A lag in currency hedge occurs when there is a delay between entering a hedging contract and the actual exposure date. For instance, a multinational corporation may hedge its foreign currency risk based on projected earnings expected in three months, but the actual cash flow may occur later or earlier than anticipated. This timing mismatch can result in ineffective hedging, causing potential losses due to currency fluctuations during the lag period. Data from financial reports reveals that firms with significant lag in their currency hedge often face increased volatility in earnings. For example, a U.S.-based company hedging euro receivables with a three-month forward contract might experience exchange rate movements before the settlement date, impacting the hedge's effectiveness. This lag requires careful monitoring of market conditions and updated forecasts to minimize risk exposure and optimize hedge performance.
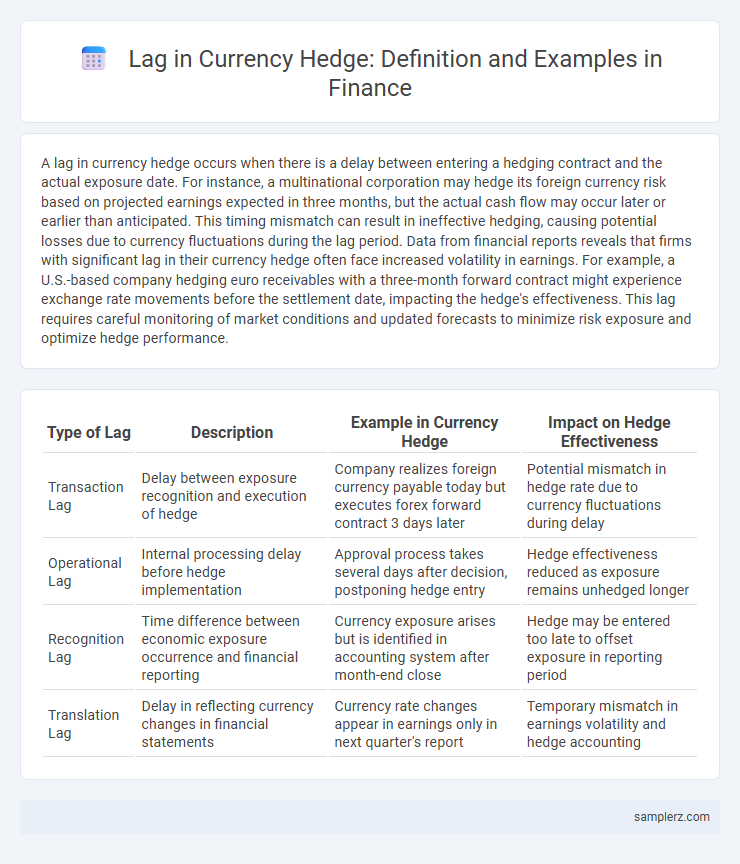
Table of Comparison
| Type of Lag | Description | Example in Currency Hedge | Impact on Hedge Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction Lag | Delay between exposure recognition and execution of hedge | Company realizes foreign currency payable today but executes forex forward contract 3 days later | Potential mismatch in hedge rate due to currency fluctuations during delay |
| Operational Lag | Internal processing delay before hedge implementation | Approval process takes several days after decision, postponing hedge entry | Hedge effectiveness reduced as exposure remains unhedged longer |
| Recognition Lag | Time difference between economic exposure occurrence and financial reporting | Currency exposure arises but is identified in accounting system after month-end close | Hedge may be entered too late to offset exposure in reporting period |
| Translation Lag | Delay in reflecting currency changes in financial statements | Currency rate changes appear in earnings only in next quarter's report | Temporary mismatch in earnings volatility and hedge accounting |
Understanding Lag in Currency Hedging
Lag in currency hedging refers to the delay between initiating a hedge and its effectiveness in offsetting currency risk. This delay often arises from market fluctuations, execution timing, or operational constraints, resulting in temporary exposure despite hedging strategies. Understanding lag is critical for managing currency risk and optimizing hedge performance in multinational financial operations.
Common Causes of Hedging Lag
Common causes of lag in currency hedging include delayed execution of hedge contracts due to market volatility and operational inefficiencies within treasury departments. Inaccurate timing of hedge adjustments often results from reliance on outdated exchange rate forecasts or slow reaction to currency fluctuations. Furthermore, limited access to real-time market data and restrictions imposed by internal risk management policies contribute significantly to hedging delays.
Real-World Example: Corporate Currency Hedging Lag
A real-world example of currency hedging lag is seen in multinational corporations like Apple Inc., which faces delays between initiating hedging contracts and actual exposure events due to complex global operations. This lag can result in temporary mismatches, where currency fluctuations impact earnings before hedging instruments fully offset risks. Effective management of lag involves dynamic adjustment of hedge ratios and real-time monitoring of currency exposures to minimize financial volatility.
Impact of Lag on Currency Hedging Outcomes
Lag in currency hedging occurs when there is a delay between the measurement of exposure and the execution of hedge transactions, often due to operational or timing constraints. This time gap can result in mismatches between the hedge and the underlying currency exposure, leading to reduced effectiveness and increased risk of unhedged currency fluctuations. Consequently, the impact of lag can cause unexpected losses or gains, affecting portfolio returns and overall hedging strategies within multinational finance management.
Case Study: Investment Fund Lag in FX Hedge
The case study of an investment fund experiencing lag in its currency hedge highlights the risk of delayed adjustments to foreign exchange exposures, resulting in potential losses during volatile currency movements. The fund's hedge ratio fell behind its target due to slow execution and market changes, causing inefficiencies in risk mitigation and impacting overall portfolio returns. Optimizing hedge rebalancing frequency and employing real-time FX risk analytics can reduce lag and enhance the effectiveness of currency risk management strategies.
Managing Time Lag in Currency Forwards
Managing time lag in currency forwards is crucial for minimizing exposure to exchange rate fluctuations during the settlement period. Effective strategies include closely monitoring market conditions and adjusting hedge tenors to align with cash flow timings, thereby reducing the risk of adverse currency movements. Utilizing forward contracts with appropriate maturity dates ensures better synchronization between hedge execution and actual currency needs.
Quantifying Performance Slippage Due to Hedge Lag
Quantifying performance slippage due to hedge lag involves measuring the variance between the currency hedge's intended protection and its actual effectiveness over time. This slippage can be calculated by comparing the realized returns on hedged currency exposures against unhedged benchmarks, accounting for market movements during the lag period. Employing statistical models like regression analysis on historical currency returns and hedge adjustments enables accurate estimation of the lag's impact on portfolio performance.
Solutions to Minimize Lag in Currency Hedging
Implementing real-time currency monitoring systems and dynamic hedging strategies significantly reduces lag in currency hedge adjustments, ensuring timely responses to market fluctuations. Utilizing automated trading platforms combined with advanced algorithms enables precise execution of hedge transactions aligned with currency movements. Incorporating forward contracts with shorter maturities and frequent portfolio rebalancing also minimizes the exposure caused by lag in currency hedging.
Consequences of Hedging Lag During Market Volatility
Hedging lag in currency management during market volatility can lead to significant financial exposure and unexpected losses due to delayed adjustments in foreign exchange positions. This temporal mismatch causes firms to miss optimal hedge windows, increasing vulnerability to exchange rate fluctuations and eroding profit margins. Effective risk management requires minimizing lag time to maintain hedge effectiveness and protect asset value in rapidly changing currency markets.
Best Practices for Reducing Currency Hedge Lag
Implementing a dynamic hedging strategy that aligns with real-time market data helps minimize currency hedge lag by ensuring timely adjustments to foreign exchange exposures. Utilizing advanced analytics and automated trading platforms enhances decision-making accuracy and execution speed, reducing the impact of currency fluctuations on portfolio value. Regularly reviewing and updating hedge parameters based on volatility forecasts and economic indicators supports effective risk mitigation and cost efficiency.
example of Lag in currency hedge Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com