A butterfly spread in finance is an options trading strategy involving three strike prices, typically with equal intervals. Traders buy one call option at the lowest strike, sell two call options at the middle strike, and buy one call option at the highest strike, creating a profit and loss graph shaped like a butterfly. This strategy is used to capitalize on minimal price movement in the underlying asset, limiting both potential gains and losses. The butterfly spread can also be constructed using put options with the same principles. Market participants employ this strategy to benefit from low volatility while managing risk exposure. Data analysis of option premiums and strike prices is crucial for optimizing entry and exit points in executing butterfly spreads effectively.
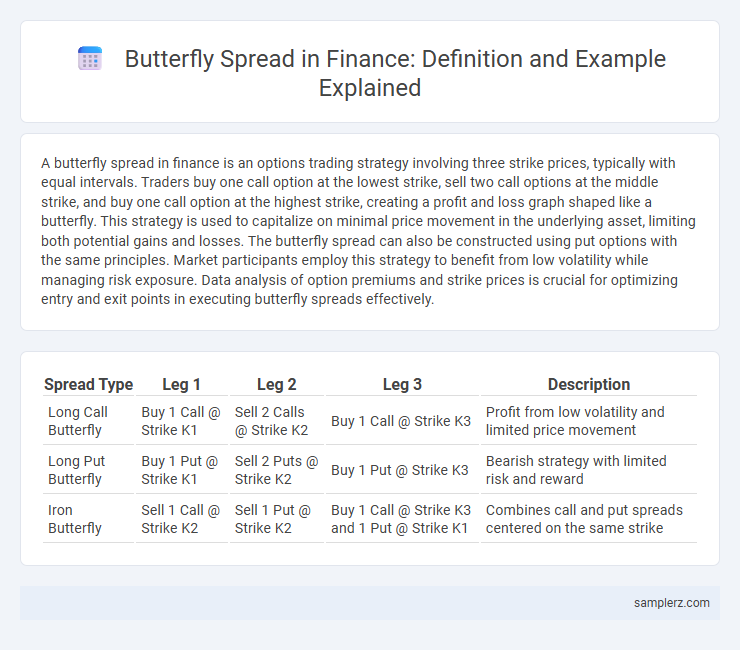
Table of Comparison
| Spread Type | Leg 1 | Leg 2 | Leg 3 | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long Call Butterfly | Buy 1 Call @ Strike K1 | Sell 2 Calls @ Strike K2 | Buy 1 Call @ Strike K3 | Profit from low volatility and limited price movement |
| Long Put Butterfly | Buy 1 Put @ Strike K1 | Sell 2 Puts @ Strike K2 | Buy 1 Put @ Strike K3 | Bearish strategy with limited risk and reward |
| Iron Butterfly | Sell 1 Call @ Strike K2 | Sell 1 Put @ Strike K2 | Buy 1 Call @ Strike K3 and 1 Put @ Strike K1 | Combines call and put spreads centered on the same strike |
Understanding Butterfly Spreads in Finance
A butterfly spread is a neutral options trading strategy that involves buying one in-the-money call, selling two at-the-money calls, and buying one out-of-the-money call with the same expiration date. This strategy limits both potential profit and loss by creating a price range where maximum gains occur if the underlying asset closes at the middle strike price. Traders use butterfly spreads to capitalize on low volatility forecasts and precisely defined risk profiles in equity and index options markets.
Key Features of Butterfly Spread Strategies
A butterfly spread in finance involves simultaneously buying and selling options at three different strike prices, creating a limited risk and reward profile that benefits from minimal price movement in the underlying asset. Key features include defined maximum profit achieved when the underlying price settles near the middle strike at expiration, limited maximum loss equal to the initial net premium paid, and reduced capital commitment compared to other multi-leg option strategies. This strategy is often used for market-neutral trading, aiming to capitalize on low volatility environments while maintaining controlled risk exposure.
How a Butterfly Spread Works: An Overview
A butterfly spread in finance involves simultaneously buying and selling options at three different strike prices, typically with equal intervals, creating a strategy that profits from low volatility in the underlying asset. Traders buy one lower strike call, sell two middle strike calls, and buy one higher strike call, limiting both potential gains and losses. This balanced risk strategy capitalizes on minimal price movement near the middle strike at expiration, optimizing potential returns while controlling downside exposure.
Example 1: Long Call Butterfly Spread
A long call butterfly spread involves buying one lower strike call, selling two middle strike calls, and buying one higher strike call, all with the same expiration date to limit risk and maximize profit potential within a narrow price range. For example, purchasing a call at a $50 strike, selling two calls at a $55 strike, and buying a call at a $60 strike creates a defined risk-reward profile, with maximum profit occurring if the underlying asset closes at the middle strike price. This strategy benefits from minimal movement outside the middle strike price, making it ideal for traders expecting low volatility.
Example 2: Short Put Butterfly Spread
A Short Put Butterfly Spread involves selling two put options at a middle strike price while buying one put option at a lower strike and another at a higher strike, all with the same expiration date. For example, an investor might sell two 100-strike puts, buy one 95-strike put, and buy one 105-strike put, thereby creating a neutral to bearish position with limited risk and potential profit. This strategy profits from minimal movement in the underlying asset and benefits from time decay, offering a risk-defined approach to volatility trading.
Real-World Scenario: Implementing a Butterfly Spread
A butterfly spread in options trading involves simultaneously buying one lower strike call, selling two middle strike calls, and buying one higher strike call to limit risk while targeting moderate price movement. In a real-world scenario, an investor anticipating minimal volatility in a stock trading at $100 might implement a butterfly spread with strike prices at $95, $100, and $105, aiming to profit from the stock price closing near $100 at expiration. This strategy reduces potential losses compared to outright calls, balancing risk and reward effectively in stable market conditions.
Payoff Diagrams for Butterfly Spread Examples
A butterfly spread in options trading involves buying one lower strike call, selling two middle strike calls, and buying one higher strike call, creating a limited risk and limited profit payoff diagram that resembles a butterfly's wings. The payoff diagram shows maximum profit at the middle strike price, where the sold calls expire worthless, while losses occur if the underlying asset price moves significantly away from the middle strike. This strategy is ideal for traders expecting low volatility as the profit potential is maximized near the strike price of the short options.
Profit and Loss Analysis of Butterfly Spreads
A butterfly spread involves simultaneously buying one lower strike call, selling two middle strike calls, and buying one higher strike call to capitalize on minimal price movement and limited risk. The maximum profit occurs when the underlying asset price at expiration is exactly at the middle strike, while losses are capped to the net premium paid. This strategy provides a favorable risk-reward ratio by balancing potential gains with controlled losses, making it ideal for traders expecting low volatility.
Butterfly Spread Risks and Rewards
A butterfly spread in options trading involves buying and selling options at three different strike prices, creating a limited risk and limited reward strategy. The maximum profit occurs when the underlying asset's price settles at the middle strike price at expiration, while losses are capped and occur if the price moves significantly away from this point. Key risks include limited upside potential and exposure to time decay, but rewards offer a favorable risk-to-reward ratio for traders anticipating low volatility.
Tips for Using Butterfly Spreads in Trading
To maximize profits using butterfly spreads in trading, focus on selecting stocks with low volatility and stable price behavior to minimize risk exposure. Implement tight stop-loss orders to limit potential losses while monitoring implied volatility to identify optimal entry points for setting up the spread. Utilize options expiration dates that align closely with anticipated price movement to enhance the probability of achieving the desired payoff within the spread structure.
example of butterfly in spread Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com