Pari passu is a Latin term meaning "equal footing," commonly used in finance to describe bonds that share equal rights to repayment. When multiple bonds are issued under a pari passu clause, each bondholder receives proportional payment without preferential treatment. This clause ensures that in case of default, all bondholders are treated equally regarding claims on assets or proceeds. An example of pari passu in bonds occurs in corporate bond issuances where senior unsecured bonds carry a pari passu ranking. If a company faces bankruptcy, holders of these pari passu bonds are repaid simultaneously and proportionally from available assets. Data from major bond markets show that pari passu clauses help maintain investor confidence by reducing priority disputes among creditors.
Table of Comparison
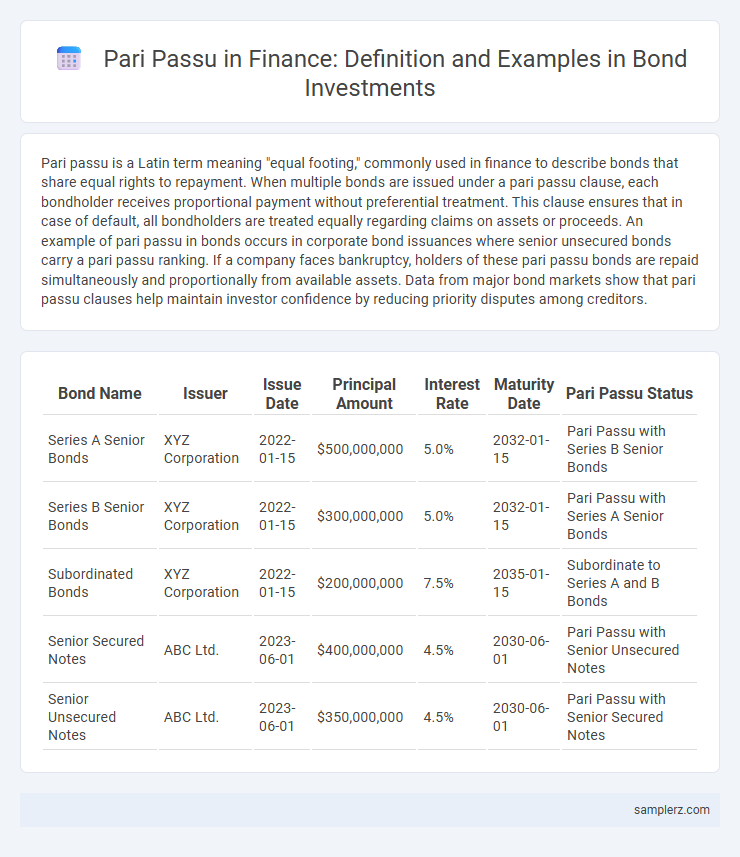
| Bond Name | Issuer | Issue Date | Principal Amount | Interest Rate | Maturity Date | Pari Passu Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Series A Senior Bonds | XYZ Corporation | 2022-01-15 | $500,000,000 | 5.0% | 2032-01-15 | Pari Passu with Series B Senior Bonds |
| Series B Senior Bonds | XYZ Corporation | 2022-01-15 | $300,000,000 | 5.0% | 2032-01-15 | Pari Passu with Series A Senior Bonds |
| Subordinated Bonds | XYZ Corporation | 2022-01-15 | $200,000,000 | 7.5% | 2035-01-15 | Subordinate to Series A and B Bonds |
| Senior Secured Notes | ABC Ltd. | 2023-06-01 | $400,000,000 | 4.5% | 2030-06-01 | Pari Passu with Senior Unsecured Notes |
| Senior Unsecured Notes | ABC Ltd. | 2023-06-01 | $350,000,000 | 4.5% | 2030-06-01 | Pari Passu with Senior Secured Notes |
Understanding Pari Passu in Bond Agreements
Pari passu in bond agreements ensures that all bondholders share equal rights to the issuer's assets and repayments, without any priority or preference. This clause protects investors by stipulating that in the event of default, payments are distributed pro rata among bonds of the same class. Understanding pari passu is crucial for evaluating risk, as it guarantees equitable treatment among creditors and affects the bond's creditworthiness and recovery rate.
Key Features of Pari Passu Clauses in Bonds
Pari passu clauses in bonds ensure that all bondholders have equal rank and share identical rights to principal and interest repayments without any preference or subordination. This key feature protects investors by guaranteeing proportional distribution of payments in cases of issuer default or restructuring, maintaining fairness among creditors. The clause also simplifies bond issuance by clearly defining equal treatment, reducing legal disputes and enhancing market confidence.
Historical Examples of Pari Passu in Bond Defaults
The 2012 Argentine debt crisis is a prominent historical example of pari passu clauses in bond defaults, where the country's refusal to equally treat bondholders led to prolonged litigation and payment disputes. During the crisis, Argentina's pari passu clause was invoked to prevent preferential treatment of certain creditors over others, emphasizing equal rank among bondholders. The case underscored the legal and financial complexities arising from pari passu provisions in sovereign bond restructurings.
How Pari Passu Impacts Bondholder Rights
Pari passu clause ensures that all bondholders have equal claim on the issuer's assets and repayments, preventing any preference in priority during liquidation or bankruptcy. This provision strengthens bondholder rights by guaranteeing proportional distribution of interest and principal, protecting them from subordination risks. Enforcement of pari passu clauses promotes transparency and fairness in debt restructuring, aligning bondholders' interests.
Pari Passu in Sovereign Bond Issuances
Pari passu in sovereign bond issuances means that all bondholders have equal rights to claim payments, ensuring no creditor is given preferential treatment over others. This principle is fundamental in maintaining investor confidence, as it guarantees that principal and interest payments are distributed proportionally and simultaneously among bondholders. Sovereign bonds with pari passu clauses help prevent disputes in debt restructuring by clearly stipulating equal rank and priority in repayment obligations.
Notable Court Cases Involving Pari Passu Bonds
In the landmark case of Elliott Associates v. Peru, the New York Court enforced the pari passu clause, preventing Peru from making preferential payments to certain bondholders and affirming equal treatment among creditors. Similarly, in the Argentina v. NML Capital case, the U.S. courts upheld pari passu provisions, blocking payments to restructured bondholders until holdout creditors were paid pro rata. These rulings have set crucial precedents emphasizing the binding nature of pari passu clauses in sovereign bond contracts, reinforcing equal priority in debt repayment.
Practical Example: Pari Passu Clause in Corporate Bonds
A practical example of a pari passu clause in corporate bonds occurs when a company issues multiple bond series that share the same seniority level, ensuring equal ranking for principal and interest payments. If the issuer faces financial distress, all pari passu bondholders receive proportional payments without preference, maintaining fair treatment among creditors. This clause prevents subordination risks and supports investor confidence by enforcing equal claims across similar debt instruments.
Differences Between Pari Passu and Subordinated Debt
Pari passu bonds share equal ranking and claims on issuer assets, ensuring all bondholders receive payments simultaneously if default occurs. Subordinated debt carries lower priority than pari passu bonds, meaning subordinated creditors are repaid only after senior and pari passu debts have been fully satisfied. The distinction impacts recovery rates and risk assessment, as pari passu creditors have stronger protection in bankruptcy proceedings compared to subordinated debt holders.
Risks Associated with Pari Passu Bond Provisions
Risks associated with pari passu bond provisions include the potential for unequal treatment during debt restructuring, where certain creditors may demand preferential repayment despite the clause's intent for equal ranking. This can lead to legal disputes and uncertainty in recovery rates for bondholders, weakening investor confidence. Furthermore, pari passu clauses may complicate enforcement actions if multiple creditors seek simultaneous claims, increasing the complexity and cost of debt resolution.
Lessons from Pari Passu Disputes in International Finance
Pari passu clauses ensure equal ranking among bondholders, preventing preferential treatment in repayment during default or restructuring. Disputes arising from ambiguous pari passu interpretations in sovereign debt highlight the critical need for clear contractual language to avoid costly litigation and safeguard investor confidence. Lessons from cases like Argentina's bond defaults emphasize the importance of precise pari passu formulations to maintain orderly debt resolutions and uphold international financial stability.
example of pari passu in bond Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com