A common example of clawback in compensation occurs when a company rescinds bonuses paid to executives after financial results are restated. If an executive received a bonus based on earnings that were later found to be inaccurate due to accounting errors or misconduct, the company may activate its clawback policy. This policy ensures repayment of the amount equivalent to the wrongly awarded bonus, protecting shareholder interests and maintaining corporate governance standards. Financial institutions often implement clawback clauses in executive contracts to mitigate risks associated with aggressive risk-taking. These clauses enable the firm to recover incentive compensation if losses arise from decisions made during the executive's tenure. Such provisions create accountability by aligning executives' interests with long-term company performance and regulatory compliance.
Table of Comparison
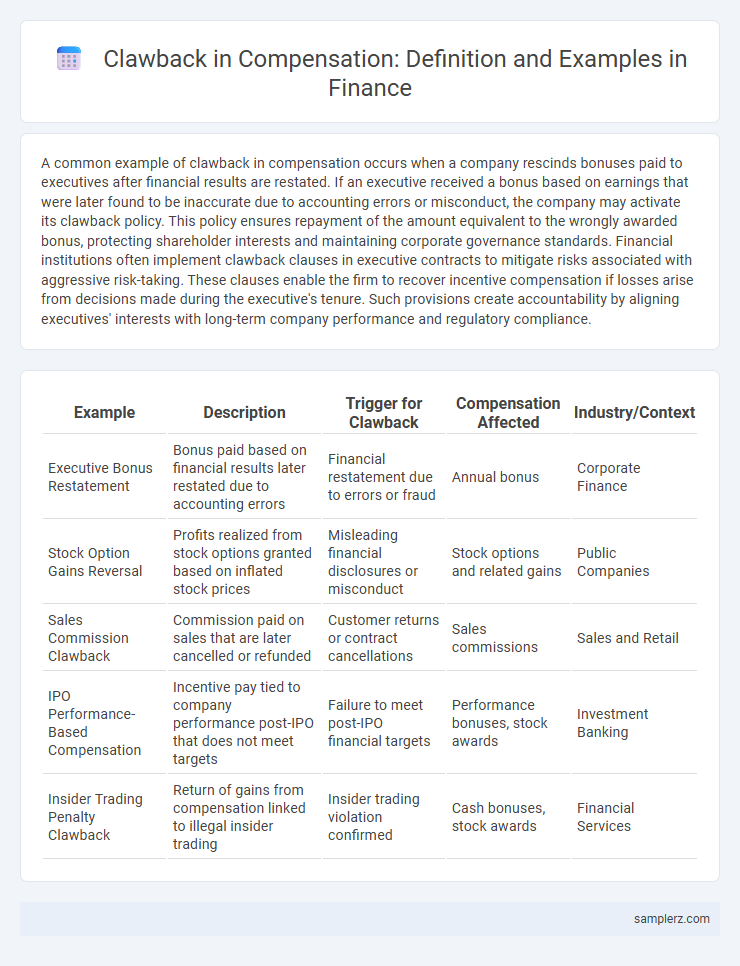
| Example | Description | Trigger for Clawback | Compensation Affected | Industry/Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Executive Bonus Restatement | Bonus paid based on financial results later restated due to accounting errors | Financial restatement due to errors or fraud | Annual bonus | Corporate Finance |
| Stock Option Gains Reversal | Profits realized from stock options granted based on inflated stock prices | Misleading financial disclosures or misconduct | Stock options and related gains | Public Companies |
| Sales Commission Clawback | Commission paid on sales that are later cancelled or refunded | Customer returns or contract cancellations | Sales commissions | Sales and Retail |
| IPO Performance-Based Compensation | Incentive pay tied to company performance post-IPO that does not meet targets | Failure to meet post-IPO financial targets | Performance bonuses, stock awards | Investment Banking |
| Insider Trading Penalty Clawback | Return of gains from compensation linked to illegal insider trading | Insider trading violation confirmed | Cash bonuses, stock awards | Financial Services |
Understanding Clawbacks in Compensation
Clawbacks in compensation refer to contractual agreements allowing employers to reclaim bonuses or incentives if financial results are restated due to errors or misconduct. These provisions are common in executive compensation plans to ensure accountability and align management's interests with long-term shareholder value. Regulatory frameworks such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act mandate clawbacks in cases of accounting fraud, protecting investors from misleading performance metrics.
Key Clawback Provisions in Executive Contracts
Key clawback provisions in executive contracts often include the recovery of bonuses or stock options linked to financial restatements or misconduct. These clauses specify triggers such as fraud, violation of company policies, or failure to meet performance metrics, ensuring alignment with shareholder interests. Enhanced regulations under the Dodd-Frank Act and SEC guidelines have increased enforcement and transparency of clawback policies in corporate governance.
Real-World Corporate Clawback Cases
In 2022, Wells Fargo executed a notable clawback by reclaiming over $75 million from former executives involved in fraudulent account scandals, emphasizing accountability in corporate governance. Similarly, in 2021, Deutsche Bank implemented clawback provisions targeting senior management bonuses following significant compliance failings that led to regulatory penalties exceeding $100 million. These real-world examples highlight the increasing use of clawbacks as a risk management tool to align executive compensation with long-term corporate performance and legal compliance.
Financial Scandals Triggering Clawbacks
Financial scandals such as the Enron collapse and the Wells Fargo fraud incident have triggered widespread clawbacks in executive compensation, reclaiming bonuses and incentives tied to misstated earnings and unethical behavior. Regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) have enforced clawback provisions under the Dodd-Frank Act, compelling companies to recover ill-gotten gains from top executives. These clawbacks serve to reinforce corporate accountability and deter future financial misconduct.
Clawbacks in Bonus and Incentive Pay
Clawbacks in bonus and incentive pay occur when companies reclaim previously awarded compensation due to financial restatements, misconduct, or failure to meet performance targets. These provisions are integral in aligning executives' incentives with long-term shareholder interests and ensuring accountability. Prominent examples include clawback policies enforced under the Dodd-Frank Act and Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which enable firms to recover bonuses tied to inaccurate financial results.
Recent Regulatory Actions on Clawback Policies
Recent regulatory actions on clawback policies have intensified scrutiny on executive compensation, particularly following high-profile corporate scandals. The SEC's updated rules now require companies to implement robust clawback provisions to reclaim incentive-based pay linked to financial statements that are later restated due to misconduct or error. These policies emphasize transparency and accountability, compelling firms to reassess compensation agreements to mitigate risks of financial misreporting.
Industry-Specific Clawback Examples
In the finance industry, clawback provisions often apply to executive bonuses linked to financial reporting accuracy, ensuring repayment if earnings are restated due to misconduct. Private equity firms implement clawbacks for carried interest when fund performance falls below projections, requiring general partners to return excess profits to limited partners. Investment banks may enforce clawbacks on traders' compensation triggered by significant losses or regulatory penalties within a defined timeframe, aligning incentives with risk management.
Clawback Enforcement: Legal Challenges
Clawback enforcement in executive compensation often faces legal challenges related to the ambiguity of contract language and varying state laws on clawback provisions. Courts frequently scrutinize the specific terms of the clawback agreement to determine whether repayment demands, triggered by misconduct or financial restatements, are enforceable. Corporate governance frameworks and regulatory guidance such as SEC rules influence the complexity and outcomes of litigation surrounding clawback enforcement.
Effects of Clawbacks on Corporate Governance
Clawbacks in executive compensation enhance corporate governance by holding leaders accountable for financial misstatements or unethical behavior, thereby deterring misconduct and promoting transparency. These provisions align management interests with shareholder value, reducing risk-taking and incentivizing more prudent decision-making. Empirical studies show firms with clawback policies experience improved financial reporting quality and increased investor confidence.
Best Practices for Implementing Clawback Clauses
Effective clawback clauses should clearly define the conditions triggering repayment, such as financial restatements or misconduct, to ensure enforceability. Incorporating transparent communication and regular training helps executives understand the implications, promoting compliance and accountability. Benchmarking against industry standards and involving legal and compensation experts can optimize the balance between risk mitigation and talent retention.
example of clawback in compensation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com