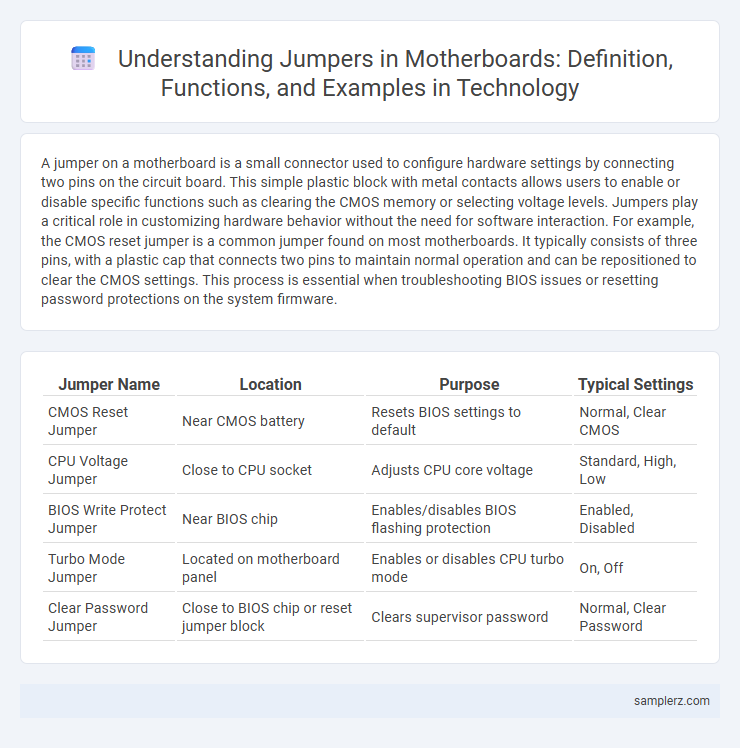
A jumper on a motherboard is a small connector used to configure hardware settings by connecting two pins on the circuit board. This simple plastic block with metal contacts allows users to enable or disable specific functions such as clearing the CMOS memory or selecting voltage levels. Jumpers play a critical role in customizing hardware behavior without the need for software interaction. For example, the CMOS reset jumper is a common jumper found on most motherboards. It typically consists of three pins, with a plastic cap that connects two pins to maintain normal operation and can be repositioned to clear the CMOS settings. This process is essential when troubleshooting BIOS issues or resetting password protections on the system firmware.
Table of Comparison
| Jumper Name | Location | Purpose | Typical Settings |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMOS Reset Jumper | Near CMOS battery | Resets BIOS settings to default | Normal, Clear CMOS |
| CPU Voltage Jumper | Close to CPU socket | Adjusts CPU core voltage | Standard, High, Low |
| BIOS Write Protect Jumper | Near BIOS chip | Enables/disables BIOS flashing protection | Enabled, Disabled |
| Turbo Mode Jumper | Located on motherboard panel | Enables or disables CPU turbo mode | On, Off |
| Clear Password Jumper | Close to BIOS chip or reset jumper block | Clears supervisor password | Normal, Clear Password |
Understanding Jumpers: Definition and Function in Motherboards
Jumpers on motherboards are small connectors that bridge specific pins to configure hardware settings such as enabling or disabling integrated components or resetting BIOS settings. They function by creating or breaking electrical circuits, allowing users to customize motherboard behavior without software intervention. Understanding jumper placement and settings is crucial for optimizing system performance and troubleshooting hardware issues.
Common Locations of Jumpers on a Motherboard
Jumpers on a motherboard are commonly located near the CMOS battery, the front panel header, and the IDE or SATA connectors, facilitating configuration adjustments such as clearing the BIOS or enabling specific hardware features. These small pins covered by a jumper cap enable users to modify low-level settings or troubleshoot hardware issues without software access. Placement tends to be clustered around essential interface points to streamline hardware configuration and maintenance.
Types of Jumpers Commonly Found on Modern Motherboards
Modern motherboards commonly feature several types of jumpers, including CMOS reset jumpers, which clear BIOS settings to factory defaults; BIOS configuration jumpers, used to enable or disable features like write protection; and CPU or memory voltage selection jumpers that help optimize hardware performance. These small connectors bridge pairs of pins to complete electrical circuits, allowing users to customize motherboard functionalities without software intervention. Understanding the specific jumper types and their locations enhances troubleshooting and hardware configuration tasks effectively.
CMOS Reset Jumper: Purpose and Example
The CMOS reset jumper on a motherboard restores the BIOS settings to factory defaults by shorting specific pins, clearing corrupted or forgotten BIOS passwords. Typically located near the CMOS battery, it consists of a three-pin header where shifting the jumper cap temporarily connects two pins to reset the CMOS memory. This process is essential for troubleshooting boot failures and hardware conflicts caused by incorrect BIOS configurations.
BIOS Configuration Jumper: How It’s Used
The BIOS configuration jumper on a motherboard allows users to reset BIOS settings to their factory defaults by temporarily altering the hardware configuration. This jumper is typically positioned near the CMOS battery and BIOS chip, enabling recovery from BIOS errors or forgotten passwords. Adjusting the jumper's position interrupts the BIOS memory, facilitating troubleshooting and system configuration without requiring software tools.
Password Reset Jumper Example
A Password Reset Jumper on a motherboard is a small connector that allows users to clear the BIOS password by temporarily shorting specific pins. This jumper is typically located near the CMOS battery and consists of three pins with a removable plastic jumper cap that bridges two pins during the reset process. Using the Password Reset Jumper restores BIOS default settings, enabling system access when the password is lost or forgotten.
Clear RTC (Real-Time Clock) Jumper Explained
The Clear RTC jumper on a motherboard resets the Real-Time Clock CMOS memory, restoring BIOS settings to default and resolving hardware conflicts or boot issues. It is typically a two or three-pin connector labeled CLR_CMOS or RTC_RESET, and users must power off the system and move the jumper from its default position to clear the RTC data. Understanding the Clear RTC jumper function is essential for troubleshooting BIOS configuration errors and system stability problems efficiently.
Jumper Settings for Enabling/Disabling Onboard Devices
Jumper settings on a motherboard allow users to enable or disable onboard devices such as integrated audio, USB controllers, and network adapters by altering specific pin configurations. For example, moving the jumper cap to connect pins 1-2 might enable the onboard LAN, while shifting it to pins 2-3 disables it, providing hardware-level control without accessing BIOS. Precise documentation in the motherboard manual is crucial for identifying the correct jumper locations and their corresponding functions to avoid hardware conflicts or malfunctions.
Examples of Jumper Pins for CPU Voltage Selection
Jumper pins for CPU voltage selection commonly include configurations like 3-pin or 4-pin jumpers, which allow users to manually adjust the CPU core voltage by altering the connected pins. Examples include ASUS motherboards featuring JP1 or JP2 jumpers that toggle between standard and overclocked voltage settings, or Gigabyte boards using a 3-pin jumper labeled VCORE for fine-tuning CPU voltage. Proper use of these jumper pins ensures stable CPU performance and prevents damage from incorrect voltage supply.
Safety Precautions When Adjusting Motherboard Jumpers
When adjusting motherboard jumpers, always power off and unplug the computer to prevent electrical shock or damage to components. Use an anti-static wrist strap or touch a grounded metal object to avoid electrostatic discharge that can harm sensitive circuitry. Carefully consult the motherboard manual to ensure correct jumper placement, as improper settings can cause hardware malfunctions or system instability.
example of jumper in motherboard Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com