A death spiral in convertible finance occurs when a company issues convertible bonds or convertible preferred stock that investors convert into common shares at a discount to the market price. As investors convert, the increased share supply puts downward pressure on the stock price. This decline triggers more conversions at even lower prices, creating a vicious cycle that continuously dilutes existing shareholders' equity. Companies experiencing a death spiral often face severe stock price erosion and loss of investor confidence. The dilution effect reduces the value of shares held by existing investors, while the increased share count decreases earnings per share and market capitalization. Financial analysts monitor metrics like conversion price, conversion ratio, and stock price trends to identify potential death spiral scenarios in convertible securities.
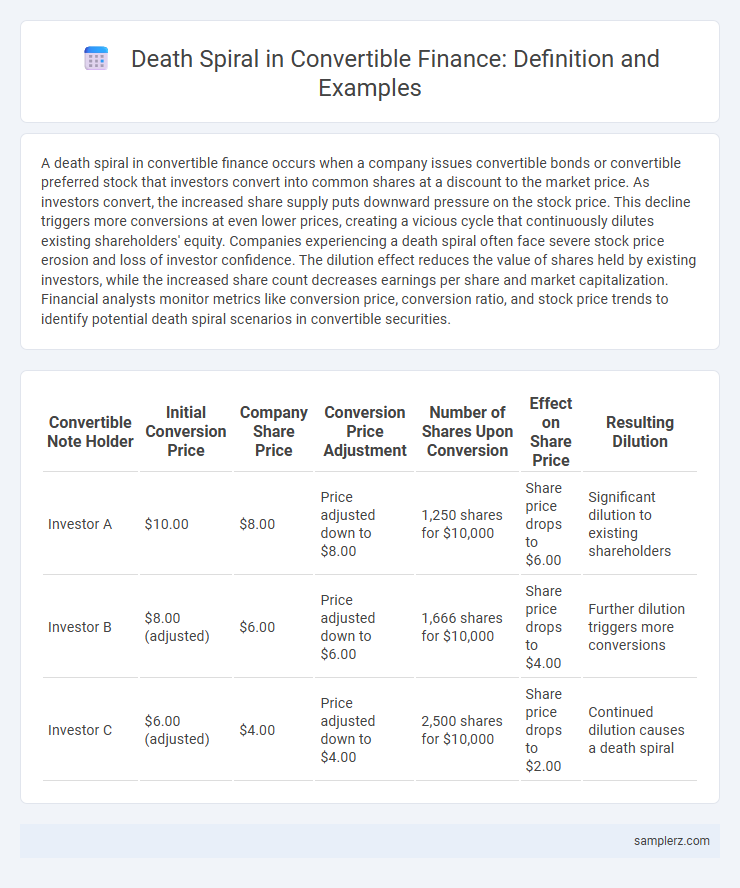
Table of Comparison
| Convertible Note Holder | Initial Conversion Price | Company Share Price | Conversion Price Adjustment | Number of Shares Upon Conversion | Effect on Share Price | Resulting Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investor A | $10.00 | $8.00 | Price adjusted down to $8.00 | 1,250 shares for $10,000 | Share price drops to $6.00 | Significant dilution to existing shareholders |
| Investor B | $8.00 (adjusted) | $6.00 | Price adjusted down to $6.00 | 1,666 shares for $10,000 | Share price drops to $4.00 | Further dilution triggers more conversions |
| Investor C | $6.00 (adjusted) | $4.00 | Price adjusted down to $4.00 | 2,500 shares for $10,000 | Share price drops to $2.00 | Continued dilution causes a death spiral |
Understanding the Death Spiral in Convertible Financing
A death spiral in convertible financing occurs when a company issues convertible debt that allows investors to convert debt into equity at a discount to the stock price, triggering continuous dilution as the stock price falls. As investors convert debt into shares and sell them, the increased supply drives the stock price down further, forcing additional conversions and accelerating the stock's decline. This negative feedback loop often causes significant loss of shareholder value and creates a challenging environment for raising future capital.
Key Characteristics of a Death Spiral Convertible
A death spiral convertible features a convertible note or bond with a conversion price that adjusts downward based on the issuer's stock price, leading to continuous dilution for existing shareholders. This mechanism typically includes a variable conversion price tied to the market price of the underlying equity, which can cause rapid share issuance if the stock price declines. Key characteristics include accelerated share dilution, downward repricing triggers, and increased downward pressure on stock value, often resulting in a destructive feedback loop for the company's equity.
How Death Spiral Convertibles Impact Share Price
Death spiral convertibles lead to significant share price dilution as issuers continuously convert debt into equity at declining stock prices, causing increased selling pressure. This conversion mechanism triggers rapid issuance of new shares, overwhelming the market supply and driving the share price downward. Investors often perceive the downward spiral as a sign of financial distress, further eroding market confidence and exacerbating share price decline.
Real-Life Example: Company X’s Death Spiral Scenario
Company X faced a death spiral when its convertible bonds continuously converted into shares, leading to excessive dilution and a plummeting stock price. The increasing share issuance triggered a downward price spiral, eroding investor confidence and market capitalization. This scenario exemplifies the risk of convertible securities causing severe financial distress through recursive dilution and asset devaluation.
The Role of Convertible Notes in Death Spiral Events
Convertible notes play a critical role in death spiral events by allowing investors to convert debt into equity at a discounted price, triggering rapid share dilution. This conversion mechanism often leads to a continuous drop in stock price, prompting further conversions and accelerating the downward spiral. The compounding effect of low conversion prices and expanding share volume severely undermines shareholder value and market confidence.
Warning Signs of an Impending Convertible Death Spiral
Rapid declines in a convertible bond's underlying stock price often signal the onset of a death spiral, as investors rush to convert shares and sell them, amplifying downward pressure. Increasing dilution and rising conversion rates lead to spiraling losses for existing shareholders, reflecting severe market distress. Abnormal trading volumes and significant spikes in volatility further indicate heightened risk of a convertible debt crisis.
Case Study: Lessons Learned from a Notable Death Spiral
The 2012 crisis involving GreenCo Inc. exemplifies a death spiral in convertible bond financing, where excessive conversion dilution triggered a sharp stock price decline, compounding investor losses. Key lessons from this case highlight the necessity for clear conversion caps and renegotiation clauses to prevent runaway dilution effects. Implementing stringent covenant protections early can mitigate the cascading impact of conversion-induced sell-offs in volatile markets.
The Investor’s Perspective: Profits and Pitfalls
From the investor's perspective, a death spiral in convertible securities occurs when continual dilution from conversion causes the stock price to plummet, eroding the value of their holdings. While initial conversions may offer attractive profits through discounted share prices, repeated conversions can trap investors in a downward price spiral, resulting in significant losses. Understanding the mechanics of conversion terms and market impact is crucial for mitigating risks associated with convertible debt death spirals.
Strategies Companies Use to Avoid a Death Spiral
Companies implement conversion price resets and set higher conversion prices to avoid a death spiral in convertible bonds, preventing excessive dilution of equity. They also use caps on conversion rates and maintain clear communication with investors to stabilize market confidence. Strategic timing of conversions and buybacks helps control stock price volatility, reducing the risk of spiraling downward.
Regulatory Concerns and Market Reactions
Death spiral conversions in convertible securities trigger regulatory concerns over market manipulation and investor protection due to the rapid dilution of shares. Regulatory bodies like the SEC scrutinize such transactions for potential violations of securities laws and unfair market practices. Market reactions often include sharp declines in stock prices and increased volatility as investors lose confidence in the company's financial stability.
example of death spiral in convertible Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com