A butterfly spread in options trading involves three strike prices and is designed to profit from low volatility in the underlying asset. Traders buy one lower strike call, sell two middle strike calls, and buy one higher strike call, creating a position with limited risk and limited profit potential. This strategy works best when the underlying asset price remains close to the middle strike price at expiration. The butterfly spread can be implemented using either calls or puts and is popular among traders seeking a defined risk-reward ratio. It requires careful selection of strike prices and expiration dates to optimize returns while minimizing exposure. Market data such as implied volatility and option premiums play a critical role in determining the feasibility and expected profitability of the butterfly spread strategy.
Table of Comparison
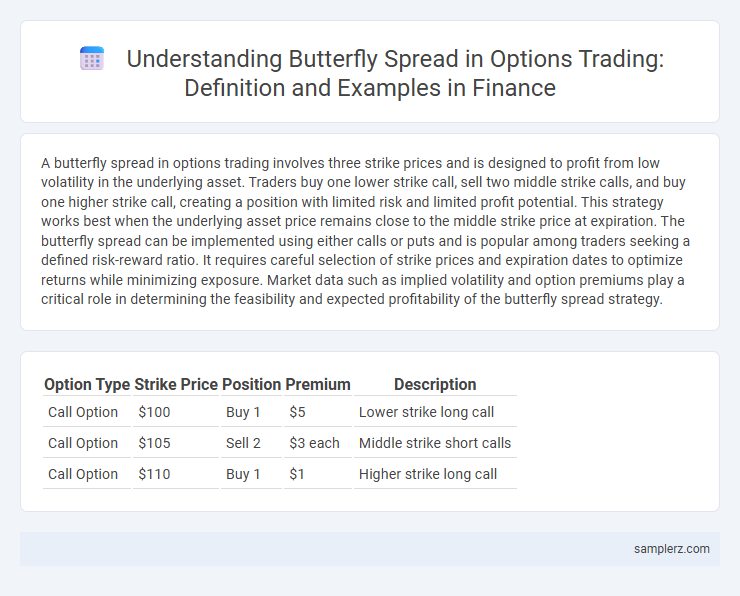
| Option Type | Strike Price | Position | Premium | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Call Option | $100 | Buy 1 | $5 | Lower strike long call |
| Call Option | $105 | Sell 2 | $3 each | Middle strike short calls |
| Call Option | $110 | Buy 1 | $1 | Higher strike long call |
Introduction to Butterfly Spread Strategies in Options
A butterfly spread strategy in options combines multiple call or put options with three strike prices equidistantly spaced to capitalize on minimal price movement in the underlying asset. This strategy involves buying one lower strike call, selling two middle strike calls, and buying one higher strike call, creating a payoff profile with limited risk and capped profit potential. Traders use butterfly spreads to profit from anticipated low volatility and to manage cost-effective risk exposure in options trading.
Understanding the Structure of a Butterfly Option
A butterfly option strategy involves simultaneously buying one lower strike call, selling two middle strike calls, and buying one higher strike call with the same expiration date to create a neutral risk profile. This structure limits both potential gains and losses by targeting profit within a narrow price range around the middle strike price. Traders often use butterfly spreads to capitalize on low volatility environments while managing risk with defined maximum loss.
Types of Butterfly Spreads: Long vs. Short
The Long Butterfly Spread involves buying one lower strike call, selling two middle strike calls, and buying one higher strike call, aiming for limited risk and profit if the underlying stays near the middle strike. Conversely, the Short Butterfly Spread entails selling one lower strike call, buying two middle strike calls, and selling one higher strike call, targeting profit from significant price movement away from the middle strike with higher risk. Both strategies use strike price differentials to control risk and potential gains, making them effective for traders expecting minimal or large volatility, respectively.
Constructing a Long Call Butterfly Spread: Step-by-Step
Constructing a Long Call Butterfly Spread involves buying one lower strike call, selling two middle strike calls, and buying one higher strike call with the same expiration date, creating a position that profits from minimal stock movement. The ideal strike prices are equidistant, for instance, buying calls at $50 and $60, while selling two calls at $55. This strategy limits risk and potential profit, with maximum gain realized if the underlying asset closes at the middle strike price at expiration.
Real-Life Example: Analyzing a Butterfly Spread Trade
A butterfly spread trade in options involves simultaneously buying one lower strike call, selling two middle strike calls, and buying one higher strike call to limit risk while targeting a specific price range. For example, if a stock is trading at $100, an investor might buy one $95 call, sell two $100 calls, and buy one $105 call, aiming to profit if the stock remains near $100 at expiration. This strategy offers limited risk and moderate reward, ideal for traders expecting low volatility around the middle strike price.
Payoff Diagrams: Visualizing Butterfly Spread Outcomes
A butterfly spread in options trading combines bull and bear spreads with three strike prices to limit risk and maximize potential profit. Payoff diagrams vividly illustrate the strategy's potential outcomes, showing limited loss outside the middle strike range and peak profit at the middle strike price at expiration. This visual tool helps traders quickly assess risk-reward scenarios and make informed decisions about positioning in volatile markets.
Key Benefits of Using Butterfly Spreads in Trading
Butterfly spreads in options trading provide key benefits such as limited risk exposure and defined profit potential, making them ideal for traders seeking controlled investment strategies. This strategy benefits from low volatility environments due to its neutral market stance, allowing traders to capitalize on minimal price movement within a specific strike price range. Additionally, butterfly spreads offer cost efficiency by requiring lower capital outlay compared to outright option purchases, increasing potential return on investment.
Potential Risks and Break-Even Points in Butterfly Strategies
Butterfly option strategies involve limited risk but require careful analysis of break-even points, which are determined by the strike prices and net premium paid. Potential risks include losses if the underlying asset price moves significantly beyond the outer strike prices, causing both wings of the butterfly to expire worthless. Traders must precisely calculate the break-even range to mitigate the risk of premiums paid exceeding potential gains, especially in volatile markets.
Adjustments and Management Techniques for Butterfly Spreads
Adjustments in butterfly spreads often involve rolling strikes or expanding wings to maintain optimal risk-reward ratios during volatility shifts. Traders commonly manage butterfly positions by adjusting leg sizes or employing delta-neutral strategies to minimize directional exposure. Effective management techniques include rebalancing position weights and using stop-loss orders to protect against unexpected price movements.
When to Use Butterfly Spreads: Market Conditions and Best Practices
Butterfly spreads in options trading are most effective during low volatility markets when price movements are expected to be minimal, allowing traders to profit from narrow price ranges. Investors typically implement butterfly spreads around anticipated earnings announcements or economic data releases to capitalize on limited price fluctuations while minimizing risk. Best practices include selecting strike prices equidistant from the current underlying asset price and carefully managing expiration dates to optimize potential returns and mitigate loss.
example of butterfly in options Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com