Tokenization in payment security replaces sensitive card information with unique identification symbols called tokens. These tokens retain essential data without compromising the original card details, enabling secure transactions across various platforms. Payment processors often use tokenization to reduce the risk of data breaches by ensuring that actual card numbers are never stored or transmitted during transactions. This method enhances security by isolating critical data from payment ecosystems, minimizing exposure to cyber threats. Merchants benefit from reduced PCI DSS compliance scope since tokens cannot be exploited if intercepted. Major entities like Visa and Mastercard have integrated tokenization protocols, supporting contactless and mobile payment solutions worldwide.
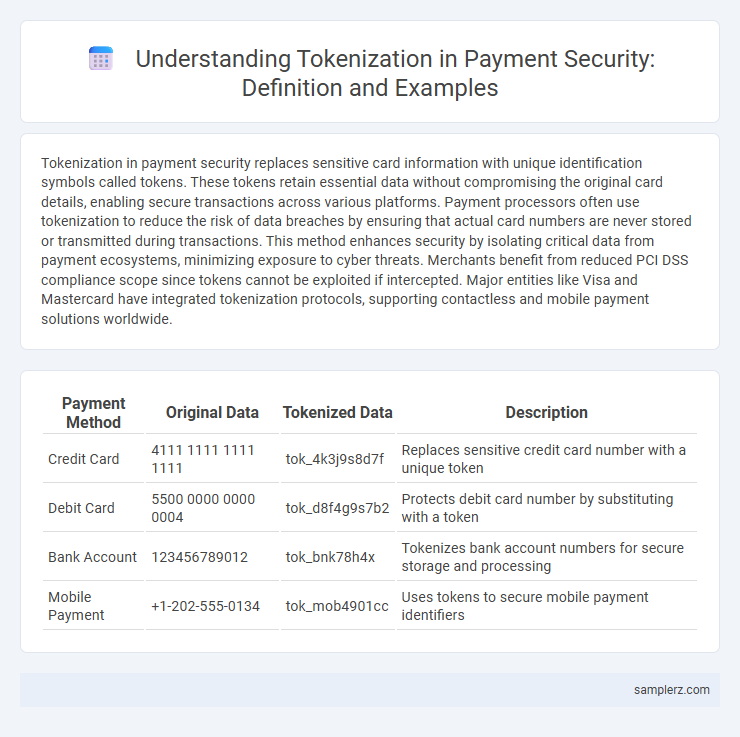
Table of Comparison
| Payment Method | Original Data | Tokenized Data | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Credit Card | 4111 1111 1111 1111 | tok_4k3j9s8d7f | Replaces sensitive credit card number with a unique token |
| Debit Card | 5500 0000 0000 0004 | tok_d8f4g9s7b2 | Protects debit card number by substituting with a token |
| Bank Account | 123456789012 | tok_bnk78h4x | Tokenizes bank account numbers for secure storage and processing |
| Mobile Payment | +1-202-555-0134 | tok_mob4901cc | Uses tokens to secure mobile payment identifiers |
Understanding Tokenization in Payment Systems
Tokenization in payment systems replaces sensitive card information with unique tokens, minimizing the risk of data breaches during transactions. Payment processors generate these tokens to represent card details without exposing actual account numbers, enhancing security across digital and contactless payments. This process reduces fraud by ensuring that tokenized data is useless if intercepted by unauthorized parties.
How Tokenization Enhances Payment Security
Tokenization enhances payment security by replacing sensitive card information with a unique, non-sensitive token that stores no exploitable data outside the payment ecosystem. During transactions, this token is transmitted instead of actual card details, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud. Major payment networks like Visa and Mastercard utilize tokenization to protect cardholder data across digital wallets and contactless payments.
Real-Life Example: Tokenization in Credit Card Transactions
Tokenization in credit card transactions replaces sensitive card information with a unique digital identifier called a token, ensuring the actual card number is never exposed during payment processing. For instance, when a customer uses Apple Pay, the device generates a token that represents the credit card data, which is transmitted instead of the real card number, minimizing fraud risk. This method secures transactions by isolating sensitive data, making intercepted tokens useless without the corresponding decryption keys held by the payment processor.
Tokenization Process During Online Purchases
During online purchases, the tokenization process replaces sensitive payment card information with a unique, encrypted token that is meaningless if intercepted. This token is used in the transaction instead of the actual card details, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches. Payment gateways and processors rely on these tokens to securely authorize and complete the purchase without exposing the original card data.
Mobile Wallets and Tokenized Payment Data
Mobile wallets use tokenization to replace sensitive payment card details with unique digital tokens during transactions, reducing the risk of data breaches. Tokenized payment data ensures that actual card information is never transmitted or stored on merchant servers, enhancing security in mobile payment environments. This method protects user credentials and enables secure, contactless payments across various devices and platforms.
Case Study: Tokenization in Contactless Payments
Tokenization in contactless payments replaces sensitive card information with unique, randomly generated tokens, enhancing transaction security by preventing exposure of actual card data. A notable case study involves Apple Pay, which uses tokenization to securely transmit payment tokens instead of card numbers during NFC transactions, reducing fraud risks and enabling seamless contactless experiences. This approach minimizes data breaches by ensuring that intercepted tokens cannot be reused or decoded.
Tokenization Use in E-Commerce Platforms
E-commerce platforms use tokenization to replace sensitive payment information, such as credit card numbers, with unique identification tokens during transaction processing. These tokens are useless if intercepted by cybercriminals, enhancing payment security by reducing the risk of data breaches. Integration of tokenization with secure payment gateways and PCI DSS compliance helps platforms safeguard customer data and build trust.
Role of Tokenization in PCI DSS Compliance
Tokenization replaces sensitive payment card data with unique identification symbols, minimizing the exposure of actual card details during transactions and significantly reducing the risk of data breaches. This method supports PCI DSS compliance by limiting the scope of systems that store, process, or transmit cardholder data, thereby simplifying security requirements and audit processes. Implementing tokenization enables merchants to meet PCI DSS standards while maintaining secure, efficient payment processing environments.
Tokenization Solutions from Leading Payment Providers
Leading payment providers such as Visa, Mastercard, and American Express implement advanced tokenization solutions to enhance transaction security by replacing sensitive card details with unique, encrypted tokens. These tokens are used during payment processing to prevent unauthorized access to actual card information, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches. Their tokenization platforms integrate seamlessly with mobile wallets, e-commerce sites, and point-of-sale systems to ensure secure and efficient payment experiences globally.
Future Trends: Evolving Tokenization Practices in Payments
Evolving tokenization practices in payments increasingly leverage dynamic tokens that refresh with each transaction, enhancing security against fraud and data breaches. Future trends emphasize integration with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, enabling real-time tokenization tied to blockchain identities for seamless cross-border payments. Advanced cryptographic techniques, such as quantum-resistant algorithms, are set to fortify tokenization frameworks, ensuring robust protection as payment systems become more interconnected and digital-first.
example of tokenization in payment Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com