A ladder in bonds is a fixed-income investment strategy where an investor purchases bonds with staggered maturities. This approach diversifies interest rate risk while providing a steady stream of income as bonds mature at different times. For example, an investor might buy bonds maturing in one, three, five, seven, and ten years. The ladder structure allows reinvestment opportunities at varying interest rates, potentially increasing returns over time. It helps balance liquidity needs by ensuring that some portion of the portfolio matures consistently. Data shows that bond ladders can reduce the impact of market volatility and interest rate fluctuations on the overall portfolio.
Table of Comparison
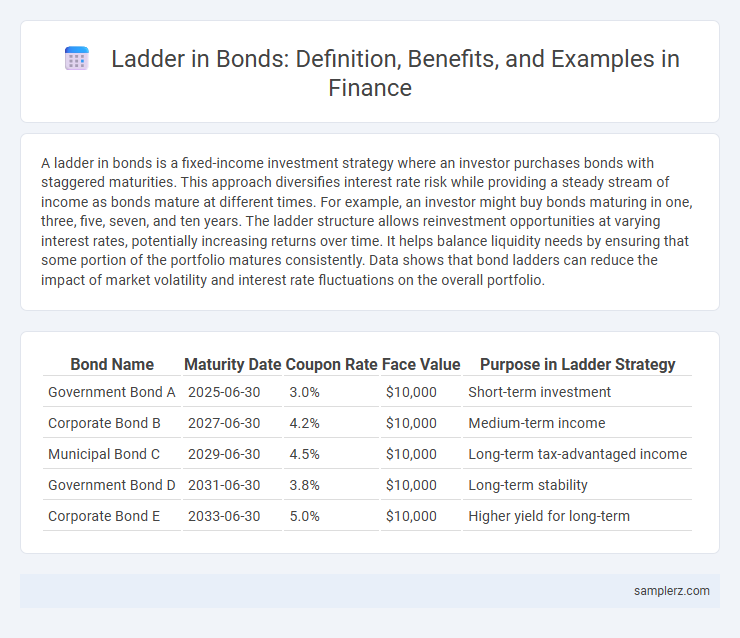
| Bond Name | Maturity Date | Coupon Rate | Face Value | Purpose in Ladder Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government Bond A | 2025-06-30 | 3.0% | $10,000 | Short-term investment |
| Corporate Bond B | 2027-06-30 | 4.2% | $10,000 | Medium-term income |
| Municipal Bond C | 2029-06-30 | 4.5% | $10,000 | Long-term tax-advantaged income |
| Government Bond D | 2031-06-30 | 3.8% | $10,000 | Long-term stability |
| Corporate Bond E | 2033-06-30 | 5.0% | $10,000 | Higher yield for long-term |
Understanding Bond Laddering: A Strategic Overview
Bond laddering involves purchasing bonds with staggered maturities to manage interest rate risk and ensure liquidity. By spreading investments across multiple maturity dates, investors can reinvest proceeds at prevailing rates and reduce exposure to market volatility. This strategy enhances portfolio stability and provides steady income streams through diversified bond maturities.
Key Components of a Bond Ladder Portfolio
A bond ladder portfolio consists of a series of bonds with staggered maturities, providing regular income and reducing interest rate risk. Key components include diversification across various bond maturities, reinvestment of maturing bonds to maintain the ladder structure, and a mix of credit qualities to balance yield and risk. This strategy enhances liquidity and helps investors manage cash flow while mitigating the impact of market volatility.
Step-by-Step Example of Setting Up a Bond Ladder
A bond ladder involves purchasing bonds with staggered maturities to manage interest rate risk and provide consistent income. For example, an investor buys bonds maturing in one, two, three, four, and five years, reinvesting each bond's principal upon maturity into a new five-year bond. This strategy maintains a diversified portfolio with rolling maturities, balancing liquidity and yield effectively.
Benefits of Implementing a Bond Ladder Strategy
Implementing a bond ladder strategy enhances portfolio diversification by staggering maturities, which reduces interest rate risk and provides consistent cash flow. This approach allows investors to reinvest matured bonds at prevailing rates, potentially increasing yield over time. Bond ladders also improve liquidity management, enabling better alignment with financial goals and unexpected expenses.
Risks and Considerations in Bond Ladder Construction
Bond ladder construction involves spreading maturities across different dates to manage interest rate risk and liquidity. Risks include reinvestment risk where maturing bonds may be reinvested at lower rates and credit risk if any issuer defaults. Careful consideration is needed to balance yield, duration, and diversification to optimize portfolio stability and income.
Real-World Scenarios: Bond Ladder Examples
A bond ladder involves purchasing bonds with staggered maturities to manage interest rate risk and provide steady income. For example, an investor might buy bonds maturing in one, three, five, seven, and ten years, ensuring that as each bond matures, funds can be reinvested at current interest rates or allocated to other needs. This strategy enhances portfolio diversification and liquidity, particularly in fluctuating interest rate environments.
Diversification through Bond Laddering
Bond laddering involves purchasing bonds with staggered maturities, such as 1-year, 3-year, 5-year, 7-year, and 10-year terms, to create a diversified income stream. This strategy mitigates interest rate risk by ensuring that bonds mature at different times, allowing reinvestment opportunities in varying interest rate environments. By diversifying maturities, investors balance liquidity needs and stable returns, enhancing portfolio resilience against market fluctuations.
Comparing Bond Ladders vs. Bullet Portfolios
Bond ladders diversify investment maturity dates by staggering bonds across various intervals, reducing interest rate risk and providing steady cash flow. Bullet portfolios concentrate bond maturities at a single point, offering potential for higher yield but increased exposure to reinvestment risk. Investors choosing bond ladders benefit from improved liquidity and risk management compared to the concentrated exposure of bullet strategies.
Optimizing Return with a Laddered Bond Portfolio
A laddered bond portfolio involves purchasing bonds with staggered maturities, allowing investors to reinvest proceeds regularly and reduce interest rate risk. This strategy optimizes returns by capturing varying yields across different maturity dates while maintaining liquidity and minimizing price volatility. By balancing short- and long-term bonds, investors can adapt to changing market conditions and enhance income stability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Building a Bond Ladder
A common mistake when building a bond ladder is failing to diversify maturities, which can expose investors to interest rate risk and reduce income stability. Another error is neglecting credit quality, leading to potential default risk that undermines portfolio safety. Overconcentration in a single issuer or sector limits the benefits of laddering and increases vulnerability to market fluctuations.
example of ladder in bond Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com