A common example of a ladder in interest rate investing involves purchasing multiple bonds with staggered maturities. An investor buys bonds maturing in one, three, five, seven, and ten years to create a structured income stream and reduce interest rate risk. This strategy allows the portfolio to benefit from higher rates on longer-term bonds while maintaining liquidity with shorter-term holdings. The ladder approach enables consistent reinvestment opportunities as each bond matures, potentially capturing rising interest rates over time. Entities such as individual investors, pension funds, and insurance companies utilize rate ladders to balance yield and risk. Data analysis of historical bond yields supports laddering as an effective method to mitigate interest rate volatility and optimize returns.
Table of Comparison
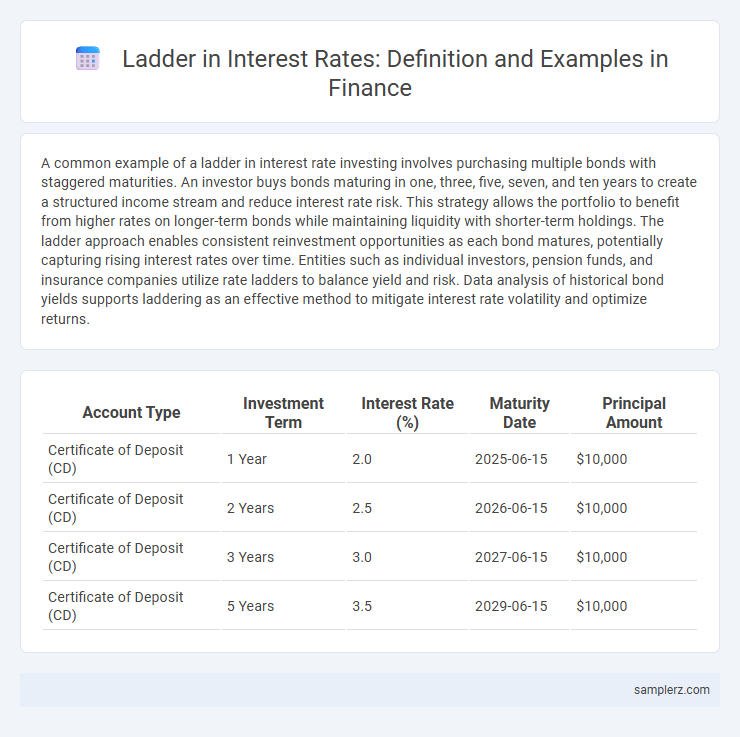
| Account Type | Investment Term | Interest Rate (%) | Maturity Date | Principal Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Certificate of Deposit (CD) | 1 Year | 2.0 | 2025-06-15 | $10,000 |
| Certificate of Deposit (CD) | 2 Years | 2.5 | 2026-06-15 | $10,000 |
| Certificate of Deposit (CD) | 3 Years | 3.0 | 2027-06-15 | $10,000 |
| Certificate of Deposit (CD) | 5 Years | 3.5 | 2029-06-15 | $10,000 |
Introduction to Interest Rate Ladders
Interest rate ladders involve structuring a portfolio of fixed-income securities with staggered maturity dates to manage risk and enhance liquidity. By dividing investments across multiple maturities, investors can capitalize on varying interest rates while reducing exposure to interest rate fluctuations. This strategy enables consistent income streams and opportunities to reinvest at prevailing rates as bonds mature.
How Interest Rate Ladders Work
Interest rate ladders involve structuring multiple fixed-income securities with staggered maturities to manage interest rate risk and enhance liquidity. By allocating investments across bonds maturing at different intervals, investors can reinvest at prevailing rates, capturing higher yields in rising rate environments while minimizing exposure during downturns. This strategy facilitates steady income streams and diversified risk exposure throughout varying market cycles.
Advantages of Laddering Interest Rates
Laddering interest rates in finance involves structuring investments across multiple fixed-income securities with varying maturities, which helps mitigate interest rate risk and enhances liquidity. This strategy allows investors to benefit from higher rates as they mature, while also providing regular opportunities to reinvest at prevailing market rates. By diversifying maturity dates, laddering reduces the impact of rate fluctuations and improves cash flow predictability.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Ladder
Creating an interest rate ladder involves dividing investments across multiple maturities to balance risk and liquidity efficiently. Start by selecting bond maturities staggered over set intervals, such as one to five years, ensuring consistent income as each bond matures. Monitor market interest rate fluctuations to reinvest matured funds at higher rates, optimizing returns throughout the ladder period.
Common Types of Interest Rate Ladders
Common types of interest rate ladders include fixed-rate ladders, where bonds or loans mature at staggered intervals with predetermined interest rates, and floating-rate ladders, which adjust based on benchmark rates like LIBOR or SOFR. Another prevalent type is the step-up ladder, featuring scheduled increases in interest rates over time to hedge against rising rates. These structures help investors manage interest rate risk while maintaining liquidity and optimizing returns.
Example: Laddering with Certificates of Deposit
Laddering with Certificates of Deposit (CDs) involves purchasing multiple CDs with staggered maturity dates to optimize interest rate returns and maintain liquidity. For example, an investor might allocate $10,000 evenly across five CDs maturing annually over five years, capturing potentially higher rates on long-term CDs while having access to funds each year. This strategy mitigates interest rate risk by preventing all investments from locking in at a single rate and allows reinvestment at prevailing rates upon each maturity.
Using Bonds in an Interest Rate Ladder
Using bonds in an interest rate ladder involves purchasing a series of bonds with varying maturities to manage interest rate risk while ensuring steady income streams. This strategy diversifies exposure across short-term, medium-term, and long-term bonds, reducing the impact of fluctuating interest rates on the overall portfolio. Financial institutions and individual investors employ bond ladders to achieve predictable cash flows and optimize returns in changing market conditions.
Risk Management in Laddered Portfolios
Laddered portfolios use staggered maturity dates to manage interest rate risk, ensuring exposure is spread across short, medium, and long-term bonds. This strategy reduces the impact of rising rates by reinvesting maturing bonds at higher yields while maintaining liquidity. Risk management in laddered portfolios involves balancing duration and credit quality to optimize returns and minimize volatility.
Interest Rate Ladder vs. Barbell Strategy
An Interest Rate Ladder involves spreading fixed-income investments across various maturities to reduce interest rate risk and provide steady income streams. In contrast, the Barbell Strategy concentrates investments in short- and long-term bonds to maximize yield from long maturities while maintaining liquidity through short-term securities. Laddering offers balanced risk management and cash flow stability, while the Barbell Strategy targets higher returns with a more polarized maturity distribution.
Best Practices for Maintaining Your Ladder
Maintaining a well-structured interest rate ladder involves regularly reviewing bond maturities to reinvest proceeds at current market rates, ensuring diversification across various time frames to mitigate interest rate risk. Best practices emphasize monitoring economic indicators and adjusting ladder intervals to capitalize on shifts in yield curves, thereby maximizing income and preserving capital. Consistent portfolio rebalancing aligns with individual risk tolerance and financial goals, enhancing the ladder's overall effectiveness in fluctuating interest rate environments.
example of ladder in interest rate Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com