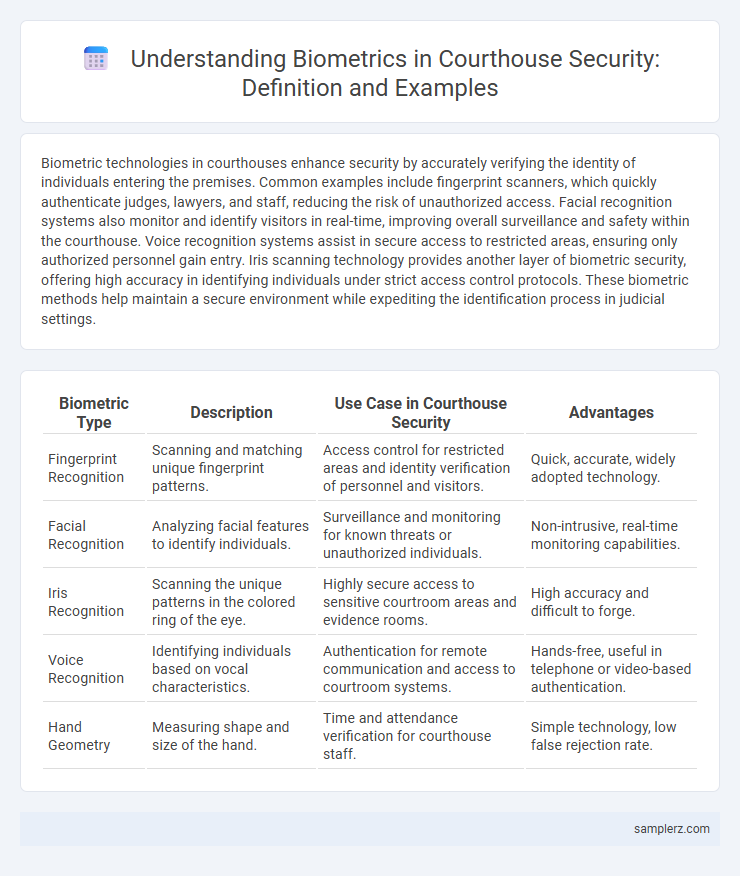
Biometric technologies in courthouses enhance security by accurately verifying the identity of individuals entering the premises. Common examples include fingerprint scanners, which quickly authenticate judges, lawyers, and staff, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Facial recognition systems also monitor and identify visitors in real-time, improving overall surveillance and safety within the courthouse. Voice recognition systems assist in secure access to restricted areas, ensuring only authorized personnel gain entry. Iris scanning technology provides another layer of biometric security, offering high accuracy in identifying individuals under strict access control protocols. These biometric methods help maintain a secure environment while expediting the identification process in judicial settings.
Table of Comparison
| Biometric Type | Description | Use Case in Courthouse Security | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fingerprint Recognition | Scanning and matching unique fingerprint patterns. | Access control for restricted areas and identity verification of personnel and visitors. | Quick, accurate, widely adopted technology. |
| Facial Recognition | Analyzing facial features to identify individuals. | Surveillance and monitoring for known threats or unauthorized individuals. | Non-intrusive, real-time monitoring capabilities. |
| Iris Recognition | Scanning the unique patterns in the colored ring of the eye. | Highly secure access to sensitive courtroom areas and evidence rooms. | High accuracy and difficult to forge. |
| Voice Recognition | Identifying individuals based on vocal characteristics. | Authentication for remote communication and access to courtroom systems. | Hands-free, useful in telephone or video-based authentication. |
| Hand Geometry | Measuring shape and size of the hand. | Time and attendance verification for courthouse staff. | Simple technology, low false rejection rate. |
Introduction to Biometrics in Courthouse Security
Biometrics in courthouse security utilize unique physiological traits such as fingerprint scans, facial recognition, and iris scans to verify identities and control access. Implementing biometric systems enhances security by reducing unauthorized entry and ensuring only verified personnel and visitors enter sensitive areas. This technology supports efficient case management by linking biometric data to court records and streamlining secure check-ins.
Fingerprint Scanning for Juror Identification
Fingerprint scanning enhances security in courthouses by providing accurate juror identification, preventing impersonation and unauthorized access. This biometric method ensures that only verified jurors participate in trials, maintaining the integrity of legal proceedings. Implementing fingerprint scanners reduces administrative errors and expedites check-in processes for jurors.
Facial Recognition at Courtroom Entrances
Facial recognition technology at courtroom entrances enhances security by quickly verifying the identity of individuals entering the premises, reducing unauthorized access. This biometric system uses advanced algorithms to match live facial images against a database of known persons, including staff, attorneys, and flagged individuals. Implementing facial recognition streamlines the check-in process while maintaining a high level of accuracy and reliability in securing courthouse environments.
Retina and Iris Scanning for Staff Access
Retina and iris scanning technologies provide highly secure biometric authentication for courthouse staff access, leveraging unique vascular patterns and iris structures that are nearly impossible to replicate. These biometric methods enhance access control by ensuring only authorized personnel can enter sensitive areas, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized intrusion. Integration with courthouse security systems enables real-time monitoring and auditing of access events, improving overall facility security.
Voice Recognition in Secure Judicial Communications
Voice recognition technology enhances secure judicial communications by accurately authenticating judges, attorneys, and court staff, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive case information. Integrating biometric voice verification within courthouse communication systems ensures real-time identification, reducing risks of impersonation and fraud during confidential discussions. This biometric approach increases the integrity of judicial processes and protects the confidentiality of legal proceedings.
Hand Geometry Systems for Restricted Areas
Hand geometry systems enhance courthouse security by verifying individuals' identities through unique hand measurements, such as finger length and palm width. These biometrics operate effectively in restricted areas, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring that only credentialed personnel enter sensitive zones. The technology offers fast, reliable authentication with minimal user inconvenience, making it suitable for high-security judicial environments.
Palm Vein Authentication for High-Security Sections
Palm vein authentication enhances courthouse security by using near-infrared light to capture the unique vein patterns beneath the skin, providing a highly accurate and tamper-resistant biometric method. This technology is particularly effective in high-security sections where strict access control is critical, such as evidence rooms and judicial chambers. Compared to fingerprint or facial recognition, palm vein authentication offers superior protection against forgery and environmental factors, ensuring only authorized personnel gain entry.
Integration of Biometric Visitor Management
Integration of biometric visitor management systems in courthouses enhances security by utilizing fingerprint and facial recognition technologies to verify identities accurately. These systems streamline access control, reducing the risk of unauthorized entry and ensuring that only approved visitors gain entry into sensitive areas. Implementing biometric data tracking also allows for real-time monitoring and detailed audit trails, which are critical for maintaining courtroom safety and compliance with legal regulations.
Biometric Evidence Submission Procedures
Biometric evidence submission procedures in courthouses require strict adherence to chain-of-custody protocols to ensure the integrity and admissibility of fingerprints, facial recognition scans, and iris scans. Advanced biometric systems capture and digitally encrypt data, enabling secure transmission directly to forensic analysts and court officials. Courts implement standardized verification methods to authenticate biometric data, reducing risks of tampering or fraud during legal proceedings.
Future Trends of Biometrics in Courthouse Security
Future trends in courthouse security emphasize advanced biometric technologies such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and iris detection to enhance identity verification and access control. Emerging AI-powered biometrics improve real-time threat detection and streamline secure entry for authorized personnel. Integration of multimodal biometrics protocols promises increased accuracy, reducing fraudulent access and boosting overall courthouse safety measures.
example of biometrics in courthouse Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com