Hedonic pricing in real estate involves evaluating property values by analyzing various characteristics such as location, size, number of bedrooms, and proximity to amenities. For example, homes near top-rated school districts typically command higher prices, reflecting the premium buyers place on education quality. This method isolates the value contribution of each attribute, enabling accurate price estimation based on market preferences. Data-driven hedonic models use features like neighborhood crime rates, walkability scores, and environmental factors to quantify their impact on housing prices. Real estate platforms and appraisers rely on these models to support pricing strategies and investment decisions. By capturing the nuanced effect of property traits, hedonic pricing aids in understanding market dynamics and forecasting price trends.
Table of Comparison
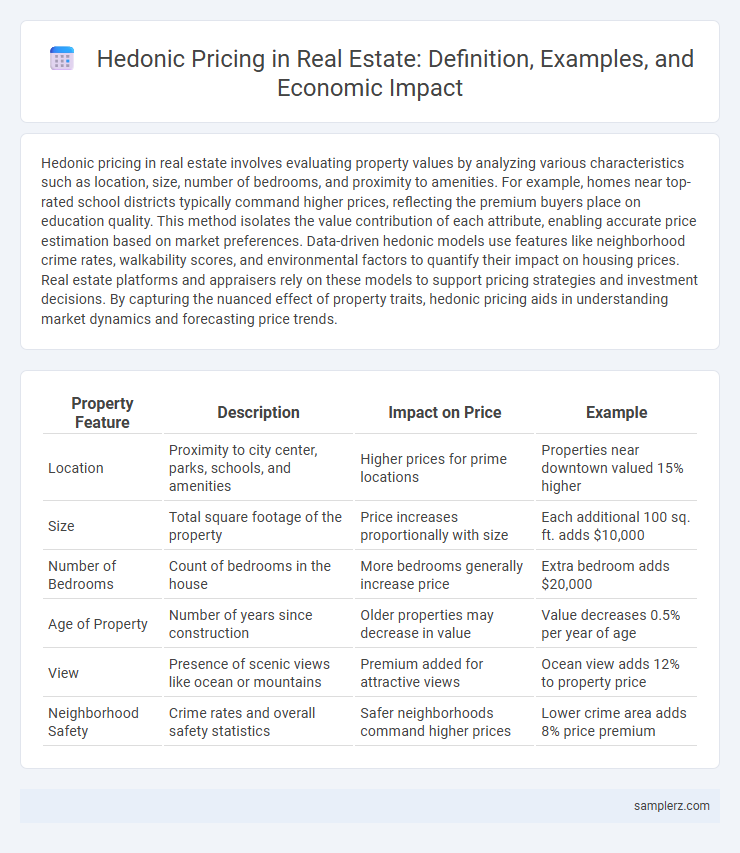
| Property Feature | Description | Impact on Price | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Proximity to city center, parks, schools, and amenities | Higher prices for prime locations | Properties near downtown valued 15% higher |
| Size | Total square footage of the property | Price increases proportionally with size | Each additional 100 sq. ft. adds $10,000 |
| Number of Bedrooms | Count of bedrooms in the house | More bedrooms generally increase price | Extra bedroom adds $20,000 |
| Age of Property | Number of years since construction | Older properties may decrease in value | Value decreases 0.5% per year of age |
| View | Presence of scenic views like ocean or mountains | Premium added for attractive views | Ocean view adds 12% to property price |
| Neighborhood Safety | Crime rates and overall safety statistics | Safer neighborhoods command higher prices | Lower crime area adds 8% price premium |
Understanding Hedonic Pricing in Real Estate
Hedonic pricing in real estate analyzes how specific factors such as location, square footage, number of bedrooms, and proximity to amenities influence property values. By isolating the impact of individual attributes, this method helps appraisers and economists estimate a property's market price based on the combined effect of its characteristics. Understanding hedonic pricing enables more accurate pricing models that reflect buyer preferences and neighborhood dynamics.
Key Features Influencing Property Values
Property values are significantly affected by key features such as location, size, and proximity to amenities, which are core elements in hedonic pricing models. Characteristics like school district quality, neighborhood safety, and access to public transportation also play critical roles in determining real estate prices. Environmental factors including air quality and noise levels further influence valuation, reflecting the comprehensive approach of hedonic pricing in capturing market dynamics.
The Role of Location in Hedonic Pricing Models
Location significantly influences property values in hedonic pricing models, as proximity to amenities, quality of local schools, and neighborhood safety directly affect housing prices. Studies show that homes closer to city centers or with access to public transportation often command higher prices, reflecting the premium buyers place on convenience and accessibility. Incorporating locational attributes into these models enhances accuracy in predicting real estate market fluctuations and guiding investment decisions.
Impact of Amenities on Real Estate Prices
The presence of amenities such as parks, gyms, and high-quality schools significantly increases real estate prices by enhancing property desirability and residents' quality of life. Hedonic pricing models quantify this impact by isolating the value contributed by each amenity, reflecting higher willingness to pay among buyers for locations with superior facilities. Empirical studies consistently show a premium of 10-20% on property values in neighborhoods with abundant amenities compared to those lacking such features.
How School Quality Affects Home Valuation
School quality significantly influences home valuation by increasing property prices in neighborhoods with highly rated schools. Research shows that homes within top-performing school districts can command premiums ranging from 10% to 30% compared to similar properties in lower-rated areas. These price differences reflect the hedonic pricing model, where educational quality acts as a key attribute affecting buyers' willingness to pay.
Environmental Factors in Hedonic Real Estate Pricing
Environmental factors such as air quality, noise levels, and proximity to green spaces significantly influence hedonic real estate pricing by affecting property values. Studies show that homes near parks or with lower pollution levels command higher prices due to enhanced livability and health benefits. This pricing approach integrates environmental attributes into market valuations, reflecting consumer preferences for sustainable and pleasant living environments.
Hedonic Pricing and Urban Versus Rural Properties
Hedonic pricing in real estate reveals that urban properties typically command higher prices due to factors like proximity to amenities, better infrastructure, and greater employment opportunities, which are less prevalent in rural areas. Differences in property valuations reflect attributes such as location, size, neighborhood quality, and environmental factors, highlighting the premium placed on urban living. This method quantifies how each characteristic contributes to price variations between urban and rural real estate markets.
Technological Advancements Affecting Property Value
Technological advancements such as smart home systems, energy-efficient appliances, and high-speed internet connectivity significantly enhance property value by meeting modern buyer preferences. Properties equipped with cutting-edge technology often command higher prices in competitive real estate markets due to increased convenience, security, and energy savings. Hedonic pricing models quantify these value increments by isolating the impact of technological features on overall property prices.
Case Studies: Successful Hedonic Pricing Applications
Case studies in real estate highlight successful applications of hedonic pricing models by quantifying the influence of attributes such as location, square footage, and proximity to amenities on property values. For example, a study in San Francisco utilized hedonic regression to isolate the premium buyers pay for homes near top-rated schools, revealing a 20% increase in price compared to similar properties further away. Another case in New York City demonstrated how access to public transportation and green spaces contributed significantly to residential property valuation, guiding developers in pricing and investment strategies.
Future Trends in Hedonic Pricing for Real Estate
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics are driving the evolution of hedonic pricing models in real estate by enabling more accurate valuation based on property features and neighborhood attributes. Future trends indicate increased integration of environmental factors like climate resilience and energy efficiency into pricing algorithms, reflecting growing buyer preferences for sustainable properties. Enhanced granularity in data collection will allow market participants to better anticipate demand shifts and price fluctuations in urban and suburban real estate markets.
example of hedonic pricing in real estate Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com