A drag-along right in venture capital allows majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company. This clause ensures that when a majority investor agrees to sell their stake, minority investors must also sell their shares on the same terms. The main goal is to facilitate smooth exit transactions and maximize the sale value for all stakeholders. For example, suppose a venture capital firm owns 60% of a startup and a smaller investor owns 10%. If the VC firm receives a lucrative buyout offer and decides to accept it, the drag-along right requires the 10% minority investor to sell their shares as well. This mechanism protects buyers by enabling them to acquire 100% ownership without minority holdouts blocking the deal.
Table of Comparison
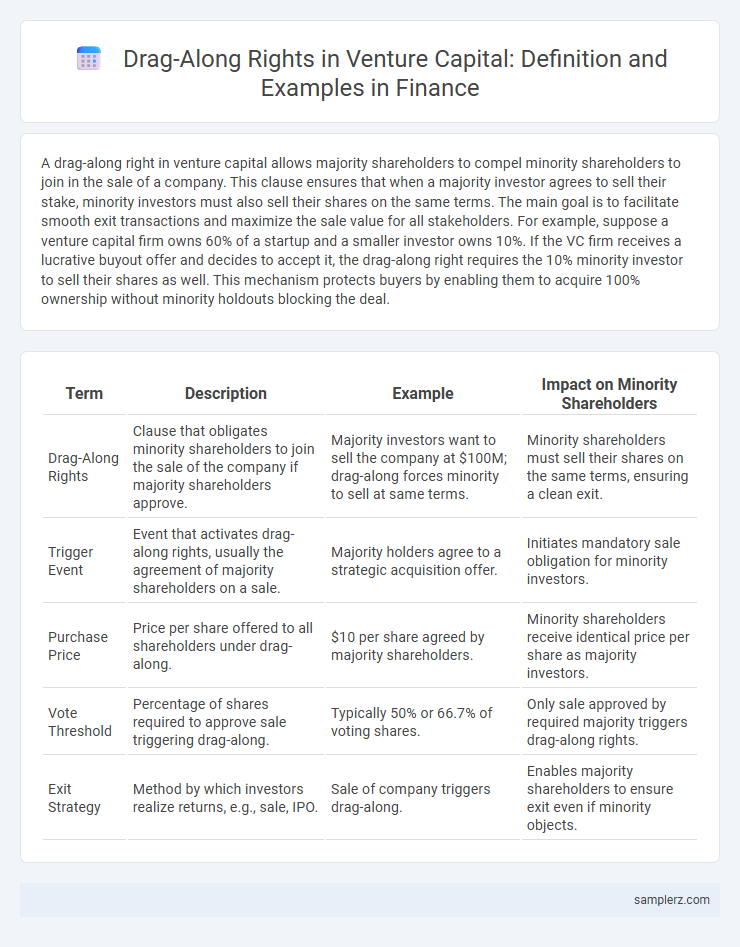
| Term | Description | Example | Impact on Minority Shareholders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drag-Along Rights | Clause that obligates minority shareholders to join the sale of the company if majority shareholders approve. | Majority investors want to sell the company at $100M; drag-along forces minority to sell at same terms. | Minority shareholders must sell their shares on the same terms, ensuring a clean exit. |
| Trigger Event | Event that activates drag-along rights, usually the agreement of majority shareholders on a sale. | Majority holders agree to a strategic acquisition offer. | Initiates mandatory sale obligation for minority investors. |
| Purchase Price | Price per share offered to all shareholders under drag-along. | $10 per share agreed by majority shareholders. | Minority shareholders receive identical price per share as majority investors. |
| Vote Threshold | Percentage of shares required to approve sale triggering drag-along. | Typically 50% or 66.7% of voting shares. | Only sale approved by required majority triggers drag-along rights. |
| Exit Strategy | Method by which investors realize returns, e.g., sale, IPO. | Sale of company triggers drag-along. | Enables majority shareholders to ensure exit even if minority objects. |
Understanding Drag-Along Rights in Venture Capital
Drag-along rights in venture capital enable majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a unified exit strategy. For example, if a startup's majority investors approve a lucrative acquisition offer, they can require minority investors to sell their shares on the same terms, preventing any holdouts. These rights protect the majority's ability to maximize returns and streamline exit processes during funding rounds or acquisition negotiations.
Key Components of Drag-Along Provisions
Drag-along provisions in venture capital agreements enable majority shareholders to compel minority investors to join in the sale of a company under predefined conditions. Key components include the triggering event, such as a bona fide third-party offer, the requirement that minority shareholders sell their shares on the same terms and conditions as the majority, and the notice period allowing all parties to prepare for the transaction. These provisions ensure exit strategies are streamlined while protecting minority investor rights and maintaining deal fairness.
Real-Life Example of Drag-Along Rights in Action
In venture capital, drag-along rights were exercised when a majority shareholder in a tech startup negotiated a buyout deal with a private equity firm, compelling minority investors to sell their shares under the same terms. This ensured a smooth exit process, maximizing the acquisition value of $50 million while preventing minority holdouts from obstructing the transaction. Real-world cases like this highlight how drag-along clauses protect majority stakeholders' interests during liquidation or acquisition events.
Case Study: Successful Drag-Along Clause Enforcement
A notable example of successful drag-along clause enforcement occurred in the 2018 Series B funding round of fintech startup FinXpress, where majority shareholders exercised the drag-along rights to compel minority investors to sell their shares during the $50 million acquisition by GlobalPay. This strategic move ensured a unified exit, maximizing valuation and streamlining negotiations without minority holdouts obstructing the deal. The enforcement of the drag-along clause protected the interests of lead investors while facilitating a smooth transaction and solidifying investor confidence in future rounds.
Implications for Minority Shareholders
Drag-along rights in venture capital agreements allow majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a smooth exit but often limiting minority shareholders' control over the timing and terms of the sale. These provisions can result in minority shareholders being compelled to sell their shares at a price set by the majority, potentially undervaluing their investment. Understanding the implications of drag-along rights is critical for minority investors to negotiate safeguards that protect their interests in exit scenarios.
Investor Advantages with Drag-Along Rights
Drag-along rights in venture capital allow majority investors to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a smoother exit process and maximizing returns. These rights protect investors by preventing holdouts from blocking lucrative acquisition deals, streamlining decision-making and avoiding protracted negotiations. By enabling collective action, drag-along provisions enhance investor control and improve liquidity prospects for all shareholders involved.
Drag-Along vs Tag-Along: Core Differences Explained
Drag-along rights in venture capital allow majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a smooth exit for investors. Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by granting them the option to sell their shares alongside majority shareholders, preventing them from being left behind in a liquidity event. The core difference lies in drag-along rights enforcing the sale for all, while tag-along rights offer voluntary participation to minority investors.
Legal Considerations Surrounding Drag-Along Rights
Drag-along rights in venture capital agreements legally require minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company when majority shareholders agree to sell, ensuring a streamlined exit process. These rights must be clearly defined in the shareholder agreement, specifying conditions such as the required majority threshold and the treatment of sale proceeds. Careful drafting prevents disputes by clarifying enforcement mechanisms and protecting minority shareholders from unfair treatment during a sale transaction.
Common Negotiation Points for Drag-Along Clauses
Drag-along clauses in venture capital often focus on negotiation points such as the scope of drag-along rights, including which shareholders are subject and the types of sale transactions covered. Key considerations include the required approval thresholds for triggering the clause, typically a majority or supermajority of preferred shareholders, and the treatment of minority holders to ensure fair exit terms. Negotiators also prioritize the definition of "sale" and protections around the price and terms to prevent forced participation in undervalued acquisitions.
Protecting Interests: Best Practices for Startups
In venture capital, drag-along rights enable majority investors to compel minority shareholders to sell their shares during an exit, ensuring a unified sale and maximizing valuation. Startups protect interests by clearly defining drag-along scenarios in shareholder agreements, specifying notice periods, and aligning terms with key investors to prevent disputes. Employing best practices like transparent communication and legal counsel during negotiations fortifies startup control while safeguarding minority stakeholders.
example of drag-along in venture capital Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com