Dim sum bonds are Chinese renminbi-denominated bonds issued in the offshore market, primarily in Hong Kong. A notable example is the issuance by China Development Bank in 2010, which marked one of the earliest large-scale dim sum bonds. This bond demonstrated growing international appetite for renminbi assets outside mainland China. Financial institutions and corporations utilize dim sum bonds to access offshore capital while managing currency exposure. These bonds provide investors with exposure to Chinese currency and offer issuers diversification from traditional US dollar or euro-denominated debt. The offshore market for dim sum bonds has expanded significantly, reflecting increasing confidence in the offshore renminbi market.
Table of Comparison
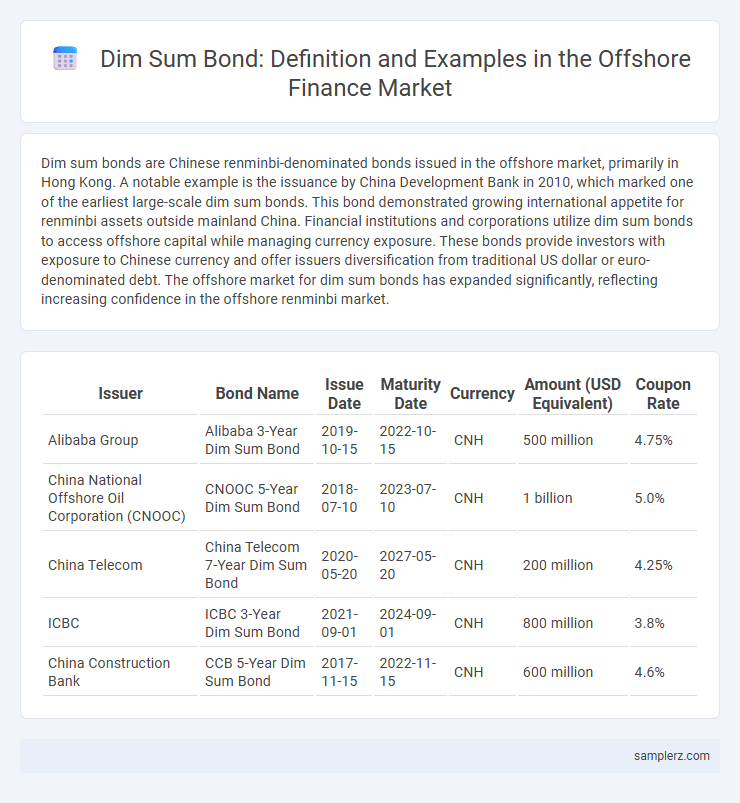
| Issuer | Bond Name | Issue Date | Maturity Date | Currency | Amount (USD Equivalent) | Coupon Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alibaba Group | Alibaba 3-Year Dim Sum Bond | 2019-10-15 | 2022-10-15 | CNH | 500 million | 4.75% |
| China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC) | CNOOC 5-Year Dim Sum Bond | 2018-07-10 | 2023-07-10 | CNH | 1 billion | 5.0% |
| China Telecom | China Telecom 7-Year Dim Sum Bond | 2020-05-20 | 2027-05-20 | CNH | 200 million | 4.25% |
| ICBC | ICBC 3-Year Dim Sum Bond | 2021-09-01 | 2024-09-01 | CNH | 800 million | 3.8% |
| China Construction Bank | CCB 5-Year Dim Sum Bond | 2017-11-15 | 2022-11-15 | CNH | 600 million | 4.6% |
Introduction to Dim Sum Bonds in Offshore Markets
Dim sum bonds are yuan-denominated bonds issued outside mainland China, primarily in Hong Kong, serving as a vital tool for offshore investors seeking exposure to Chinese currency assets. These bonds offer diversification opportunities and access to China's growing economy without direct onshore restrictions. The offshore dim sum bond market has expanded significantly, driven by international demand and Chinese government initiatives to internationalize the yuan.
Key Features of Dim Sum Bonds
Dim Sum bonds are renminbi-denominated bonds issued outside mainland China, primarily in the offshore market of Hong Kong. Key features include their currency denomination in RMB, allowing international investors to gain exposure to Chinese currency without onshore restrictions, and typically they offer attractive yields compared to domestic bonds. These bonds enhance liquidity in the offshore RMB market and provide issuers with diversification of funding sources in a flexible regulatory environment.
Historical Background of Offshore Dim Sum Bonds
The historical background of offshore Dim Sum bonds dates back to 2007 when the Chinese government aimed to internationalize the yuan by allowing foreign investors to purchase yuan-denominated bonds outside mainland China. The first offshore Dim Sum bond was issued in Hong Kong by the China Development Bank, marking a significant milestone in the offshore RMB market. This development facilitated increased liquidity and diversification for global investors while promoting the yuan's role as a global currency in offshore markets.
Prominent Issuers of Dim Sum Bonds
Prominent issuers of Dim Sum bonds in the offshore market include multinational corporations like Starbucks and the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), which leverage these yuan-denominated bonds to attract international investors. Sovereign entities such as the Hong Kong SAR government have also tapped the Dim Sum bond market to finance infrastructure projects and stabilize liquidity. The popularity of these bonds stems from their ability to provide access to offshore yuan capital with lower currency risk and diversified investor bases.
Notable Dim Sum Bond Issuance Examples
The China Development Bank's 2010 issuance of a CNH 3 billion Dim Sum bond marked a significant milestone in the offshore Renminbi debt market, attracting global investors seeking Chinese currency exposure. Another notable example includes HSBC's 2011 Dim Sum bond offering, raising CNH 1.9 billion and highlighting confidence in China's financial reforms and Renminbi internationalization. These landmark issuances demonstrated strong demand and paved the way for increased diversity in offshore RMB bond markets.
Case Study: HSBC’s Dim Sum Bond Offering
HSBC's Dim Sum bond issuance in the offshore market demonstrated a strategic approach to raising yuan-denominated capital outside mainland China, attracting global investors seeking exposure to Chinese currency. The bond, valued at approximately RMB 1 billion, leveraged Hong Kong's regulatory framework to tap into international demand while providing diversification benefits. This case underscored the growing importance of Dim Sum bonds as a vehicle for multinational corporations to access offshore RMB funding efficiently.
Major Markets for Offshore Dim Sum Bonds
The major markets for offshore Dim Sum bonds include Hong Kong, which serves as the primary hub due to its robust regulatory framework and close ties with mainland China. Singapore has emerged as a significant secondary market, attracting issuers seeking access to international investors while benefiting from its strategic location and strong financial infrastructure. Other growing markets such as London and Luxembourg are also gaining prominence, providing diversified options for global investors interested in Renminbi-denominated debt instruments outside China.
Benefits for International Investors
Dim sum bonds, issued in the offshore Chinese yuan (CNY) market, offer international investors access to China's currency exposure without direct onshore market restrictions. These bonds provide diversification benefits, attractive yields compared to domestic bonds, and lower currency risk due to their issuance in yuan. By investing in dim sum bonds, investors can capitalize on China's growing economy while managing geopolitical and foreign exchange risks effectively.
Challenges in the Offshore Dim Sum Bond Market
Offshore Dim Sum bonds face challenges such as limited liquidity and regulatory constraints imposed by both Chinese authorities and international markets. Currency risks arise from the bonds being denominated in Chinese yuan, complicating hedging strategies for foreign investors. Market volatility and the inconsistent demand for yuan-denominated debt contribute to pricing inefficiencies and reduced market depth.
Future Trends in Offshore Dim Sum Bond Issuance
Future trends in offshore Dim Sum bond issuance highlight increasing participation from technology and green energy sectors seeking RMB funding outside mainland China. Market analysts predict a surge in diversification as issuers tap into expanding investor bases in Hong Kong and other financial hubs. Growing regulatory harmonization between China and offshore markets is expected to facilitate smoother cross-border capital flows and enhance issuance volume.
example of dim sum bond in offshore market Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com