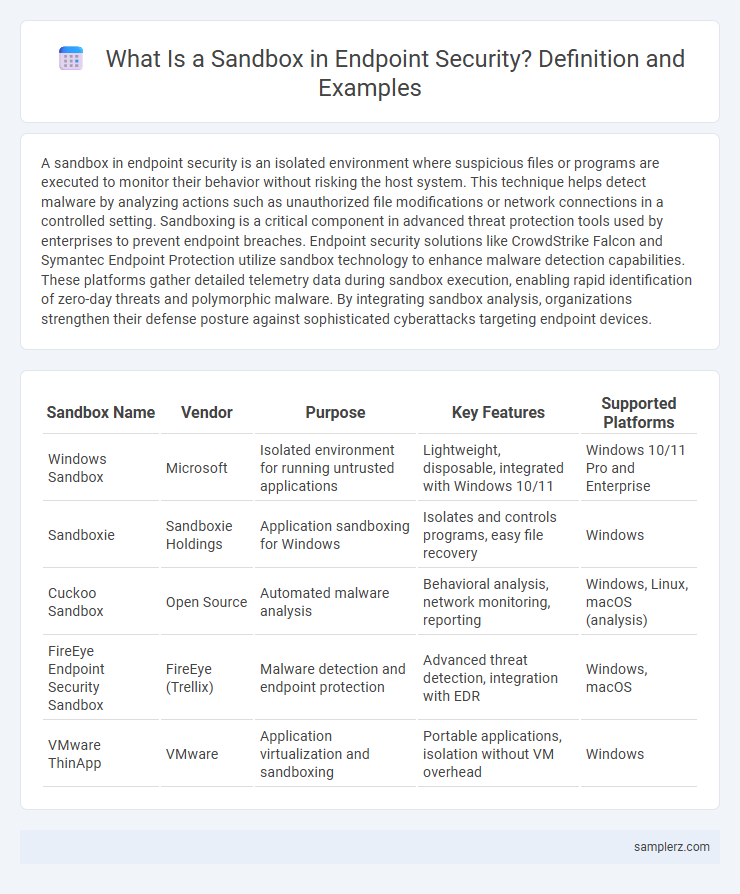
| Sandbox Name | Vendor | Purpose | Key Features | Supported Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Sandbox | Microsoft | Isolated environment for running untrusted applications | Lightweight, disposable, integrated with Windows 10/11 | Windows 10/11 Pro and Enterprise |
| Sandboxie | Sandboxie Holdings | Application sandboxing for Windows | Isolates and controls programs, easy file recovery | Windows |
| Cuckoo Sandbox | Open Source | Automated malware analysis | Behavioral analysis, network monitoring, reporting | Windows, Linux, macOS (analysis) |
| FireEye Endpoint Security Sandbox | FireEye (Trellix) | Malware detection and endpoint protection | Advanced threat detection, integration with EDR | Windows, macOS |
| VMware ThinApp | VMware | Application virtualization and sandboxing | Portable applications, isolation without VM overhead | Windows |
Introduction to Endpoint Sandboxing
Endpoint sandboxing isolates suspicious files in a controlled virtual environment to analyze their behavior without risking system integrity. This technique detects zero-day threats and malware by observing execution patterns and preventing malicious code from affecting endpoint devices. Advanced endpoint sandbox solutions integrate with antivirus and threat intelligence platforms for comprehensive protection.
Key Features of Endpoint Sandboxing
Endpoint sandboxing provides isolated environments to analyze suspicious files or code without risking the host system's integrity. Key features include real-time threat detection, behavioral analysis of malware, and automated remediation actions to prevent endpoint compromise. This technique enhances endpoint protection by identifying zero-day attacks and advanced persistent threats through controlled execution and monitoring.
Benefits of Using Sandboxing on Endpoints
Sandboxing on endpoints isolates suspicious files and applications in a secure environment, preventing potential malware from impacting the operating system or network. This containment approach enhances threat detection accuracy by allowing real-time analysis without risking endpoint integrity. Organizations benefit from reduced infection rates and improved incident response times through sandbox technology integration.
Common Use Cases for Endpoint Sandboxes
Endpoint sandboxes are primarily used to analyze suspicious files and detect zero-day malware by executing them in a controlled environment. They help identify ransomware behavior, phishing attachments, and advanced persistent threats (APTs) before these threats can impact the endpoint. This proactive threat detection enhances overall security posture by enabling swift isolation and remediation of malicious activities.
Real-World Examples of Endpoint Sandbox Solutions
Carbon Black's sandbox in endpoint security isolates suspicious files from the main system, allowing detailed analysis of malware behavior without risking infection. CrowdStrike Falcon utilizes cloud-based sandboxing to execute and monitor endpoint threats in a virtual environment, enhancing threat detection accuracy. Microsoft Defender ATP integrates sandbox technology that automatically detonates unknown files to identify zero-day threats and prevent endpoint compromise.
How Endpoint Sandboxing Prevents Malware
Endpoint sandboxing isolates suspicious files in a secure, virtual environment to analyze their behavior without risking the host system. By detecting malicious activities such as unauthorized access attempts, code injections, or data exfiltration in real-time, sandboxing prevents malware from executing harmful actions on endpoints. This proactive containment and inspection ensure threats are identified and blocked before impacting the network or device integrity.
Comparing Endpoint Sandboxing to Network Sandboxing
Endpoint sandboxing analyzes suspicious files and behavior directly on user devices, providing granular insights into malware execution and preventing threats from affecting the system. Network sandboxing inspects traffic at perimeter points, offering broader visibility but delayed detection and less precision in identifying endpoint-specific exploits. Choosing endpoint sandboxing enhances real-time, device-level threat isolation critical for advanced persistent threat mitigation.
Challenges When Implementing Endpoint Sandboxing
Endpoint sandboxing faces challenges such as resource intensiveness, often requiring significant CPU and memory allocation which can degrade device performance. Compatibility issues arise with diverse operating systems and application types, limiting sandbox effectiveness and deployment scope. Ensuring real-time threat detection and accurate behavioral analysis without generating false positives remains a critical difficulty in sandbox implementation.
Best Practices for Endpoint Sandbox Deployment
Implement endpoint sandbox deployment by isolating suspicious files in a virtualized environment to prevent malware from affecting the host system. Use behavior analysis and real-time monitoring to detect malicious activities without compromising endpoint performance. Regularly update sandbox signatures and integrate with endpoint detection and response (EDR) platforms for comprehensive threat intelligence and rapid incident response.
Future Trends in Endpoint Sandboxing Technologies
Future trends in endpoint sandboxing technologies emphasize AI-driven behavioral analysis to detect zero-day threats with higher accuracy. Integration of cloud-based sandbox environments enables scalable and real-time threat simulation across diverse endpoint devices. Enhanced automation and machine learning models facilitate faster threat remediation, reducing the window of vulnerability significantly.
example of sandbox in endpoint Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com