A death spiral in convertible bonds occurs when a company issues convertible bonds with conversion prices tied to the stock's market value, leading to excessive dilution. As the stock price declines, bondholders convert bonds into shares at lower prices, increasing the share supply and driving the stock price further down. This vicious cycle creates a continuous downward spiral in the company's stock value and deteriorates investor confidence. Investors in companies experiencing a death spiral often face significant losses due to the plummeting stock price and dilution of their shares. Companies resort to issuing these convertible bonds to raise capital quickly, usually when facing financial distress. Data indicates that firms with high debt levels and poor stock performance are more prone to entering death spiral scenarios with convertible securities.
Table of Comparison
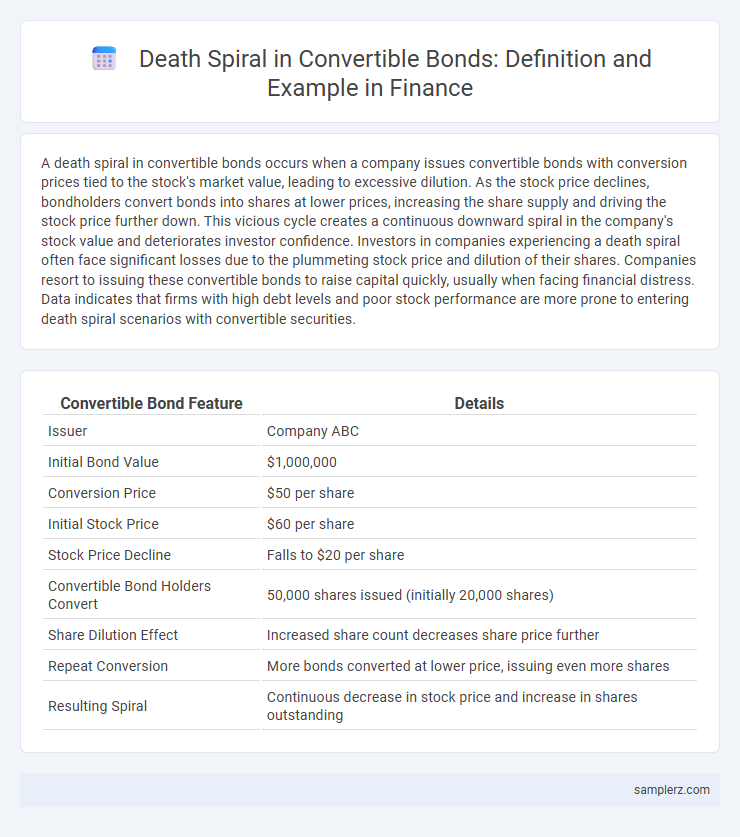
| Convertible Bond Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Issuer | Company ABC |
| Initial Bond Value | $1,000,000 |
| Conversion Price | $50 per share |
| Initial Stock Price | $60 per share |
| Stock Price Decline | Falls to $20 per share |
| Convertible Bond Holders Convert | 50,000 shares issued (initially 20,000 shares) |
| Share Dilution Effect | Increased share count decreases share price further |
| Repeat Conversion | More bonds converted at lower price, issuing even more shares |
| Resulting Spiral | Continuous decrease in stock price and increase in shares outstanding |
Understanding the Death Spiral Phenomenon in Convertible Bonds
The death spiral in convertible bonds occurs when rapid, repeated conversions by bondholders dilute stock value and accelerate share price declines. This phenomenon often triggers a negative feedback loop, as falling prices prompt more conversions, further eroding investor confidence. Understanding this cycle is crucial for managing convertible bond structures and mitigating risks in corporate finance.
Key Characteristics of Death Spiral Financing
Death spiral financing is characterized by convertible bonds with low conversion prices, which can lead to significant dilution of existing shareholders as the bondholder converts debt into equity at successively decreasing prices. The key features include heavy discounting, rapid conversion triggers, and escalating share issuance that drives down the stock price further. This negative feedback loop can cause a steep decline in market value, making it a high-risk financing option for companies.
How Death Spirals Erode Shareholder Value
Death spirals in convertible bonds erode shareholder value by triggering continuous dilution as bondholders convert debt into an increasing number of shares, flooding the market and driving the stock price downward. This relentless reduction in share price not only diminishes existing shareholders' ownership percentage but also undermines market confidence, reducing capital-raising potential. The compounding effect accelerates the decline in market capitalization, causing substantial financial harm to both the company and its investors.
Real-World Example: Death Spiral in a Tech Startup
A notable example of a death spiral in a convertible bond occurred with a fledgling tech startup whose rapidly declining stock price triggered continuous bond conversions, exponentially increasing share dilution. Investors' forced conversions at progressively lower prices led to a vicious cycle of sell-offs, eroding market confidence and collapsing the startup's valuation. This spiral ultimately undermined the company's capital structure, resulting in bankruptcy despite promising technology and initial investor enthusiasm.
Case Study: Biotech Firm Facing Death Spiral Crisis
A biotech firm issued convertible bonds priced at a significant discount, triggering a death spiral as bondholders continuously converted debt into shares, massively diluting equity and driving down stock prices. The falling share price forced further conversions to cover the bond's principal, exacerbating the stock's decline and causing a liquidity crisis. This case exemplifies how poorly structured convertible debt can accelerate financial distress, highlighting the importance of conversion price floors to prevent spiraling dilution.
The Role of Hedge Funds in Promoting Death Spiral Scenarios
Hedge funds often amplify death spiral scenarios in convertible bonds by aggressively short selling the issuer's stock while converting debt to equity, intensifying downward pressure on share prices. Their rapid conversion and sales of bonds into stock dilute existing shareholders and trigger a self-reinforcing cycle of price declines. This coordinated activity exploits convertible bonds' structural vulnerabilities, hastening the issuer's financial distress and accelerating the spiral effect.
Impact of Death Spiral on Stock Prices and Investor Confidence
The death spiral in convertible bonds causes a rapid dilution of stock shares as bondholders convert debt into equity at falling prices, sharply depressing stock prices. This downward price pressure erodes investor confidence, triggering sell-offs and increased market volatility. The resulting lack of trust in the company's financial stability often leads to higher capital costs and challenges in future fundraising.
Regulatory Responses to Death Spiral Financing
Regulatory responses to death spiral financing in convertible bonds have intensified, with agencies like the SEC implementing stricter disclosure requirements to enhance transparency around conversion terms and pricing. Measures such as price collars and mandatory issuance caps are increasingly mandated to prevent excessive dilution and protect shareholder value. Enhanced monitoring frameworks and investor education programs further aim to mitigate the systemic risks associated with death spiral mechanisms in bond markets.
Lessons Learned from Notorious Death Spiral Cases
Notorious death spiral cases involving convertible bonds reveal critical lessons in risk management and capital structure. Companies like Dell and Valeant Pharmaceuticals experienced severe stock price dilution due to aggressive short-selling and conversion triggers, emphasizing the importance of clear terms and market conditions in convertible bond agreements. These cases underscore the necessity of thorough due diligence and prudent financial planning to prevent disastrous dilution effects and protect shareholder value.
Strategies to Avoid Death Spiral When Issuing Convertible Bonds
Issuers can avoid death spiral scenarios in convertible bonds by implementing price-floor mechanisms, such as setting a fixed conversion price or including anti-dilution provisions to protect against excessive share dilution. Another effective strategy involves structuring conversion terms with issuance caps or time restrictions to limit rapid conversions that negatively impact stock price. Employing clear communication with investors about conversion guidelines and monitoring market conditions can further mitigate risks associated with a death spiral in convertible bond issuance.
example of death spiral in convertible bond Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com