A lockbox in cash management is a service provided by banks to streamline the collection and processing of payments. Businesses direct their customers to send payments to a specialized PO box managed by the bank. The bank then collects, processes, and deposits these payments directly into the company's account, speeding up cash flow and reducing the risk of internal fraud. Companies in finance frequently use lockbox services to improve efficiency in accounts receivable management. By outsourcing payment processing, firms minimize manual handling of checks and enhance accuracy in data entry. This system provides valuable data insights, such as daily remittance reports, which support better forecasting and liquidity management.
Table of Comparison
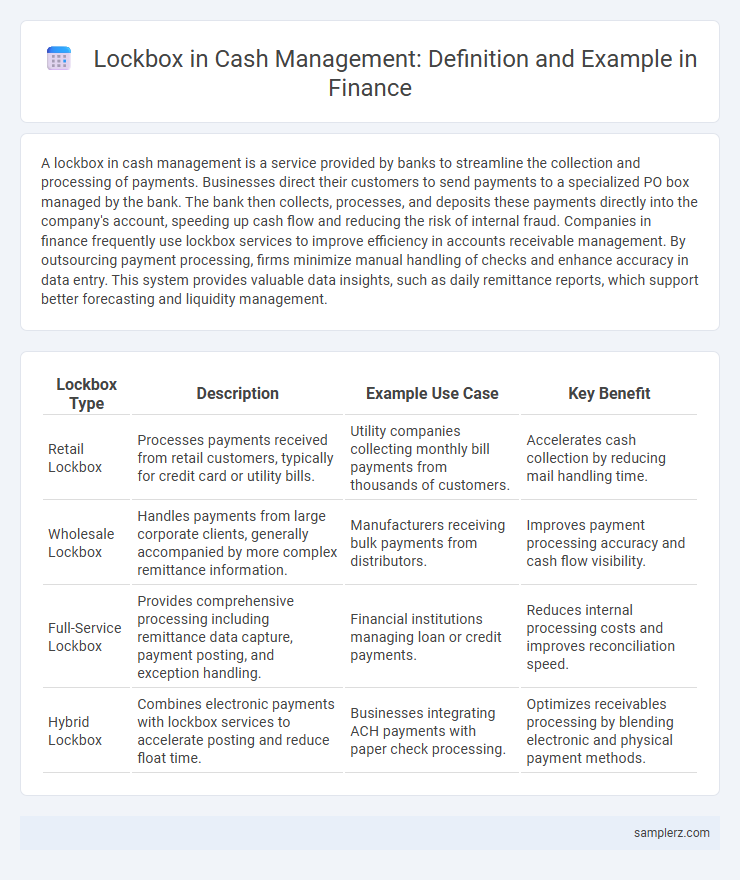
| Lockbox Type | Description | Example Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail Lockbox | Processes payments received from retail customers, typically for credit card or utility bills. | Utility companies collecting monthly bill payments from thousands of customers. | Accelerates cash collection by reducing mail handling time. |
| Wholesale Lockbox | Handles payments from large corporate clients, generally accompanied by more complex remittance information. | Manufacturers receiving bulk payments from distributors. | Improves payment processing accuracy and cash flow visibility. |
| Full-Service Lockbox | Provides comprehensive processing including remittance data capture, payment posting, and exception handling. | Financial institutions managing loan or credit payments. | Reduces internal processing costs and improves reconciliation speed. |
| Hybrid Lockbox | Combines electronic payments with lockbox services to accelerate posting and reduce float time. | Businesses integrating ACH payments with paper check processing. | Optimizes receivables processing by blending electronic and physical payment methods. |
Understanding Lockbox Services in Cash Management
Lockbox services streamline accounts receivable processing by directing customer payments to a dedicated post office box, allowing the bank to collect, process, and expedite the deposit of funds. This method enhances cash flow efficiency, reduces processing time, and minimizes the risk of errors or fraud in payment handling. Businesses benefit from faster access to funds and improved accuracy in cash management through automated check processing and electronic data capture.
Types of Lockbox Arrangements Used by Businesses
Businesses commonly use retail, wholesale, and hybrid lockbox arrangements to streamline cash management. Retail lockboxes handle high volumes of consumer payments with quick processing, while wholesale lockboxes focus on larger, less frequent transactions requiring detailed remittance information. Hybrid lockboxes combine features of both types, optimizing efficiency and cash flow management tailored to specific business needs.
How Lockbox Processing Works: Step-by-Step Example
Lockbox processing begins when customers send payments directly to a secure post office box managed by the bank, bypassing the company's internal mailroom. Upon receipt, the bank collects, processes, and deposits the payments into the company's account, while simultaneously providing electronic data files containing payment details. This system accelerates cash flow, reduces processing errors, and enhances reconciliation efficiency in cash management operations.
Real-World Example: Lockbox Solution for Utility Companies
Utility companies implement lockbox services to streamline cash management by redirecting customer payments to a secure post office box managed by their bank. This arrangement accelerates deposit processing, reduces mail float, and enhances cash flow visibility, ultimately improving collection efficiency. The bank processes payments and electronically transmits transaction data, enabling utility companies to reconcile accounts faster and allocate funds more effectively.
Benefits of Lockbox Services for Accounts Receivable
Lockbox services accelerate cash flow by reducing the time between customer payments and deposit processing, improving liquidity and working capital management. By outsourcing payment collection to a third-party, companies minimize errors and enhance security in handling receivables. The automated processing of lockbox payments streamlines accounts receivable operations, lowering administrative costs and improving cash forecasting accuracy.
Lockbox Example: Accelerating Cash Flow for Retailers
A lockbox system accelerates cash flow for retailers by directing customer payments to a secure PO box, where the bank processes and deposits funds rapidly. This method reduces mail float and check processing time, enabling retailers to access funds more quickly and improve working capital management. Enhanced cash flow visibility supports timely inventory replenishment and operational decisions.
Comparing Traditional vs. Electronic Lockbox Systems
Traditional lockbox systems rely on physical mail collection and manual data entry, leading to delays and higher processing costs. Electronic lockbox systems automate payment processing by capturing remittance data digitally, significantly accelerating cash flow and reducing errors. Businesses benefit from enhanced efficiency and improved liquidity management when using electronic lockboxes over traditional methods.
Lockbox Use Case: Reducing Payment Processing Time
A lockbox accelerates payment processing by directing customer payments to a secure PO box managed by a bank, which immediately deposits funds and transmits payment data to the company. This system reduces mail float and processing delays, enabling faster cash availability and improved liquidity management. Companies in utilities, insurance, and healthcare commonly use lockboxes to streamline receivables and enhance operational efficiency.
Example of Lockbox Integration with Treasury Management
A common example of lockbox integration with treasury management involves a company outsourcing the receipt of customer payments to a bank-operated lockbox facility, where payments are processed and digitized swiftly. The lockbox system automatically uploads payment data into the treasury management system, accelerating cash application and improving liquidity forecasting accuracy. This seamless integration enhances working capital efficiency and reduces manual errors in cash flow reconciliation.
Key Considerations When Implementing a Lockbox System
Key considerations when implementing a lockbox system include selecting a geographically strategic processing location to minimize mail time and ensure faster deposit of customer payments. Integration with existing cash management software and accounting systems is essential for seamless reconciliation and real-time monitoring of incoming payments. Security measures, such as controlled access, encryption, and regulatory compliance, are critical to protect sensitive financial information throughout the lockbox processing cycle.
example of lockbox in cash management Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com