War walking is a security practice where individuals walk through areas while scanning for wireless networks using portable devices. These devices collect data such as network names (SSIDs), signal strengths, encryption types, and access point locations. This method helps identify vulnerable or unsecured wireless networks that may be exploited by attackers. Data gathered during war walking can include open Wi-Fi networks, networks using weak encryption protocols like WEP, and rogue access points posing security risks. Security professionals use this information to assess network vulnerabilities and improve wireless security measures. Entities conducting war walking often map network coverage and detect unauthorized devices to enhance overall network protection.
Table of Comparison
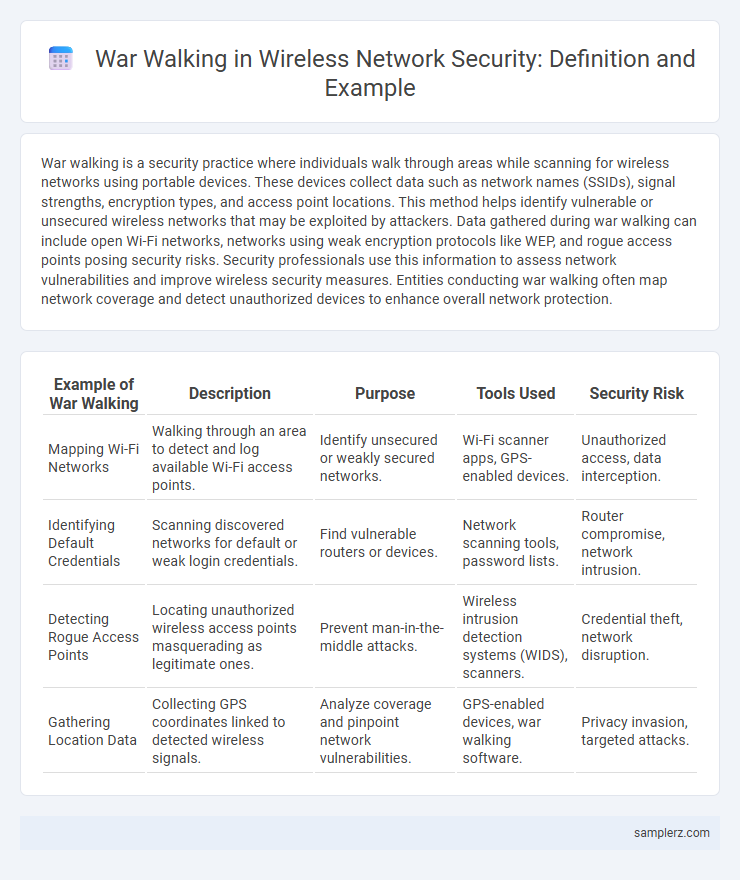
| Example of War Walking | Description | Purpose | Tools Used | Security Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mapping Wi-Fi Networks | Walking through an area to detect and log available Wi-Fi access points. | Identify unsecured or weakly secured networks. | Wi-Fi scanner apps, GPS-enabled devices. | Unauthorized access, data interception. |
| Identifying Default Credentials | Scanning discovered networks for default or weak login credentials. | Find vulnerable routers or devices. | Network scanning tools, password lists. | Router compromise, network intrusion. |
| Detecting Rogue Access Points | Locating unauthorized wireless access points masquerading as legitimate ones. | Prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. | Wireless intrusion detection systems (WIDS), scanners. | Credential theft, network disruption. |
| Gathering Location Data | Collecting GPS coordinates linked to detected wireless signals. | Analyze coverage and pinpoint network vulnerabilities. | GPS-enabled devices, war walking software. | Privacy invasion, targeted attacks. |
Introduction to War Walking in Wireless Networks
War walking involves systematically traversing physical areas while using wireless devices to detect and map unsecured or poorly secured Wi-Fi networks. This method helps security professionals identify vulnerabilities in wireless network configurations, such as open access points or weak encryption standards. Understanding war walking is crucial for developing robust wireless security policies and preventing unauthorized network access.
Historical Background of War Walking
War walking emerged in the late 1990s as a technique to map wireless networks by physically moving through areas while scanning for Wi-Fi signals, often using laptops or handheld devices. This practice evolved from war driving but shifted focus from vehicles to pedestrian exploration, allowing more granular data collection in urban environments. Early adopters targeted open or poorly secured networks to identify vulnerabilities, influencing the development of wireless security protocols like WPA and WPA2.
How War Walking Differs from Wardriving
War walking involves physically moving on foot to detect wireless networks, enabling closer inspection of network signals and security vulnerabilities in environments with obstacles or limited vehicle access. Wardriving, by contrast, utilizes vehicles equipped with wireless detection tools to map network coverage over larger geographic areas more quickly but with less proximity detail. The on-foot approach in war walking allows for granular signal strength measurements and pinpointing rogue access points within complex indoor or urban settings, enhancing threat detection precision.
Common Tools Used in War Walking
Common tools used in war walking include wireless network scanners like NetStumbler and Kismet, which detect and map Wi-Fi signals in an area. Portable devices equipped with GPS receivers enable precise location tagging of wireless networks to create detailed signal coverage maps. These tools assist security professionals in identifying unauthorized access points and assessing network vulnerabilities during physical site surveys.
Real-World Examples of War Walking Incidents
In 2017, war walking revealed unsecured wireless networks in major cities like New York and London, exposing critical vulnerabilities in corporate and public infrastructures. Researchers mapped thousands of unencrypted Wi-Fi access points, enabling potential attackers to intercept sensitive communications and launch man-in-the-middle attacks. These real-world incidents underscore the urgent need for robust encryption protocols and regular wireless network audits to prevent unauthorized access.
Techniques Employed During War Walking
War walking involves systematically scanning wireless networks using portable devices equipped with Wi-Fi adapters and GPS receivers to map signal strengths and locations. Techniques employed include passive sniffing to capture broadcast packets without connecting to networks, active probing to identify hidden or non-broadcast SSIDs, and using specialized software like Kismet or NetStumbler for real-time network analysis. Data collected enables attackers to identify vulnerable access points, insecure encryption protocols like WEP, and potential entry points for unauthorized access or network intrusion.
Security Risks Associated with War Walking
War walking exposes wireless networks to significant security risks such as unauthorized access, data interception, and network infiltration by cybercriminals. Attackers can exploit unsecured Wi-Fi signals detected during war walking to launch man-in-the-middle attacks, steal sensitive information, or introduce malware. These vulnerabilities highlight the importance of robust encryption protocols and continuous network monitoring to prevent exploitation in wireless environments.
Legal and Ethical Implications of War Walking
War walking involves traversing public spaces while scanning for wireless networks, raising significant legal concerns such as unauthorized access and potential violation of privacy laws. Ethical implications arise from the intrusion into private networks without consent, which can be perceived as invasive or malicious, potentially damaging trust and reputations. Understanding the boundaries defined by laws like the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and respecting network owners' privacy rights is crucial to maintaining ethical standards in war walking activities.
Prevention Strategies Against War Walking
War walking, the practice of mapping unsecured wireless networks by physically moving through an area, poses significant security risks such as unauthorized access and data breaches. Prevention strategies include implementing strong WPA3 encryption, disabling SSID broadcasting to reduce network visibility, and using MAC address filtering to restrict device connections. Regularly updating router firmware and employing network intrusion detection systems further enhance protection against war walking threats in wireless environments.
Future Trends in Wireless Network Security
War walking, involving the systematic detection of unsecured wireless networks via mobile devices, highlights vulnerabilities that future wireless network security must address. Emerging trends emphasize AI-driven anomaly detection and quantum encryption to preemptively identify and neutralize threats during such reconnaissance. Enhanced integration of blockchain for secure authentication and real-time adaptive protocols promises to fortify defenses against evolving war walking tactics.
example of war walking in wireless network Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com