Remote Access Trojans (RATs) pose significant security threats by allowing unauthorized users to control infected systems remotely. Common examples of RATs include DarkComet, NanoCore, and Gh0st RAT, which are known for their capabilities to capture keystrokes, access files, and activate webcams without the victim's knowledge. These malicious programs are often disguised within seemingly legitimate software or delivered through phishing campaigns to gain silent access to targeted computers. Security professionals focus on detecting unusual network traffic and monitoring system behaviors to identify RAT infections early. Using endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, analysts can extract indicators of compromise (IOCs) related to RAT activity such as unexpected remote connections and encrypted data transfers. Understanding the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of RAT operators helps strengthen defenses against remote access threats in enterprise environments.
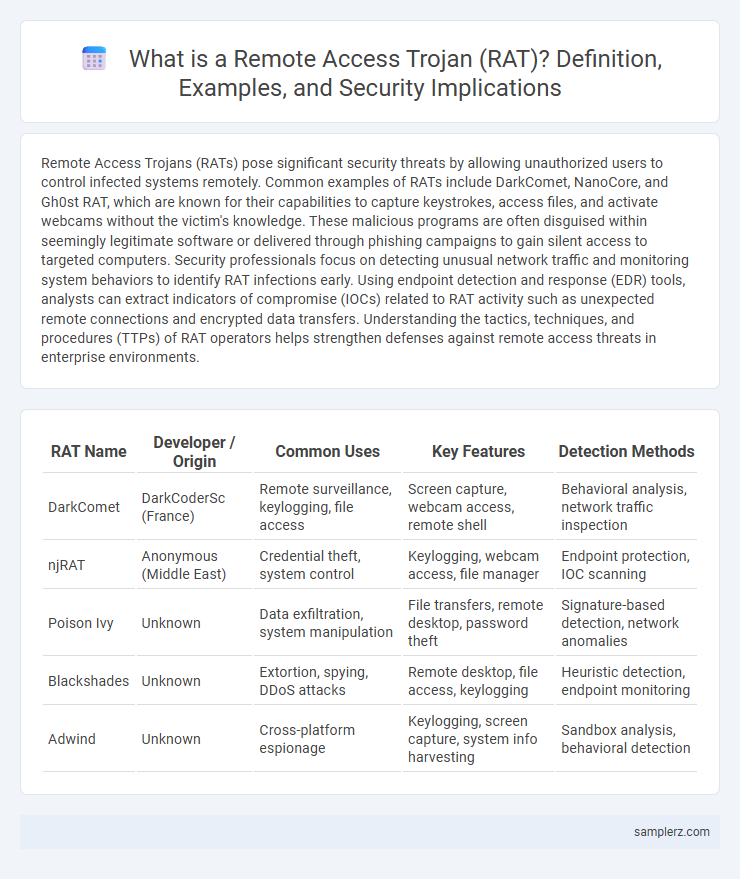
Table of Comparison
| RAT Name | Developer / Origin | Common Uses | Key Features | Detection Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DarkComet | DarkCoderSc (France) | Remote surveillance, keylogging, file access | Screen capture, webcam access, remote shell | Behavioral analysis, network traffic inspection |
| njRAT | Anonymous (Middle East) | Credential theft, system control | Keylogging, webcam access, file manager | Endpoint protection, IOC scanning |
| Poison Ivy | Unknown | Data exfiltration, system manipulation | File transfers, remote desktop, password theft | Signature-based detection, network anomalies |
| Blackshades | Unknown | Extortion, spying, DDoS attacks | Remote desktop, file access, keylogging | Heuristic detection, endpoint monitoring |
| Adwind | Unknown | Cross-platform espionage | Keylogging, screen capture, system info harvesting | Sandbox analysis, behavioral detection |
Overview of Remote Access Trojans (RATs)
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) are malicious software programs that provide attackers with unauthorized remote control over infected devices, enabling data theft, surveillance, and system manipulation. Common examples of RATs include DarkComet, njRAT, and Gh0st RAT, which exploit vulnerabilities to establish persistent access while evading detection. These RATs facilitate cybercriminal activities such as credential harvesting, keystroke logging, and launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks on targeted networks.
Common Features of RATs in Cybersecurity
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) commonly exhibit features such as keylogging to capture user credentials, remote desktop control for unauthorized access, and file manipulation capabilities including uploading, downloading, and deletion. These malicious tools often utilize stealth techniques like encryption and rootkit functionality to evade detection by antivirus software. Network communication with Command and Control (C2) servers enables attackers to execute commands remotely and maintain persistent access to compromised systems.
How RATs Enable Unauthorized Remote Access
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) enable unauthorized remote access by covertly infiltrating target devices and creating hidden control channels for attackers. These malicious programs capture keystrokes, access files, activate webcams, and manipulate system processes without user consent, making them powerful tools for espionage and data theft. Exploiting system vulnerabilities or phishing schemes, RATs maintain persistent access while evading detection by traditional security software.
Popular Examples of RATs in Recent Attacks
Popular examples of Remote Access Trojans (RATs) in recent cyberattacks include Gh0st RAT, used extensively in espionage campaigns, and njRAT, known for targeting Windows systems to gain control over infected machines. Another prevalent RAT, DarkComet, has been employed by threat actors for data theft and surveillance operations. These tools enable attackers to remotely access, monitor, and manipulate compromised devices, posing significant security risks to individuals and organizations.
Notorious RAT Variants Targeting Organizations
Notorious remote access trojans (RATs) targeting organizations include DarkComet, known for its ability to capture keystrokes, screenshots, and webcam feeds, enabling extensive espionage and data theft. NjRAT remains prevalent for its modular architecture and ease of deployment in corporate networks, often used to steal credentials and propagate laterally. Other significant RATs such as Gh0st RAT facilitate long-term surveillance and command-and-control capabilities, making them highly dangerous in targeted cyber espionage against enterprises.
Real-world Cases of RAT Exploitation
Real-world cases of Remote Access Trojan (RAT) exploitation highlight severe security breaches, such as the infamous DarkComet RAT used in cyber espionage targeting government networks and financial institutions. Attackers leverage RATs like njRAT to gain unauthorized access, execute malicious payloads, and exfiltrate sensitive data remotely. These incidents underscore the critical need for robust endpoint protection and continuous monitoring to detect and mitigate RAT-based intrusions.
Techniques Used by RATs to Evade Detection
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) employ advanced techniques such as encryption to conceal communication channels and polymorphic code to alter their signatures dynamically, making detection by traditional antivirus software challenging. They utilize rootkit functionalities to hide processes and files from system monitoring tools, while employing keylogging and screen capturing discreetly to gather sensitive information without triggering alerts. RATs also leverage command and control (C2) servers with fast-flux DNS to obscure their network infrastructure, complicating traceability and mitigation efforts.
Indicators of RAT Infection on Networks
Indicators of Remote Access Trojan (RAT) infection on networks include unusual outbound traffic patterns, especially connections to unfamiliar or suspicious IP addresses and domains. Frequent, unauthorized remote access sessions combined with abnormal CPU or memory usage on affected devices can signify RAT presence. Monitoring for unexpected file modifications, persistent backdoor processes, and anomalies in network latency are critical for early detection and response.
Best Practices to Prevent RAT Intrusions
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) such as DarkComet and njRAT exemplify serious cybersecurity threats by enabling unauthorized control over infected systems. Best practices to prevent RAT intrusions include implementing advanced endpoint protection, enforcing strict network access controls, and maintaining regular software updates with security patches. User education on phishing avoidance and utilizing multi-factor authentication further reduce the risk of RAT-based compromises.
Response Steps After RAT Detection
Upon detecting a Remote Access Trojan (RAT), immediate isolation of the affected system from the network prevents further unauthorized access and data exfiltration. Conducting a thorough forensic analysis identifies the RAT variant, infection vector, and any compromised credentials to guide remediation efforts. Initiating password resets, patching vulnerabilities, and deploying advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools minimize the risk of reinfection and strengthen organizational security posture.
example of RAT in remote access Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com