An evil maid attack exemplifies a physical security breach where an unauthorized individual gains access to a device to install malicious hardware or software. This type of attack often targets unattended computers or servers in hotel rooms, data centers, or offices. Attackers exploit moments when devices are left in vulnerable states, allowing them to tamper with encryption keys, implant keyloggers, or install backdoor malware. These physical intrusions compromise critical assets such as laptops containing sensitive corporate data or servers holding customer information. The implanted devices or software can capture passwords, decrypt sensitive files, or provide persistent remote access to attackers. Organizations must implement strict access controls, tamper-evident seals, and hardware encryption to mitigate the risks posed by evil maid attacks on high-value physical assets.
Table of Comparison
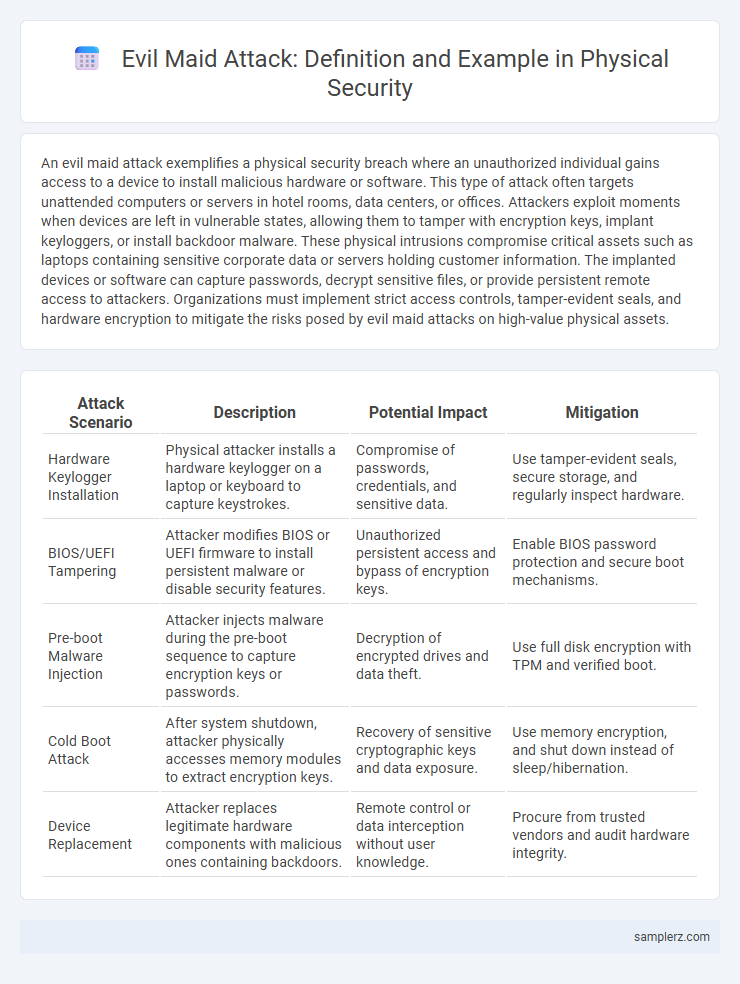
| Attack Scenario | Description | Potential Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Keylogger Installation | Physical attacker installs a hardware keylogger on a laptop or keyboard to capture keystrokes. | Compromise of passwords, credentials, and sensitive data. | Use tamper-evident seals, secure storage, and regularly inspect hardware. |
| BIOS/UEFI Tampering | Attacker modifies BIOS or UEFI firmware to install persistent malware or disable security features. | Unauthorized persistent access and bypass of encryption keys. | Enable BIOS password protection and secure boot mechanisms. |
| Pre-boot Malware Injection | Attacker injects malware during the pre-boot sequence to capture encryption keys or passwords. | Decryption of encrypted drives and data theft. | Use full disk encryption with TPM and verified boot. |
| Cold Boot Attack | After system shutdown, attacker physically accesses memory modules to extract encryption keys. | Recovery of sensitive cryptographic keys and data exposure. | Use memory encryption, and shut down instead of sleep/hibernation. |
| Device Replacement | Attacker replaces legitimate hardware components with malicious ones containing backdoors. | Remote control or data interception without user knowledge. | Procure from trusted vendors and audit hardware integrity. |
Understanding the Evil Maid Attack in Physical Security
An evil maid attack involves an unauthorized individual gaining physical access to a device, such as a laptop or server, to install malicious hardware or software without the owner's knowledge. This type of physical security breach exploits unattended or poorly secured devices in locations like hotels or offices, allowing attackers to bypass encryption or gather sensitive data. Preventive measures include full disk encryption, tamper-evident seals, and strict access controls to mitigate the risk of such physical intrusions.
Real-World Examples of Evil Maid Attacks
Real-world examples of evil maid attacks include the 2015 incident where attackers accessed a hotel guest's laptop by implanting hardware keyloggers, capturing sensitive credentials over several days without the victim's knowledge. Another case involved a high-profile political figure whose devices were compromised after unauthorized access to their hotel room, leading to data exfiltration and espionage. These attacks demonstrate how physical access in seemingly secure environments allows adversaries to bypass encryption and authentication measures through malicious hardware or firmware tampering.
How Attackers Bypass Physical Defenses
Attackers bypass physical defenses in evil maid attacks by exploiting unattended devices, gaining temporary access to install malicious firmware or hardware keyloggers. They leverage weaknesses such as unencrypted hard drives or disabled BIOS passwords to manipulate system boot processes and extract sensitive data. Physical tampering techniques like keyboard overlay installation or cold boot attacks enable attackers to compromise security without detection.
Case Study: Laptop Compromise in Hotel Rooms
A notable example of an evil maid attack occurred when a hotel maid accessed a guest's unattended laptop, installing a hardware keylogger to capture sensitive credentials. This physical breach exploited the trust placed in hotel staff and the lack of adequate tamper-evident protections on the device. The attack led to unauthorized access to corporate networks, demonstrating the critical need for encryption and physical security measures in hotel environments.
Key Targets: High-Value Devices and Sensitive Data
High-value devices such as laptops, external hard drives, and smartphones are primary targets in evil maid attacks due to their access to sensitive corporate and personal data. Attackers exploit physical access to implant malicious software or hardware, enabling data theft or surveillance without the user's knowledge. Protecting these devices requires robust physical security measures, encrypted storage, and tamper-evident seals to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Common Tools Used by Evil Maid Attackers
Evil maid attackers commonly use tools such as USB rubber duckies, keyloggers, and bootable USB drives to gain unauthorized access to locked or unattended devices. These tools allow them to inject malicious code, capture keystrokes, or install persistent malware bypassing traditional security measures. Physical access combined with these specialized tools enables attackers to compromise data confidentiality and integrity effectively.
Signs Your Device May Have Been Tampered With
Unexplained scratches or dents on the device casing often indicate physical tampering associated with evil maid attacks. Unexpected changes in firmware behavior or boot sequences suggest unauthorized modifications by attackers. Devices exhibiting unusual hardware components, such as hidden keyloggers or microSD cards, are strong signs of compromise in physical security contexts.
Mitigation Strategies Against Physical Attacks
Evil maid attacks exploit physical access to compromise device security, often targeting laptops or servers with malicious hardware implants or firmware tampering. Mitigation strategies include implementing full disk encryption with secure boot, using tamper-evident seals, and employing hardware security modules that detect unauthorized physical access. Regular inspection and controlled physical access policies further reduce the risk of such physical attacks.
The Role of Encryption in Preventing Evil Maid Attacks
Encryption secures data by converting it into unreadable code, preventing unauthorized access during physical attacks like evil maid scenarios. In such attacks, an intruder with temporary device access attempts to install malware or extract sensitive data, but strong encryption renders the information inaccessible without the decryption key. Full disk encryption and secure boot protocols play critical roles in safeguarding against these threats by ensuring data integrity and device authenticity even if physical tampering occurs.
Lessons Learned: Strengthening Physical and Digital Security
The evil maid attack highlights vulnerabilities in unattended devices, demonstrating the critical need for tamper-evident seals and secure boot mechanisms to prevent unauthorized physical access. Implementing full disk encryption combined with strong authentication protocols significantly mitigates the risk of data compromise from physical intrusions. Regular security audits and user awareness training reinforce both physical and digital defenses against sophisticated attacker tactics.
example of evil maid in physical attack Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com