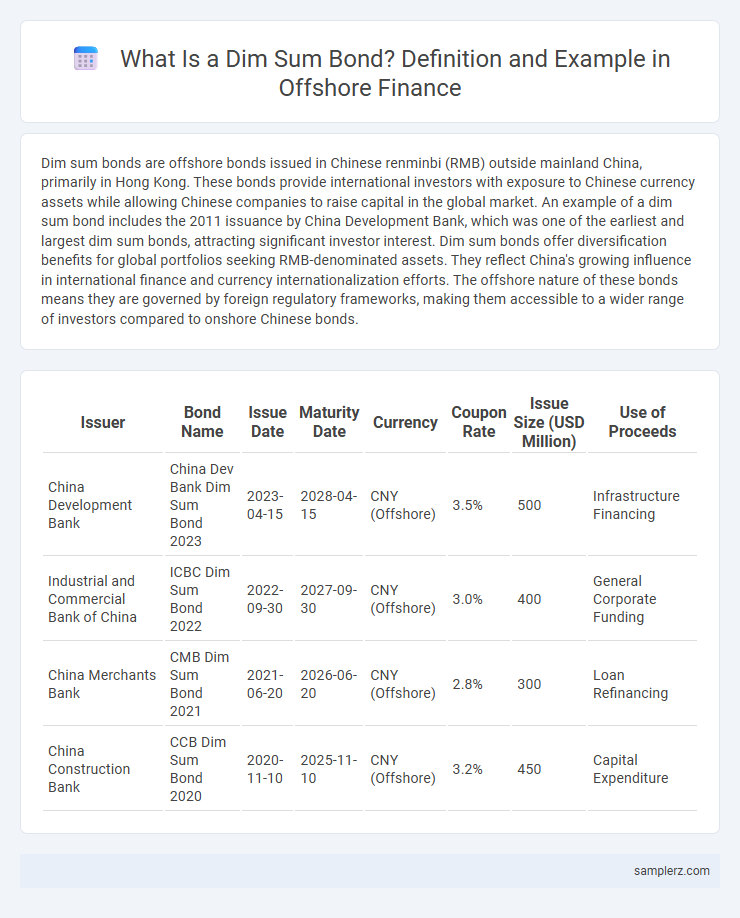
Dim sum bonds are offshore bonds issued in Chinese renminbi (RMB) outside mainland China, primarily in Hong Kong. These bonds provide international investors with exposure to Chinese currency assets while allowing Chinese companies to raise capital in the global market. An example of a dim sum bond includes the 2011 issuance by China Development Bank, which was one of the earliest and largest dim sum bonds, attracting significant investor interest. Dim sum bonds offer diversification benefits for global portfolios seeking RMB-denominated assets. They reflect China's growing influence in international finance and currency internationalization efforts. The offshore nature of these bonds means they are governed by foreign regulatory frameworks, making them accessible to a wider range of investors compared to onshore Chinese bonds.
Table of Comparison
| Issuer | Bond Name | Issue Date | Maturity Date | Currency | Coupon Rate | Issue Size (USD Million) | Use of Proceeds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China Development Bank | China Dev Bank Dim Sum Bond 2023 | 2023-04-15 | 2028-04-15 | CNY (Offshore) | 3.5% | 500 | Infrastructure Financing |
| Industrial and Commercial Bank of China | ICBC Dim Sum Bond 2022 | 2022-09-30 | 2027-09-30 | CNY (Offshore) | 3.0% | 400 | General Corporate Funding |
| China Merchants Bank | CMB Dim Sum Bond 2021 | 2021-06-20 | 2026-06-20 | CNY (Offshore) | 2.8% | 300 | Loan Refinancing |
| China Construction Bank | CCB Dim Sum Bond 2020 | 2020-11-10 | 2025-11-10 | CNY (Offshore) | 3.2% | 450 | Capital Expenditure |
Introduction to Dim Sum Bonds in Offshore Finance
Dim Sum bonds are renminbi-denominated bonds issued outside Mainland China, primarily in Hong Kong's offshore financial market. These bonds enable international investors to access China's currency while allowing Chinese issuers to raise capital globally without relying on domestic markets. The growth of Dim Sum bonds reflects China's expanding role in offshore finance and promotes the internationalization of the renminbi.
Key Features of Dim Sum Offshore Bonds
Dim sum offshore bonds are yuan-denominated bonds issued outside Mainland China, primarily in Hong Kong, offering foreign investors access to China's debt market. Key features include issuance in RMB, typically with maturities ranging from 1 to 10 years, and yields influenced by both Chinese monetary policy and global currency fluctuations. These bonds provide diversification benefits, liquidity in offshore markets, and exposure to China's economic growth, making them attractive for investors seeking RMB-denominated assets outside the mainland.
Historical Development of Dim Sum Bonds
Dim sum bonds, first issued in 2007, represent a significant development in offshore bond markets by allowing foreign investors to access Chinese yuan-denominated debt outside mainland China. The historical growth of dim sum bonds was driven by China's gradual financial liberalization and rising global demand for yuan assets, with issuance volumes peaking notably before regulatory tightening in the late 2010s. Key issuers include multinational corporations, financial institutions, and sovereign entities seeking diversification and exposure to the offshore yuan market.
Advantages of Issuing Dim Sum Bonds Offshore
Issuing Dim Sum bonds offshore provides Chinese issuers access to a broader pool of international investors seeking renminbi-denominated assets, enhancing liquidity and market depth. These bonds allow issuers to diversify funding sources while mitigating currency risk through natural hedging with offshore RMB holdings. Offshore issuance also benefits from favorable regulatory environments and potentially lower borrowing costs compared to onshore markets.
Notable Examples of Dim Sum Bond Issuance
Notable examples of Dim Sum bond issuance include Alibaba Group's record-breaking $1 billion bond offering in 2015, which significantly boosted offshore RMB market liquidity. Other key issuers such as China Construction Bank and Industrial and Commercial Bank of China have also leveraged Dim Sum bonds to diversify funding sources and attract international investors. These offshore renminbi bonds continue to play a critical role in expanding China's financial market presence globally.
Market Performance of Offshore Dim Sum Bonds
Offshore Dim Sum bonds, primarily issued in Hong Kong but denominated in Chinese yuan, have demonstrated robust market performance due to increasing investor appetite for yuan-denominated assets outside mainland China. Market data from 2023 indicates a substantial growth in issuance volume, with a record $25 billion raised, reflecting strong liquidity and investor confidence. Pricing trends reveal tightening spreads compared to similar instruments, underscoring improved credit profiles and greater integration of the offshore yuan bond market within global fixed income portfolios.
Investor Demand for Dim Sum Bonds in Global Markets
Investor demand for Dim Sum bonds in global markets has surged due to their attraction as RMB-denominated offshore debt instruments offering diversification and access to China's growing economy. These bonds, issued outside mainland China mainly in Hong Kong, provide favorable yields compared to onshore debt, appealing to international fixed-income portfolios seeking exposure to RMB assets. Institutional investors prioritize Dim Sum bonds for currency diversification, regulatory benefits, and liquidity in the offshore bond market.
Regulatory Environment for Offshore Dim Sum Bonds
Offshore Dim Sum bonds, issued outside China but denominated in Chinese renminbi (RMB), operate within a regulatory environment shaped by both Chinese authorities and host countries' financial regulators. The People's Bank of China (PBOC) and the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) set guidelines on capital controls and currency conversion, ensuring stability and compliance in cross-border RMB transactions. Host countries require adherence to local securities laws and disclosure standards, creating a dual-layer regulatory framework that impacts issuance, pricing, and investor protection in the offshore bond market.
Risks Associated with Offshore Dim Sum Bonds
Offshore Dim Sum bonds, issued outside of China but denominated in Chinese yuan, expose investors to currency risk due to fluctuating exchange rates between the yuan and their home currency. Credit risk is significant because these bonds are often issued by entities with less transparent financial disclosures compared to onshore issuers, potentially affecting repayment capacity. Regulatory risk also plays a role, as changes in cross-border capital controls or monetary policy by Chinese authorities can impact bond liquidity and market access.
Future Outlook for Dim Sum Bonds in International Finance
Dim sum bonds, issued outside China but denominated in Chinese yuan, are gaining traction as foreign investors seek yuan-denominated assets amid China's financial opening. The future outlook for dim sum bonds in international finance is positive, driven by China's push for yuan internationalization and growing demand for currency diversification. Increased regulatory clarity and expanding offshore yuan liquidity pools are set to enhance market depth and investor confidence.
example of dim sum in offshore bond Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com