Share overhang refers to the large number of shares that are available for sale but have not yet been sold in the market. This overhang can exert downward pressure on a company's stock price as investors anticipate dilution or increased supply. An example of share overhang occurs when a company issues a significant number of employee stock options that have not yet been exercised or shares held by insiders subject to lock-up periods. In finance, managing share overhang is crucial because it affects investor sentiment and market liquidity. When a firm's restricted shares or convertible securities come close to expiration, large block sales may flood the market. Monitoring the volume of these potential shares enables analysts to assess the risk of share price depreciation due to overhang effects.
Table of Comparison
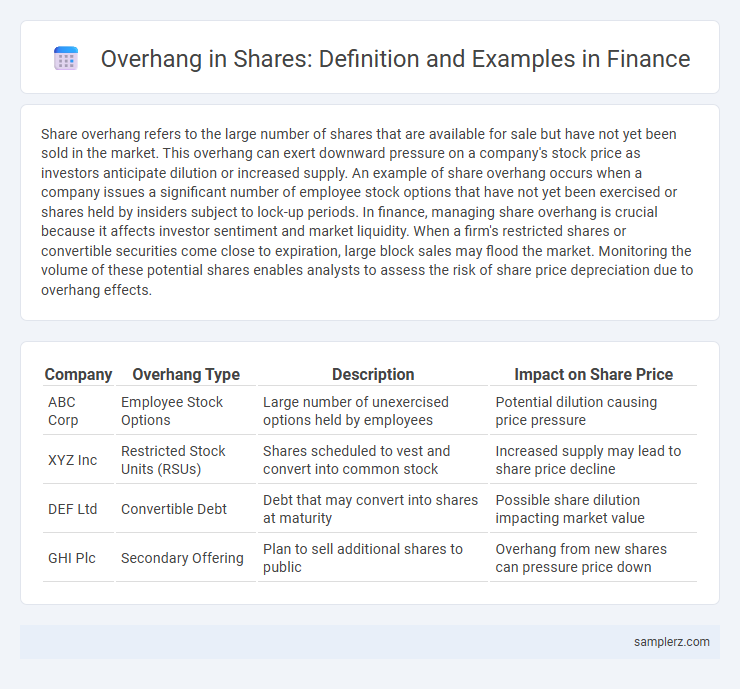
| Company | Overhang Type | Description | Impact on Share Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Corp | Employee Stock Options | Large number of unexercised options held by employees | Potential dilution causing price pressure |
| XYZ Inc | Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) | Shares scheduled to vest and convert into common stock | Increased supply may lead to share price decline |
| DEF Ltd | Convertible Debt | Debt that may convert into shares at maturity | Possible share dilution impacting market value |
| GHI Plc | Secondary Offering | Plan to sell additional shares to public | Overhang from new shares can pressure price down |
Understanding Share Overhang: Definition and Basics
Share overhang refers to the situation where a large number of shares are held by insiders, institutions, or insiders with selling restrictions, creating potential downward pressure on stock prices when these shares become available for sale. A classic example is a company issuing stock options to employees that later vest and flood the market once the lock-up period expires, increasing supply and potentially diluting existing shareholders' value. Understanding this concept is vital for investors as excessive share overhang can signal future volatility and affect stock valuation.
Causes of Overhang in Company Shares
Overhang in company shares often results from large blocks of restricted stock or convertible securities poised for imminent conversion, increasing potential share supply. Employee stock option plans and warrant exercises create additional pressure on share prices by expanding the pool of shares available on the open market. High insider holdings locked under vesting schedules also contribute to overhang when restrictions lift, signaling possible share dilution to investors.
Real-World Examples of Share Overhang
A notable example of share overhang occurred when Tesla's significant convertible bond offerings led investors to anticipate substantial future share dilution, affecting stock price volatility. Similarly, Alphabet faced share overhang issues due to large stakes held by early investors locked under selling restrictions, creating uncertainty about potential market supply. These real-world cases highlight how impending share releases from insiders or convertible securities can suppress share price momentum and investor confidence.
The Impact of Share Overhang on Stock Prices
Share overhang occurs when a significant number of shares held by insiders, institutions, or large shareholders remain available for sale, creating downward pressure on stock prices. This excess supply may lead investors to anticipate future dilution or selling, causing reduced demand and increased volatility. Empirical studies show that stocks with high share overhang often experience suppressed price appreciation and delayed recovery after earnings announcements.
Insider Lock-Up Expiry: Case Studies of Overhang
Insider lock-up expiry often triggers significant share overhang as insiders sell large blocks of shares post-IPO or secondary offerings, impacting stock liquidity and price. Notable cases include Zoom Video Communications, where the expiration of a 180-day lock-up led to increased share supply and temporary price pressure. Such overhang episodes highlight the importance of monitoring insider selling schedules for anticipating market movements and managing investment risk.
Overhang Due to Convertible Securities: Notable Examples
Overhang due to convertible securities occurs when a significant number of convertible bonds or preferred shares could potentially convert into common shares, increasing supply and diluting existing shareholders. Notable examples include Tesla's convertible notes issued in 2019, which created uncertainty about future share dilution until maturity or conversion events. Another case is Snap Inc., whose convertible debt raised concerns about share overhang impacting stock price stability during periods of potential conversion.
Mergers and Acquisitions Leading to Share Overhang
Mergers and acquisitions often create share overhang when the acquiring company issues new shares to finance the deal, increasing the total shares outstanding and potentially diluting existing shareholders' value. This overhang impacts stock price performance as the market anticipates the dilution effect and possible shifts in control dynamics. Analysts closely monitor the volume of newly issued shares tied to M&A transactions to assess the magnitude of the overhang and its effect on equity valuation.
Overhang in IPOs: Famous Instances and Lessons
Overhang in IPOs occurs when a significant number of shares held by insiders or early investors remain restricted from the market, creating potential supply pressure once unlocked. Famous instances include Facebook's 2012 IPO, where a large overhang of restricted shares delayed full market circulation, impacting initial share price performance. These cases highlight the importance of managing share release schedules to maintain stock price stability and investor confidence.
Corporate Debt and Potential Equity Overhang Explained
Corporate debt overhang occurs when a company carries excessive debt that deters new equity investment due to anticipated use of new capital primarily for debt repayment. Potential equity overhang arises when existing shareholders fear dilution of their ownership, leading to reluctance in accepting new equity issuances despite the company needing capital. This dynamic creates a funding challenge, where the cost of capital increases and shareholder value may be compromised, impacting the firm's growth and financial flexibility.
Strategies to Manage and Mitigate Share Overhang
Share overhang occurs when a large block of shares, often from insiders or institutions, is expected to be sold, potentially depressing the stock price. Common strategies to manage overhang include lock-up agreements that restrict sale periods, staggered release schedules to gradually introduce shares, and shareholder engagement to align expectations. Firms may also execute share buybacks or implement communication plans emphasizing strong fundamentals to mitigate market concerns.
example of overhang in share Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com