Drag-along rights in venture capital protect majority investors by ensuring they can require minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company. For example, if a venture capital firm owning 60% of a startup decides to sell its shares to a third party, the drag-along clause forces minority shareholders to sell their shares under the same terms. This mechanism helps streamline exits and prevents minority investors from blocking lucrative acquisition deals. In financial terms, drag-along rights impact shareholder agreements and valuation negotiations within startup funding rounds. Data shows that around 75% of venture capital term sheets include drag-along provisions to facilitate smoother liquidity events. Corporate lawyers and investors analyze these clauses closely to maintain alignment on exit strategies and avoid protracted disputes during mergers or acquisitions.
Table of Comparison
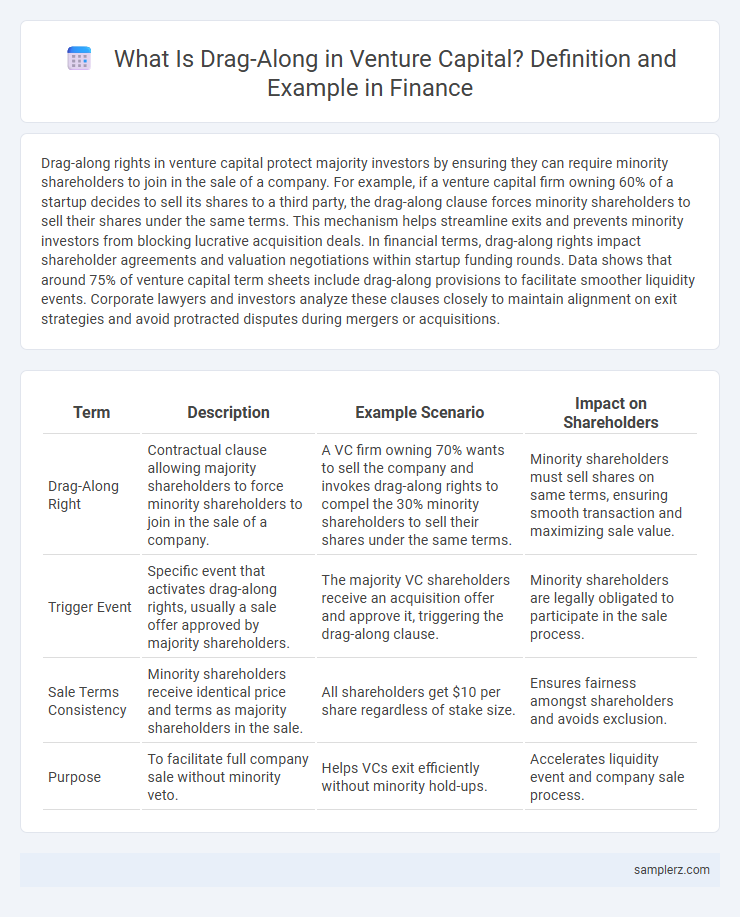
| Term | Description | Example Scenario | Impact on Shareholders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drag-Along Right | Contractual clause allowing majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company. | A VC firm owning 70% wants to sell the company and invokes drag-along rights to compel the 30% minority shareholders to sell their shares under the same terms. | Minority shareholders must sell shares on same terms, ensuring smooth transaction and maximizing sale value. |
| Trigger Event | Specific event that activates drag-along rights, usually a sale offer approved by majority shareholders. | The majority VC shareholders receive an acquisition offer and approve it, triggering the drag-along clause. | Minority shareholders are legally obligated to participate in the sale process. |
| Sale Terms Consistency | Minority shareholders receive identical price and terms as majority shareholders in the sale. | All shareholders get $10 per share regardless of stake size. | Ensures fairness amongst shareholders and avoids exclusion. |
| Purpose | To facilitate full company sale without minority veto. | Helps VCs exit efficiently without minority hold-ups. | Accelerates liquidity event and company sale process. |
Understanding Drag-Along Rights in Venture Capital
Drag-along rights in venture capital allow majority shareholders to compel minority investors to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a unified exit strategy. For example, if the majority shareholder receives an attractive acquisition offer, they can invoke drag-along rights to force minority shareholders to sell their shares on the same terms. This mechanism protects majority owners' ability to negotiate deals without minority holdouts blocking or complicating the transaction.
Importance of Drag-Along Clauses for Investors
Drag-along clauses in venture capital are crucial for protecting majority investors by ensuring they can compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, preserving deal integrity and maximizing exit value. These clauses minimize holdout risks and streamline acquisition processes, enhancing liquidity and return potential for investors. By enforcing collective action, drag-along provisions safeguard investor interests and facilitate smoother exits in competitive venture ecosystems.
How Drag-Along Provisions Work in Practice
Drag-along provisions in venture capital enable majority shareholders to compel minority investors to join in the sale of a company under the same terms, ensuring a smoother exit process. For example, if a startup's founding team secures a lucrative acquisition offer, the drag-along clause forces all shareholders, including early investors, to sell their shares on the agreed terms, preventing holdouts. This mechanism protects majority stakeholders by facilitating unified decision-making and maximizing the company's valuation during exit events.
Typical Scenarios Triggering Drag-Along Rights
Drag-along rights in venture capital are typically triggered during exit events such as a majority shareholder deciding to sell their stake to a third party. This right ensures that minority shareholders are compelled to join the sale on the same terms, preventing holdouts and facilitating smoother acquisitions. Common scenarios include mergers, acquisitions, or significant asset sales where alignment among all shareholders is critical.
Key Parties Affected by Drag-Along Agreements
Drag-along agreements primarily affect minority shareholders, venture capital investors, and company founders by enabling majority shareholders to compel minority holders to join in the sale of a company. This provision ensures that venture capital firms can facilitate a smooth exit without facing holdouts from smaller stakeholders. Founders must also be aware of these clauses as they can impact their control over the timing and terms of a sale during liquidity events.
Real-World Examples of Drag-Along in VC Deals
In venture capital, a real-world example of a drag-along clause occurred during the 2017 acquisition of a startup by a major tech firm, where majority investors compelled minority shareholders to sell their stakes under the same terms. This provision ensured a smooth exit by aligning interests and preventing minority holdouts from blocking the deal. Such clauses are essential in VC deals to facilitate strategic acquisitions and liquidity events.
Legal Considerations for Enforcing Drag-Along Rights
Enforcing drag-along rights in venture capital requires careful adherence to the shareholder agreement terms, ensuring proper notice is given to minority shareholders as stipulated in the contract. Courts typically examine the fairness of the transaction and whether the majority acted in good faith, emphasizing the integrity of the sale process and compliance with statutory requirements. Legal challenges often arise from ambiguous provisions or inadequate communication, making precise drafting and thorough documentation essential for enforceability.
Drag-Along vs. Tag-Along: Key Differences
Drag-along rights in venture capital allow majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a smoother exit process by preventing holdouts. In contrast, tag-along rights protect minority investors by granting them the option to join a sale initiated by majority shareholders, thus securing proportional ownership liquidity. Understanding the differences between drag-along and tag-along rights is crucial for structuring shareholder agreements that balance control and protection in venture financing.
Negotiating Drag-Along Terms in Startup Investments
Negotiating drag-along terms in startup investments requires clear definitions of triggering events, such as a qualified acquisition or sale, to protect majority investors while ensuring minority shareholders participate in exit opportunities. Precise valuation mechanisms and notice periods must be established to minimize disputes and align interests among founders, venture capitalists, and other stakeholders. Tailored drag-along provisions help preserve deal flexibility and enhance the startup's attractiveness to future investors.
Protecting Minority Shareholders in Drag-Along Situations
In venture capital, drag-along rights enable majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring smooth exit transactions. These provisions often include protections for minority shareholders, such as requiring that they receive the same price and terms as the majority, preventing unfair treatment during acquisitions. Contracts commonly incorporate notice periods and thresholds on sale approvals to safeguard minority interests while facilitating efficient deal execution.
example of dragalong in venture capital Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com