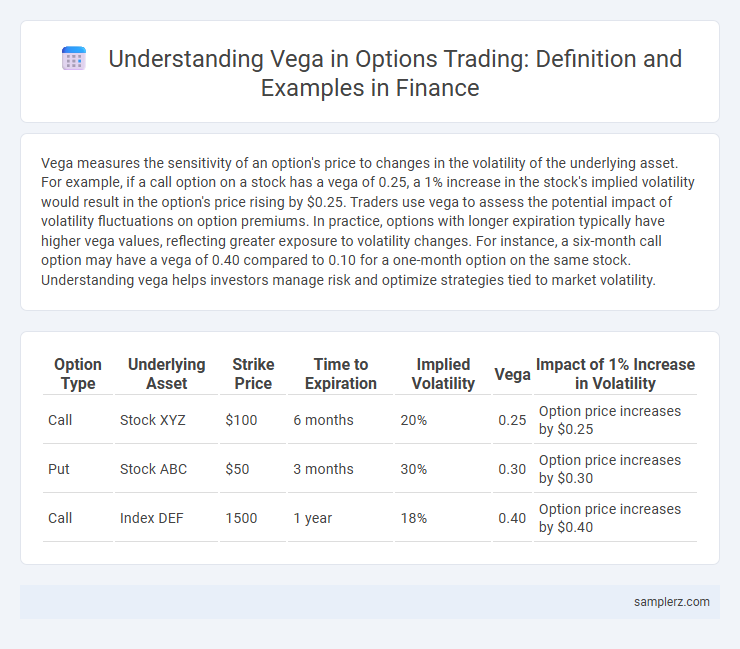
Vega measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the volatility of the underlying asset. For example, if a call option on a stock has a vega of 0.25, a 1% increase in the stock's implied volatility would result in the option's price rising by $0.25. Traders use vega to assess the potential impact of volatility fluctuations on option premiums. In practice, options with longer expiration typically have higher vega values, reflecting greater exposure to volatility changes. For instance, a six-month call option may have a vega of 0.40 compared to 0.10 for a one-month option on the same stock. Understanding vega helps investors manage risk and optimize strategies tied to market volatility.
Table of Comparison
| Option Type | Underlying Asset | Strike Price | Time to Expiration | Implied Volatility | Vega | Impact of 1% Increase in Volatility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Call | Stock XYZ | $100 | 6 months | 20% | 0.25 | Option price increases by $0.25 |
| Put | Stock ABC | $50 | 3 months | 30% | 0.30 | Option price increases by $0.30 |
| Call | Index DEF | 1500 | 1 year | 18% | 0.40 | Option price increases by $0.40 |
Understanding Vega: Definition and Importance in Options
Vega measures an option's sensitivity to changes in implied volatility, indicating how much the option's price will change for a 1% increase in volatility. Higher vega values are typical for at-the-money options with longer times until expiration, reflecting greater risk exposure to market fluctuations. Traders use vega to hedge portfolios and predict price movements in response to shifts in market sentiment and volatility.
How Vega Responds to Volatility Changes
Vega measures an option's sensitivity to changes in volatility, indicating how much the option's price will rise or fall with a 1% change in implied volatility. When market uncertainty increases, Vega typically rises, causing option premiums to become more expensive due to higher expected volatility. This characteristic makes Vega crucial for traders managing risk in volatile markets, especially for options with longer time to expiration.
Example of High Vega Option in Practice
A high vega option occurs with at-the-money options or those with longer expiration dates, where volatility shifts significantly impact option prices. For instance, a six-month ATM call option on a stock trading at $100 often has a vega value around 0.25, meaning a 1% increase in implied volatility boosts the option price by $0.25. Traders favor these high vega options to capitalize on anticipated volatility spikes, such as before earnings announcements or economic data releases.
Calculating Vega: A Step-by-Step Example
Calculating vega involves determining how much an option's price changes with a 1% change in the underlying asset's volatility; for example, if a call option on a stock priced at $100 has a vega of 0.25, a 1% increase in volatility will increase the option's price by $0.25. Using the Black-Scholes model, inputs such as the current stock price, strike price, time to expiration, interest rate, and volatility are required to compute vega precisely. Traders utilize this sensitivity measure to gauge the impact of volatility shifts on option value and to adjust hedging strategies effectively.
Vega Impact: Case Study Using a Call Option
Vega measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's volatility, highlighting its critical role in options trading strategies. In a case study using a call option on a stock with an initial implied volatility of 30%, a 5% increase in volatility raised the option's price by approximately 0.12 per share, demonstrating how Vega directly influences option premiums. Traders leverage this metric to adjust positions in volatile markets, optimizing risk and return based on anticipated volatility shifts.
Real Market Scenario: Vega’s Effect on Option Pricing
Vega measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in implied volatility, playing a critical role in option pricing during market fluctuations. For example, in a real market scenario, if a stock experiences heightened uncertainty due to an upcoming earnings report, implied volatility typically rises, increasing the value of calls and puts sensitive to vega. Traders leverage vega to hedge risks or capitalize on expected volatility shifts, demonstrating its dynamic impact on option premiums.
Comparing Vega: ATM, ITM, and OTM Options
Vega measures an option's sensitivity to changes in implied volatility, with at-the-money (ATM) options exhibiting the highest vega due to their maximum exposure to volatility shifts. In-the-money (ITM) options have lower vega because intrinsic value dominates their price movements, reducing volatility impact. Out-of-the-money (OTM) options show moderate vega but remain less sensitive than ATM options as their lack of intrinsic value limits volatility's influence.
Vega and Earnings Announcements: Practical Example
Vega measures an option's sensitivity to implied volatility changes, which often surge around earnings announcements due to heightened market uncertainty. For example, a call option on a stock trading at $100 with a vega of 0.25 will increase in value by approximately $0.25 for each 1% rise in implied volatility as earnings approach. Traders monitor vega to capitalize on volatility spikes before earnings and protect positions from rapid premium changes post-announcement.
Managing Vega Risk: Hedging with Options
Managing vega risk involves using options to hedge against changes in implied volatility that can significantly impact an option's price. Traders often buy or sell options with different strike prices and expirations to create a portfolio with minimal sensitivity to volatility shifts, effectively neutralizing vega exposure. This approach helps stabilize returns in volatile markets by balancing the vega of long and short option positions.
Key Takeaways from Vega Example in Finance
Vega measures an option's sensitivity to changes in the underlying asset's volatility, directly impacting the option's premium as volatility fluctuates. A higher vega indicates greater price responsiveness to volatility shifts, crucial when trading options during earnings announcements or market uncertainty. Understanding vega helps investors manage risk and optimize strategies in volatility-sensitive environments, ensuring more informed option pricing and portfolio hedging.
example of vega in option Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com