A keylogger is a type of malicious software used in endpoint security breaches to capture and record keystrokes from a compromised device. Entities such as hackers deploy keyloggers to steal sensitive data including passwords, credit card numbers, and personal information. These programs operate silently in the background, making detection challenging without specialized security solutions like antivirus or endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools. In endpoint security frameworks, keyloggers represent a significant threat to organizational data integrity and confidentiality. Data captured by keyloggers can lead to unauthorized access to corporate networks and critical business applications. Monitoring endpoint activity and employing behavioral analytics can help identify suspicious patterns indicative of keylogger activity.
Table of Comparison
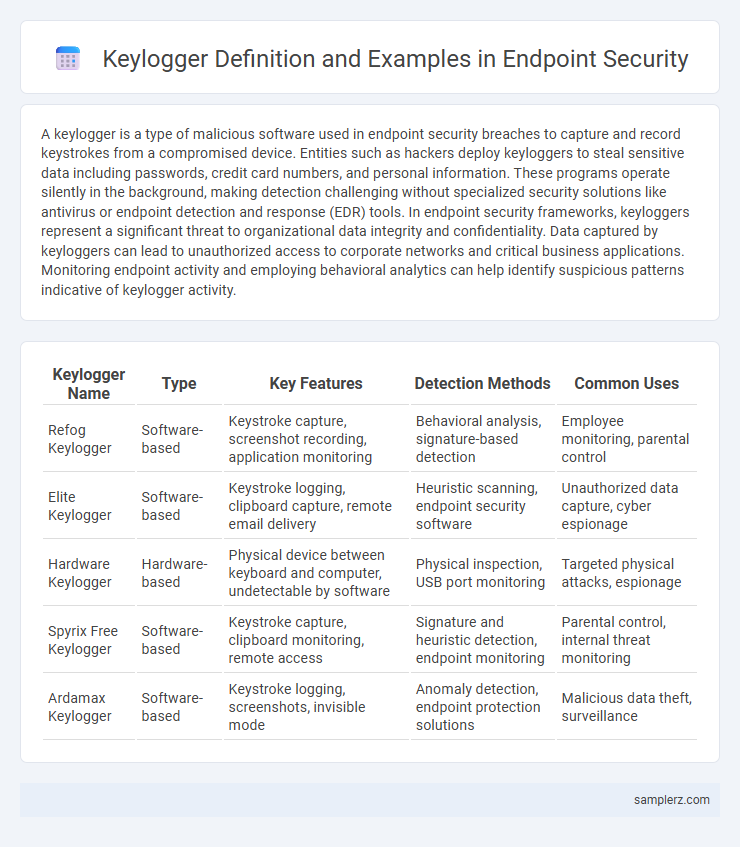
| Keylogger Name | Type | Key Features | Detection Methods | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refog Keylogger | Software-based | Keystroke capture, screenshot recording, application monitoring | Behavioral analysis, signature-based detection | Employee monitoring, parental control |
| Elite Keylogger | Software-based | Keystroke logging, clipboard capture, remote email delivery | Heuristic scanning, endpoint security software | Unauthorized data capture, cyber espionage |
| Hardware Keylogger | Hardware-based | Physical device between keyboard and computer, undetectable by software | Physical inspection, USB port monitoring | Targeted physical attacks, espionage |
| Spyrix Free Keylogger | Software-based | Keystroke capture, clipboard monitoring, remote access | Signature and heuristic detection, endpoint monitoring | Parental control, internal threat monitoring |
| Ardamax Keylogger | Software-based | Keystroke logging, screenshots, invisible mode | Anomaly detection, endpoint protection solutions | Malicious data theft, surveillance |
Understanding Keyloggers in Endpoint Security
Keyloggers in endpoint security are malicious software or hardware tools designed to secretly record keystrokes on a user's device, capturing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and confidential business data. Endpoint protection platforms deploy advanced threat detection techniques, including behavioral analysis and real-time monitoring, to identify and block keylogger activity before data exfiltration occurs. Understanding keyloggers' operational methods, such as kernel-level logging and hooking keyboard APIs, is critical for implementing robust endpoint security strategies that prevent unauthorized data capture.
Common Types of Keyloggers Detected on Endpoints
Common types of keyloggers detected on endpoints include software keyloggers, hardware keyloggers, and acoustic keyloggers. Software keyloggers operate stealthily within the operating system to capture keystrokes, while hardware keyloggers are physical devices attached between the keyboard and computer. Acoustic keyloggers analyze sound patterns of typing to reconstruct input, posing sophisticated threats in endpoint security environments.
Real-World Keylogger Attacks on Enterprises
Real-world keylogger attacks on enterprises often exploit vulnerabilities in endpoint security by covertly capturing keystrokes to steal sensitive data such as login credentials and intellectual property. Notable incidents include the 2018 Magecart attacks, where keyloggers embedded in web applications compromised corporate financial information. Enterprises must implement advanced endpoint protection platforms (EPP) combined with behavioral analysis to detect and mitigate sophisticated keylogger threats effectively.
How Keyloggers Infiltrate Endpoint Devices
Keyloggers infiltrate endpoint devices primarily through phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links that, when opened, install the keylogging software silently. They exploit vulnerabilities in outdated operating systems or unsecured applications to gain unauthorized access without user detection. Attackers often deploy keyloggers via drive-by downloads from compromised websites or bundled in seemingly legitimate software to capture sensitive credentials and confidential data.
Behavioral Indicators of Keylogger Activity
Behavioral indicators of keylogger activity in endpoint security include unusual CPU and memory usage spikes during idle times, frequent unexplained outbound network connections, and unexpected keystroke patterns or input delays detected through advanced monitoring systems. Keyloggers often create hidden processes that intercept keyboard inputs, triggering abnormal file access or modification events within security logs. Continuous anomaly detection using machine learning algorithms can identify these behavioral patterns, enabling early detection and mitigation of keylogger threats.
Keylogger Detection Techniques for Endpoints
Keylogger detection techniques for endpoints primarily involve behavior-based analysis and signature-based scanning to identify abnormal keystroke logging activities. Endpoint security solutions utilize heuristic algorithms to monitor keypress patterns, system API calls, and unauthorized access to input devices, effectively flagging potential keylogger threats. Machine learning models enhance detection accuracy by correlating endpoint data with known keylogger signatures and anomalous user behavior indicators.
Notable Keylogger Malware Examples
Notable keylogger malware examples in endpoint security include Spyrix Keylogger, which captures keystrokes, screenshots, and clipboard data covertly. Another example is Perfect Keylogger, known for its ability to log passwords, chat messages, and visited websites on Windows systems. These keyloggers pose significant risks by enabling unauthorized access to sensitive credentials and personal information.
Endpoint Security Solutions Against Keyloggers
Endpoint security solutions deploy advanced behavioral analysis and real-time scanning to detect and block keyloggers that compromise user credentials and sensitive data. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools continuously monitor keystroke patterns and system processes, identifying anomalies indicative of keylogger activity. Integration of machine learning algorithms enhances protection by recognizing zero-day keyloggers and preventing unauthorized data exfiltration from endpoints.
Steps to Remediate Keylogger Infections
Identifying keylogger infections on endpoints requires running comprehensive antivirus and anti-malware scans using tools like Malwarebytes or Windows Defender. Removing detected keylogger software involves quarantining or deleting malicious files and restoring system registry settings to their default state. Implementing endpoint security measures such as regularly updating software, enabling firewalls, and using multi-factor authentication prevents reinfection and enhances overall protection against keyloggers.
Best Practices to Prevent Keylogger Threats
Implementing advanced endpoint security solutions with real-time keylogger detection algorithms significantly reduces keylogging risks. Regularly updating software and employing multi-factor authentication minimizes unauthorized access from captured keystrokes. Enforcing strict user privilege controls alongside continuous employee training on phishing and social engineering strengthens defense against stealth keylogger attacks.
example of keylogger in endpoint security Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com