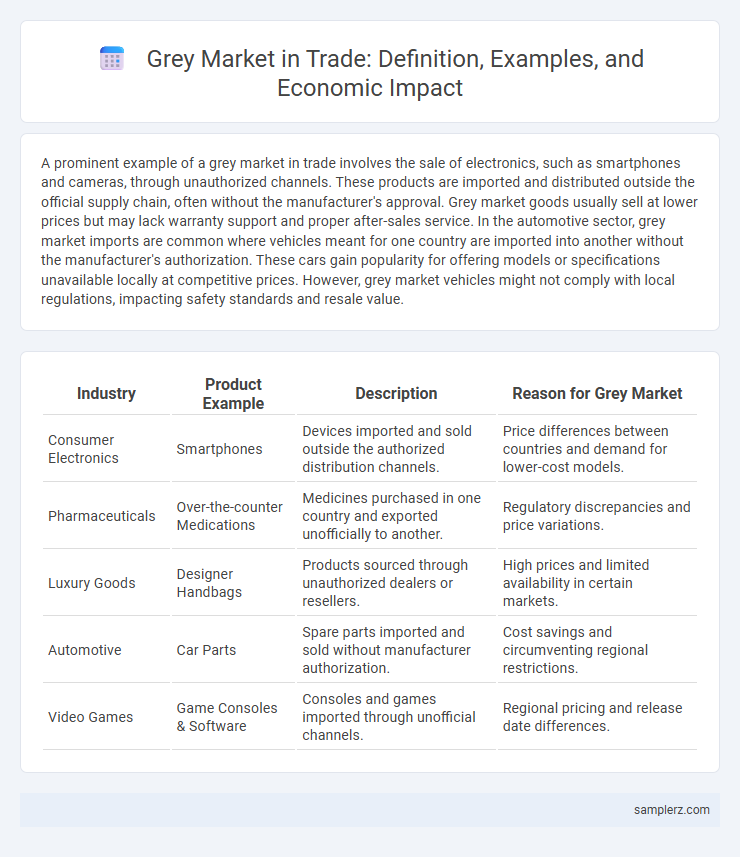
A prominent example of a grey market in trade involves the sale of electronics, such as smartphones and cameras, through unauthorized channels. These products are imported and distributed outside the official supply chain, often without the manufacturer's approval. Grey market goods usually sell at lower prices but may lack warranty support and proper after-sales service. In the automotive sector, grey market imports are common where vehicles meant for one country are imported into another without the manufacturer's authorization. These cars gain popularity for offering models or specifications unavailable locally at competitive prices. However, grey market vehicles might not comply with local regulations, impacting safety standards and resale value.
Table of Comparison
| Industry | Product Example | Description | Reason for Grey Market |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphones | Devices imported and sold outside the authorized distribution channels. | Price differences between countries and demand for lower-cost models. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Over-the-counter Medications | Medicines purchased in one country and exported unofficially to another. | Regulatory discrepancies and price variations. |
| Luxury Goods | Designer Handbags | Products sourced through unauthorized dealers or resellers. | High prices and limited availability in certain markets. |
| Automotive | Car Parts | Spare parts imported and sold without manufacturer authorization. | Cost savings and circumventing regional restrictions. |
| Video Games | Game Consoles & Software | Consoles and games imported through unofficial channels. | Regional pricing and release date differences. |
Understanding Grey Markets in Global Trade
Grey markets in global trade involve the unauthorized sale of genuine products through distribution channels not intended by the original manufacturers. These markets often arise in electronics, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods, where price discrepancies between regions create opportunities for third parties to import and sell items without official approval. Understanding grey markets is crucial for businesses to manage risks related to brand reputation, warranty claims, and regulatory compliance in international commerce.
Key Characteristics of Grey Market Activities
Grey market activities involve the unauthorized import and sale of genuine products outside official distribution channels, often exploiting price differentials between regions. Key characteristics include the absence of manufacturer approval, competitive pricing due to bypassing taxes or tariffs, and potential risks such as lack of warranty or after-sales service. These markets thrive on high demand for discounted goods like electronics, pharmaceuticals, and luxury items, affecting legitimate trade and regulatory enforcement.
Popular Grey Market Goods and Commodities
Popular grey market goods include electronics, luxury watches, and pharmaceuticals, which are often imported without official authorization, bypassing tariffs and regulations. Commodities like unbranded apparel and smuggled alcohol circulate widely, exploiting price differentials between regions. These goods challenge formal trade systems by offering lower prices but pose risks related to quality control and legal compliance.
The Role of Parallel Imports in Grey Markets
Parallel imports, also known as grey market goods, involve the unauthorized importation and resale of genuine products without the permission of the original manufacturer. These goods often bypass official distribution channels, leading to price disparities that attract consumers seeking lower-cost alternatives. The existence of parallel imports impacts brand control, warranty enforcement, and market pricing strategies within the global trade economy.
Real-World Examples of Grey Market Electronics
Grey market electronics include imported smartphones and laptops sold through unauthorized channels, bypassing official distributors and warranty services. Popular brands like Apple and Samsung often face these unauthorized sales, where products are priced lower but lack manufacturer support. This market thrives in regions with high import duties or limited product availability, impacting local economies and brand reputation.
Grey Market Pharmaceuticals: A Growing Concern
Grey market pharmaceuticals involve the trade of genuine medicines sold through unauthorized channels, bypassing official distribution networks. This practice undermines regulatory oversight, often resulting in compromised drug quality and safety, posing significant health risks to consumers worldwide. The increasing prevalence of grey market drugs highlights the urgent need for stricter enforcement and improved supply chain transparency in the pharmaceutical industry.
Automotive Trade through Grey Channels
The automotive trade through grey channels involves the import and distribution of vehicles without the authorization of official manufacturers or dealerships. These grey market cars often bypass local safety regulations and tax frameworks, impacting government revenue and consumer protection. Despite potential risks, grey market vehicles provide access to cheaper or unique models that are unavailable through official trade routes.
Impact of Grey Markets on Authorized Retailers
Grey markets, such as the unauthorized sale of smartphones imported from regions with lower prices, significantly impact authorized retailers by undercutting official pricing structures and reducing profit margins. These sales channels bypass manufacturer controls, leading to warranty issues and diminished brand loyalty among consumers who experience inconsistent service. Authorized retailers face challenges in maintaining competitive pricing and customer trust, which can ultimately erode market share and disrupt supply chain integrity.
Regulatory Challenges in Controlling Grey Markets
Grey markets in trade, such as parallel imports of electronics or pharmaceuticals, present significant regulatory challenges due to their operation outside authorized distribution channels. These markets often bypass trademark and patent controls, complicating enforcement by customs and regulatory agencies tasked with protecting intellectual property rights and consumer safety. The lack of standardized oversight hinders governments' ability to monitor product quality, tax compliance, and fair competition, exacerbating economic distortions in both domestic and international markets.
Economic Implications of Grey Market Transactions
Grey market transactions, such as the unauthorized sale of electronics imported from regions with lower prices, disrupt official distribution channels and reduce tax revenues for governments. These dealings can lead to price distortions, undermining legitimate businesses and causing market inefficiencies. The lack of regulatory oversight also increases risks of counterfeit products, which can harm consumer trust and long-term economic stability.
example of grey market in trade Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com