In project finance, ringfencing refers to legally isolating project assets and cash flows from the parent company's other operations. This structure ensures that creditors can claim only the project's revenues and assets in case of default, reducing risk exposure. A common example is a special purpose vehicle (SPV) created to finance and operate a power plant, where the SPV's resources are distinct from the parent company's balance sheet. Ringfencing safeguards investors by limiting liability and exposing them solely to the project's performance. This mechanism is crucial in infrastructure projects, such as toll roads or renewable energy installations, where the cash flow is dedicated exclusively to debt repayment and operating expenses. By segregating the project's financials, ringfencing enhances creditworthiness and facilitates financing through non-recourse or limited recourse loans.
Table of Comparison
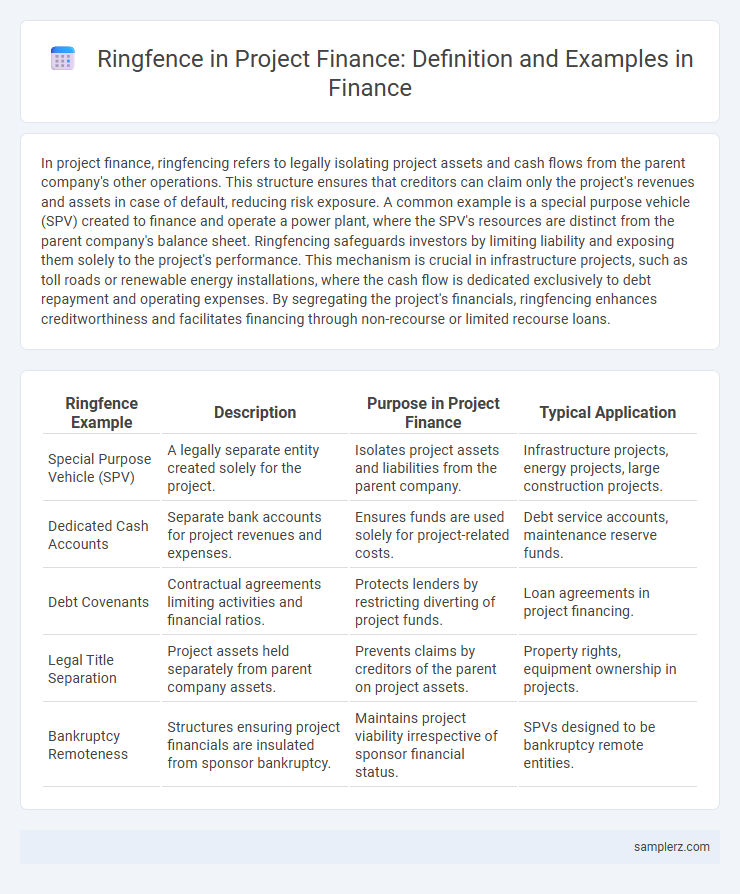
| Ringfence Example | Description | Purpose in Project Finance | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) | A legally separate entity created solely for the project. | Isolates project assets and liabilities from the parent company. | Infrastructure projects, energy projects, large construction projects. |
| Dedicated Cash Accounts | Separate bank accounts for project revenues and expenses. | Ensures funds are used solely for project-related costs. | Debt service accounts, maintenance reserve funds. |
| Debt Covenants | Contractual agreements limiting activities and financial ratios. | Protects lenders by restricting diverting of project funds. | Loan agreements in project financing. |
| Legal Title Separation | Project assets held separately from parent company assets. | Prevents claims by creditors of the parent on project assets. | Property rights, equipment ownership in projects. |
| Bankruptcy Remoteness | Structures ensuring project financials are insulated from sponsor bankruptcy. | Maintains project viability irrespective of sponsor financial status. | SPVs designed to be bankruptcy remote entities. |
Understanding Ringfencing in Project Finance
Ringfencing in project finance isolates the project's assets, liabilities, and cash flows from the parent company's financial risks, ensuring creditors have a dedicated claim on the project's resources. This mechanism provides risk mitigation by allowing lenders to evaluate the project's creditworthiness independently. An example is a renewable energy plant funded through a special purpose vehicle (SPV), where ringfencing protects project assets from the parent corporation's potential financial distress.
Key Characteristics of Ringfenced Project Structures
Ringfenced project finance structures isolate project assets, liabilities, and cash flows from the parent company, ensuring limited recourse lending. Key characteristics include dedicated special purpose vehicles (SPVs), restricted access to project cash flows, and strict contractual frameworks like off-take agreements and sponsor support. This isolation minimizes sponsor risks, enhances creditworthiness, and secures lender interests through defined security packages and covenants.
Real-World Examples of Ringfenced Project Finance
The Thames Tideway Tunnel project in London exemplifies ringfenced project finance, where cash flows and assets are isolated to ensure creditor security and limit risk exposure. This large-scale infrastructure initiative used special purpose vehicles (SPVs) to ringfence liabilities, enabling long-term debt financing without impacting the parent companies' balance sheets. Ringfencing in such projects protects investors by segregating project-specific risks from broader corporate financial risks.
Case Study: Power Plant Project Ringfencing
The Power Plant Project utilized ringfencing by isolating project assets, cash flows, and liabilities within a special purpose vehicle (SPV), ensuring that financial risks were contained and not transferred to the parent company. Debt servicing was secured exclusively from the plant's revenue streams under a long-term power purchase agreement (PPA), minimizing investor exposure to external market fluctuations. This ringfence structure enhanced creditworthiness, facilitating favorable loan terms and protecting stakeholders from operational risks beyond the project's scope.
Infrastructure Projects Utilizing Ringfence Mechanisms
Infrastructure projects often use ringfence mechanisms to isolate project assets and revenues, ensuring that cash flows are dedicated solely to servicing the project's debt and operating expenses. For example, a toll road project may establish a special purpose vehicle (SPV) that holds the concession rights and segregates toll collections from the parent company's financial risks. This ringfencing protects investors by limiting their exposure to the project's standalone performance and enhances creditworthiness for refinancing.
Advantages of Ringfencing in PPP Projects
Ringfencing in Public-Private Partnership (PPP) projects isolates project assets and revenues from the sponsoring entity's other financial obligations, enhancing creditworthiness and reducing investor risk. This segregation ensures that project cash flows are dedicated exclusively to debt service and operational expenses, improving lender confidence and facilitating access to lower-cost financing. By protecting project finance structures from external financial distress, ringfencing strengthens project viability and long-term financial sustainability.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Ringfencing
Ringfencing in project finance isolates assets and liabilities within a special purpose vehicle (SPV) to protect creditors and ensure project viability under specific legal frameworks. Regulatory requirements often mandate ringfenced structures to mitigate risk exposure, enforce bankruptcy remoteness, and comply with jurisdictional insolvency laws. Legal covenants within financing agreements typically restrict asset transfers and guarantee cash flow segregation, enhancing creditor protection and facilitating project-specific risk management.
Risk Mitigation through Ringfenced Financing
In project finance, ringfenced financing isolates a project's cash flows and assets from the parent company's financial risks, ensuring that creditors have a claim solely on the project's revenues. This approach mitigates credit risk by restricting access to funds exclusively to project-related activities, preventing contamination from external liabilities. By creating a legal and financial separation, ringfencing enhances lender confidence and facilitates tailored risk allocation in complex infrastructure and energy projects.
Ringfencing in Renewable Energy Project Finance
Ringfencing in renewable energy project finance involves isolating project assets and cash flows to protect investors and lenders from risks associated with the parent company's liabilities. This technique ensures that revenues generated by solar farms or wind turbines are exclusively used to service project debt and operational costs, enhancing creditworthiness. By legally separating project finances, stakeholders reduce exposure to external financial disturbances, promoting stable and predictable returns.
Lessons Learned from Ringfencing Failures in Project Finance
Failures in project finance ringfencing often stem from inadequate legal frameworks, insufficient asset segregation, and poor risk allocation among stakeholders. For example, the Dabhol Power Project in India faced significant failures due to weak ringfencing, leading to creditor disputes and project delays. Lessons learned emphasize the necessity of robust contractual agreements and transparent governance to ensure effective ringfencing and mitigate financial risk.
example of ringfence in project finance Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com