Dim sum bonds are RMB-denominated bonds issued outside mainland China, primarily in Hong Kong. These bonds provide foreign investors with access to Chinese currency assets without the restrictions of mainland markets. For example, in 2023, the China Development Bank issued dim sum bonds worth 15 billion RMB to finance infrastructure projects. The dim sum bond market reflects growing international interest in China's financial instruments. Entities like Chinese corporations and government-backed institutions often use these bonds to raise offshore capital. Data from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority shows that the outstanding amount of dim sum bonds reached over 300 billion RMB by mid-2024, indicating significant market growth.
Table of Comparison
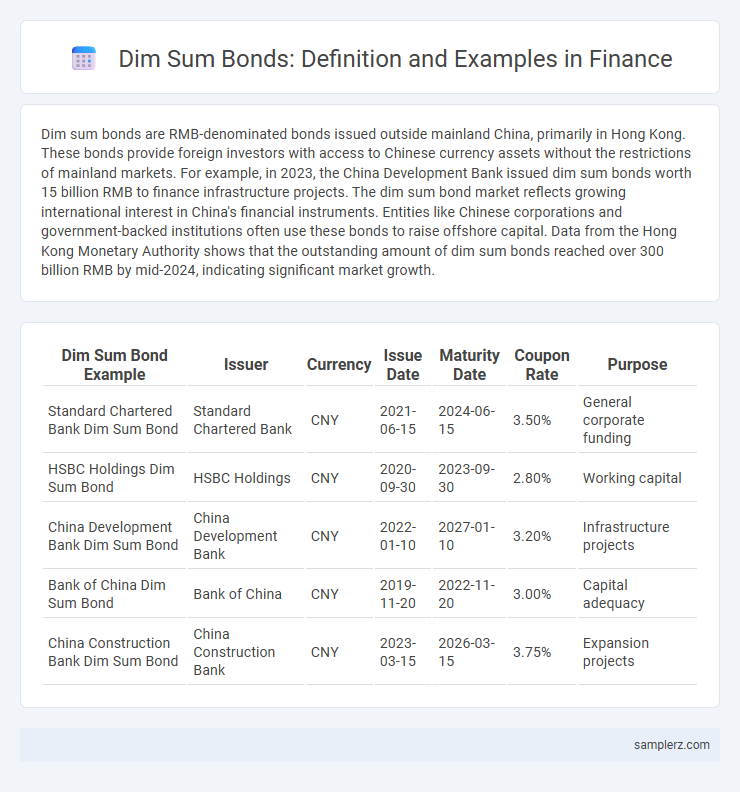
| Dim Sum Bond Example | Issuer | Currency | Issue Date | Maturity Date | Coupon Rate | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Chartered Bank Dim Sum Bond | Standard Chartered Bank | CNY | 2021-06-15 | 2024-06-15 | 3.50% | General corporate funding |
| HSBC Holdings Dim Sum Bond | HSBC Holdings | CNY | 2020-09-30 | 2023-09-30 | 2.80% | Working capital |
| China Development Bank Dim Sum Bond | China Development Bank | CNY | 2022-01-10 | 2027-01-10 | 3.20% | Infrastructure projects |
| Bank of China Dim Sum Bond | Bank of China | CNY | 2019-11-20 | 2022-11-20 | 3.00% | Capital adequacy |
| China Construction Bank Dim Sum Bond | China Construction Bank | CNY | 2023-03-15 | 2026-03-15 | 3.75% | Expansion projects |
Introduction to Dim Sum Bonds
Dim Sum bonds are yuan-denominated bonds issued outside mainland China, primarily in Hong Kong, allowing international investors exposure to Chinese currency without direct mainland market access. These bonds are issued by Chinese entities, foreign corporations, and financial institutions, providing diversification and hedging opportunities in international portfolios. The growing market size and liquidity of Dim Sum bonds reflect increasing global demand for renminbi-denominated assets.
Key Features of Dim Sum Bonds
Dim Sum bonds are bonds denominated in Chinese yuan and issued outside mainland China, primarily in Hong Kong, providing foreign investors access to Chinese currency debt markets. Key features include their issuance under Hong Kong law, liquidity in offshore yuan markets, and ability to offer diversification benefits with usually higher yields compared to onshore bonds. These bonds also carry currency risk but facilitate international investors' exposure to China's economic growth without direct mainland market restrictions.
History and Evolution of Dim Sum Bonds
Dim sum bonds originated in the early 2000s as Chinese yuan-denominated bonds issued outside mainland China, primarily in Hong Kong, to attract foreign investment while promoting the internationalization of the yuan. Initially dominated by Asian financial institutions and government entities, the market expanded rapidly after the 2009 global financial crisis, with corporate issuers and international players increasing participation. The evolution of dim sum bonds reflects China's growing economic influence and efforts to establish the yuan as a key global currency in cross-border finance.
Purpose of Issuing Dim Sum Bonds
Dim sum bonds are issued primarily to attract foreign investment by allowing investors to access Chinese currency (renminbi) in offshore markets, promoting international use of the yuan. They serve as a strategic financing tool for companies and governments seeking to diversify funding sources while benefiting from China's growing economic influence. These bonds help issuers hedge currency risks and tap into China's expanding capital market without onshore regulatory restrictions.
Example of Dim Sum Bond Issuance
A notable example of Dim Sum bond issuance is the 2011 offering by the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), which raised RMB 3 billion in the Hong Kong offshore market. This bond issuance targeted international investors seeking exposure to Chinese currency outside mainland China, enhancing liquidity and diversifying funding sources. The success of ICBC's Dim Sum bond paved the way for other Chinese entities to tap into offshore RMB financing.
Major Issuers of Dim Sum Bonds
Major issuers of dim sum bonds include Chinese financial institutions like the Bank of China and ICBC, as well as multinational corporations such as China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC). These entities leverage dim sum bonds to raise offshore RMB funding in the Hong Kong market. Sovereign issuers like the China Development Bank also actively participate, enhancing liquidity and market depth.
Investor Profile for Dim Sum Bonds
Dim sum bonds primarily attract international investors seeking exposure to Chinese yuan-denominated assets without direct market access. These bonds appeal to institutional investors, such as pension funds and asset managers, due to their diversification benefits and relatively stable yield returns. Retail investors with moderate risk tolerance also participate, aiming to capitalize on potential currency appreciation and China's growing economic influence.
Currency and Yield Structure in Dim Sum Bonds
Dim Sum bonds are yuan-denominated bonds issued outside mainland China, predominantly in Hong Kong, attracting investors seeking exposure to Chinese currency without direct onshore restrictions. These bonds typically offer competitive yields compared to onshore Chinese bonds, reflecting the offshore market's risk perception and liquidity conditions. The yield structure often includes a spread over comparable US Treasury or Hong Kong dollar bonds, influenced by factors such as currency exchange risk, issuer credit quality, and prevailing interest rates in both China and global markets.
Risks Associated with Dim Sum Bonds
Dim sum bonds, issued in Chinese yuan outside mainland China, pose currency risk due to fluctuations in the offshore yuan market. Credit risk arises from the issuer's financial stability, often influenced by geopolitical tensions and regulatory changes between China and global markets. Liquidity risk is also significant, as dim sum bonds typically have lower trading volumes compared to bonds issued in major currencies like USD or EUR.
Future Outlook for Dim Sum Bond Market
The future outlook for the dim sum bond market shows significant growth potential as increasing Chinese issuers seek offshore financing in the Hong Kong market. With China's ongoing economic reforms and greater market liberalization, investor confidence is expected to rise, attracting more global participation. Enhanced regulatory frameworks and currency stability further support the expansion and liquidity of dim sum bonds.
example of dim sum in bond Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com