Ring fencing in bankruptcy refers to the legal practice of isolating specific assets or funds to protect them from being used to pay off general creditors. This strategy is often employed in financial institutions to shield client funds, ensuring they remain accessible despite the company's insolvency. For instance, a bank may ring fence customer deposits to prevent them from being included in the bank's bankruptcy estate. Another example is in the case of a bankruptcy involving a parent company and its subsidiaries. Regulatory authorities might require ring fencing of the subsidiaries' assets to prevent cross-contamination of liabilities, safeguarding operational entities from the parent's financial troubles. This data protection helps maintain critical services and preserves value for stakeholders during bankruptcy proceedings.
Table of Comparison
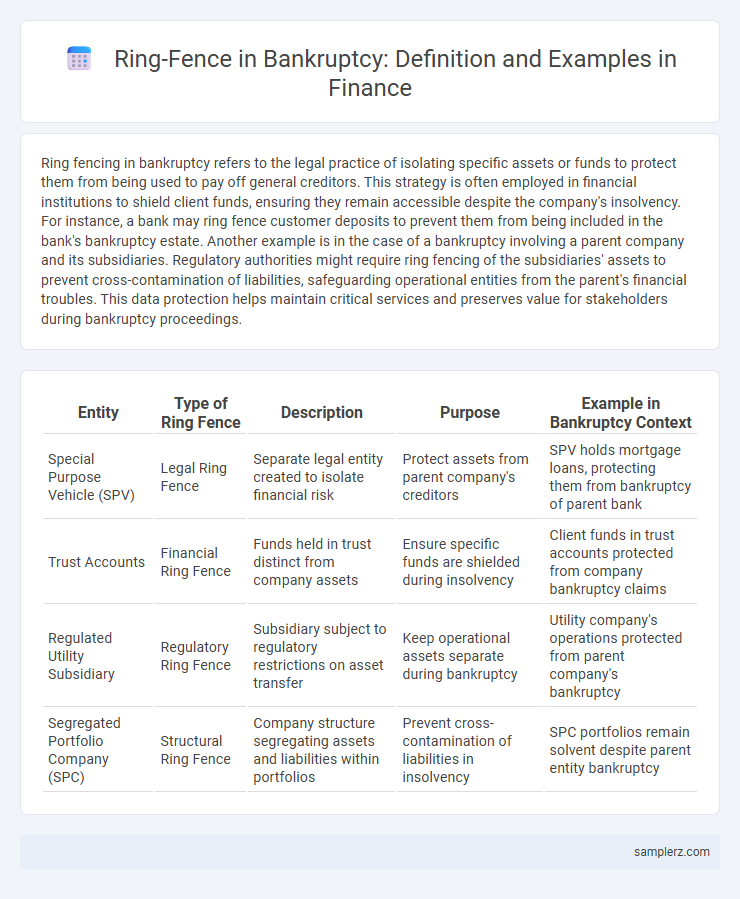
| Entity | Type of Ring Fence | Description | Purpose | Example in Bankruptcy Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) | Legal Ring Fence | Separate legal entity created to isolate financial risk | Protect assets from parent company's creditors | SPV holds mortgage loans, protecting them from bankruptcy of parent bank |
| Trust Accounts | Financial Ring Fence | Funds held in trust distinct from company assets | Ensure specific funds are shielded during insolvency | Client funds in trust accounts protected from company bankruptcy claims |
| Regulated Utility Subsidiary | Regulatory Ring Fence | Subsidiary subject to regulatory restrictions on asset transfer | Keep operational assets separate during bankruptcy | Utility company's operations protected from parent company's bankruptcy |
| Segregated Portfolio Company (SPC) | Structural Ring Fence | Company structure segregating assets and liabilities within portfolios | Prevent cross-contamination of liabilities in insolvency | SPC portfolios remain solvent despite parent entity bankruptcy |
Understanding Ring Fencing in Bankruptcy
Ring fencing in bankruptcy involves legally isolating specific assets or subsidiaries to protect them from creditors' claims during insolvency proceedings. This mechanism ensures that critical or solvent parts of a business are preserved and continue operating, safeguarding value for stakeholders. By establishing clear boundaries around these assets, ring fencing minimizes risk exposure and enhances creditor confidence in complex financial restructurings.
Key Features of Ring Fence Structures
Ring fence structures in bankruptcy isolate specific assets or cash flows from the general estate, ensuring creditor claims are restricted to designated collateral. Key features include legal separation of protected resources, dedicated cash flow streams, and enforceable priority rights that shield ring-fenced assets from general creditors. This containment enhances predictability for secured lenders and preserves value for critical business units during insolvency proceedings.
Common Scenarios for Ring Fencing in Corporate Bankruptcies
Common scenarios for ring-fencing in corporate bankruptcies include isolating profitable subsidiaries from the parent company's liabilities to protect their assets and cash flow. Ring-fencing is often applied to separate secured creditors' collateral, ensuring that specific assets like real estate or intellectual property remain dedicated to debt repayment. This practice helps preserve operational units and safeguards critical business functions during restructuring.
Real-World Examples of Ring Fence Applications
In the bankruptcy case of Lehman Brothers, ring-fencing was applied to isolate hedge fund assets from the broader collapse, protecting client interests and enabling structured asset recovery. Similarly, during the 2008 financial crisis, Icelandic banks utilized ring-fencing to separate domestic banking operations from international subsidiaries, safeguarding national financial stability. These real-world examples demonstrate how ring-fencing serves as a critical mechanism in managing asset segregation and minimizing systemic risk in bankruptcy proceedings.
Legal Frameworks Supporting Ring Fencing in Bankruptcy
Legal frameworks supporting ring fencing in bankruptcy include statutory provisions like the U.S. Bankruptcy Code's Section 362, which imposes automatic stays to isolate debtor assets from creditor claims. Jurisdictions often implement trust structures or segregated accounts to legally separate specific assets, ensuring protection during insolvency proceedings. Courts may enforce ring fencing through recognition of secured interests and priority claims, preserving asset pools for designated creditors and preventing asset commingling.
Impact of Ring Fence Measures on Creditors
Ring fence measures in bankruptcy isolate specific assets or liabilities to protect creditor interests by preventing the commingling of funds, thereby ensuring priority repayment. Creditors benefit from enhanced security and clarity in asset distribution, reducing the risk of loss due to the debtor's other financial obligations. This segregation improves creditor confidence and potentially increases recovery rates during insolvency proceedings.
Case Study: Subsidiary Ring Fencing During Parent Bankruptcy
In the bankruptcy case of Lehman Brothers, the firm utilized subsidiary ring fencing to protect key assets within its brokerage arm, Lehman Brothers Inc., from claims against the parent company. This legal structure ensured that Lehman Brothers Inc.'s client assets remained segregated and insulated, allowing the subsidiary to continue operations and facilitate an orderly liquidation process. Ring fencing effectively isolated the subsidiary's liabilities, minimizing contagion risk and safeguarding creditor interests during complex bankruptcy proceedings.
Regulatory Ring Fencing in the Financial Sector
Regulatory ring fencing in the financial sector isolates critical banking functions to protect essential services from risks associated with a firm's other operations during bankruptcy. For instance, the UK's approach post-2008 financial crisis mandates that retail banking activities be separated from investment banking within large financial groups to safeguard consumer deposits and payment infrastructures. This structural separation ensures that core banking services remain operational and solvent even if non-essential or high-risk segments face insolvency.
Benefits and Criticisms of Bankruptcy Ring Fences
Bankruptcy ring fences protect specific assets from creditors, ensuring that critical funds or collateral remain intact to support reorganized business operations or satisfy prioritized claims. These structures benefit stakeholders by enhancing financial stability, preserving value, and facilitating clearer asset allocation during insolvency processes. Critics argue that ring fences can complicate the bankruptcy by fragmenting asset pools, potentially reducing the total recoverable amount for general creditors and increasing administrative costs.
Future Trends in the Use of Ring Fencing in Insolvency
Ring fencing in insolvency is increasingly utilized to protect critical assets and segregate operational units from bankruptcy estates, ensuring continuity of essential services and preserving stakeholder value. Emerging trends include the integration of blockchain technology to enhance transparency and enforceability of ring-fenced assets, alongside regulatory shifts encouraging more granular asset protection frameworks in complex financial restructurings. Firms are progressively adopting ring fencing to isolate non-core liabilities, which facilitates targeted recovery strategies and mitigates systemic risks during insolvency proceedings.
example of ring fence in bankruptcy Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com