A dribble in a block trade refers to the practice of executing a large trade order in multiple smaller transactions instead of a single bulk trade. This technique helps to minimize market impact and reduce price slippage by spreading out the order over time. Financial institutions often use dribbling to discreetly offload or acquire large positions without significantly affecting the stock price. Block trades typically involve high volumes of securities, often exceeding 10,000 shares or $200,000 in value, conducted privately outside the open market. Dribbling allows traders to maintain liquidity and optimize execution prices by avoiding sudden spikes or drops in demand. This approach is essential for institutional investors seeking to manage risk and achieve efficient trade execution in volatile markets.
Table of Comparison
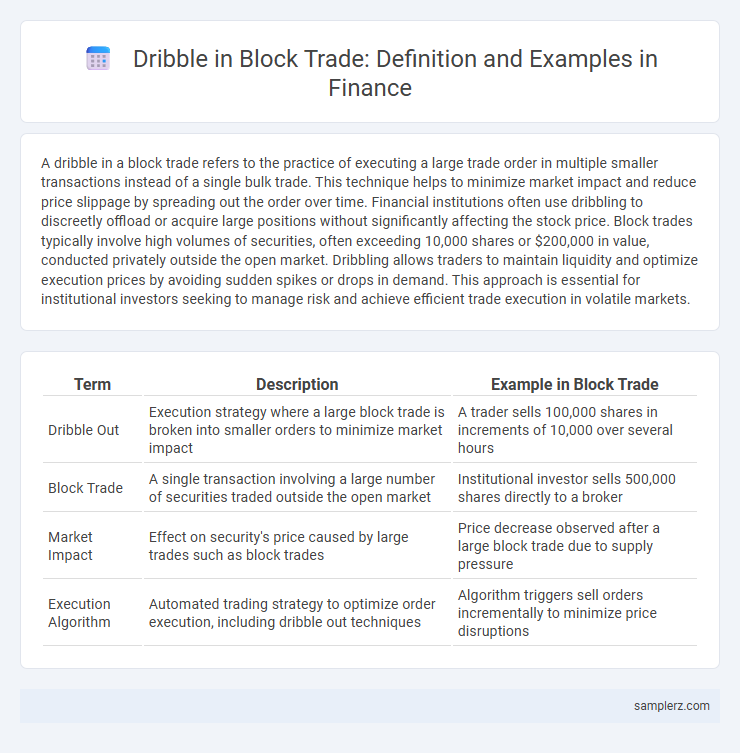
| Term | Description | Example in Block Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Dribble Out | Execution strategy where a large block trade is broken into smaller orders to minimize market impact | A trader sells 100,000 shares in increments of 10,000 over several hours |
| Block Trade | A single transaction involving a large number of securities traded outside the open market | Institutional investor sells 500,000 shares directly to a broker |
| Market Impact | Effect on security's price caused by large trades such as block trades | Price decrease observed after a large block trade due to supply pressure |
| Execution Algorithm | Automated trading strategy to optimize order execution, including dribble out techniques | Algorithm triggers sell orders incrementally to minimize price disruptions |
Understanding Dribble in Block Trades: An Overview
Dribble in block trades refers to the strategy of executing large orders in smaller increments to minimize market impact and reduce price slippage. This method helps institutional investors manage liquidity risk by gradually releasing shares, preserving anonymity and preventing significant price fluctuations. Effective dribble execution enhances trade efficiency in high-volume transactions within equity markets.
Key Characteristics of Dribble Trading Techniques
Dribble trading in block trades involves executing large orders in smaller increments to minimize market impact and price disruption. Key characteristics include stealthy order placement, time-based or volume-based slicing, and adaptive pacing to align with market liquidity conditions. This technique allows institutional traders to achieve better average execution prices while reducing signaling risk.
Real-Life Examples of Dribble in Block Trade Transactions
A notable real-life example of dribble in block trade transactions occurred when a hedge fund gradually executed a 1 million-share sale of a tech company over several days to avoid market impact and price slippage. By breaking the large order into smaller, strategically timed trades, the fund minimized signaling risk and preserved the stock's market price stability. This technique allowed institutional investors to efficiently manage liquidity and execute block trades without triggering adverse price movements.
Strategic Reasons for Dribble Trading in Block Trades
Dribble trading in block trades allows institutional investors to strategically minimize market impact and avoid signaling their intentions to competitors. By breaking large orders into smaller, discrete trades over time, they can achieve better execution prices and reduce price volatility. This method also helps maintain market stability and preserves confidentiality in highly sensitive financial transactions.
Risk Management in Dribble Block Trade Executions
Dribble block trade executions mitigate market impact by breaking large orders into smaller, timed increments, reducing price slippage and signaling risk. Effective risk management involves continuous monitoring of order flow and market volatility to adjust execution speed and size, minimizing adverse price movements. Utilizing advanced algorithms helps balance the trade-off between execution risk and market impact, optimizing transaction costs in block trading strategies.
Impact of Dribble Trades on Market Liquidity
Dribble trades in block trading involve executing large orders in small increments to minimize market impact and reduce price slippage. This strategy can sustain market liquidity by preventing sudden price changes and allowing continuous order flow, but it may also obscure true supply and demand levels, complicating price discovery. Empirical studies show that while dribble trades help maintain orderly markets, excessive fragmentation can lead to reduced transparency and increased volatility.
Regulatory Considerations for Dribble in Block Trades
Regulatory considerations for dribble in block trades emphasize compliance with market manipulation rules and transparency requirements set by bodies such as the SEC and FINRA. Institutions must carefully monitor trade execution to avoid triggering price distortions or misleading signals during incremental sales of large securities positions. Accurate reporting and adherence to predetermined trading plans help mitigate the risk of regulatory scrutiny and ensure fair market practices.
Comparing Dribble vs. Single-Transaction Block Trades
Dribble block trades involve executing a large order through multiple smaller trades over time, reducing market impact and price slippage compared to single-transaction block trades, which often cause immediate price fluctuations. This method enhances liquidity management by minimizing signaling risk and allowing for better price discovery in volatile markets. Institutions prefer dribble trades to maintain anonymity and achieve more favorable average execution prices than lump-sum block trades.
How Institutional Investors Utilize Dribble in Block Trades
Institutional investors utilize dribble in block trades by gradually executing large orders in smaller increments over time to minimize market impact and price slippage. This strategy helps preserve confidentiality and prevents adverse price movements that could occur from revealing the full size of the order at once. Employing dribble execution algorithms optimizes trade efficiency, ensuring better average pricing in volatile markets.
Best Practices for Executing Dribble Strategies in Block Trades
Dribble strategies in block trades involve breaking large orders into smaller, discrete executions to minimize market impact and avoid signaling intentions to other traders. Best practices include using algorithmic trading tools that adapt to real-time market conditions, maintaining execution discretion, and continuously monitoring volume-weighted average price (VWAP) benchmarks to optimize trade timing. Employing this approach enhances liquidity management and reduces price slippage in institutional equity or fixed-income transactions.
example of dribble in block trade Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com