Dark fiber refers to unused optical fiber cables that have been laid but are not currently active or transmitting data in telecommunication networks. Network providers and enterprises often lease or purchase dark fiber to establish private, high-capacity communication links that offer enhanced control and security. This infrastructure is commonly used for expanding broadband networks, supporting data center interconnects, and enabling ultra-fast internet services. An example of dark fiber deployment is seen in metropolitan area networks (MANs), where telecom companies install extensive dark fiber rings to facilitate future network growth and redundancy. Large corporations and cloud service providers utilize dark fiber to create dedicated pathways between offices or data centers, ensuring low latency and high bandwidth. In this context, dark fiber acts as a critical asset for managing data traffic in large-scale telecommunications projects and smart city implementations.
Table of Comparison
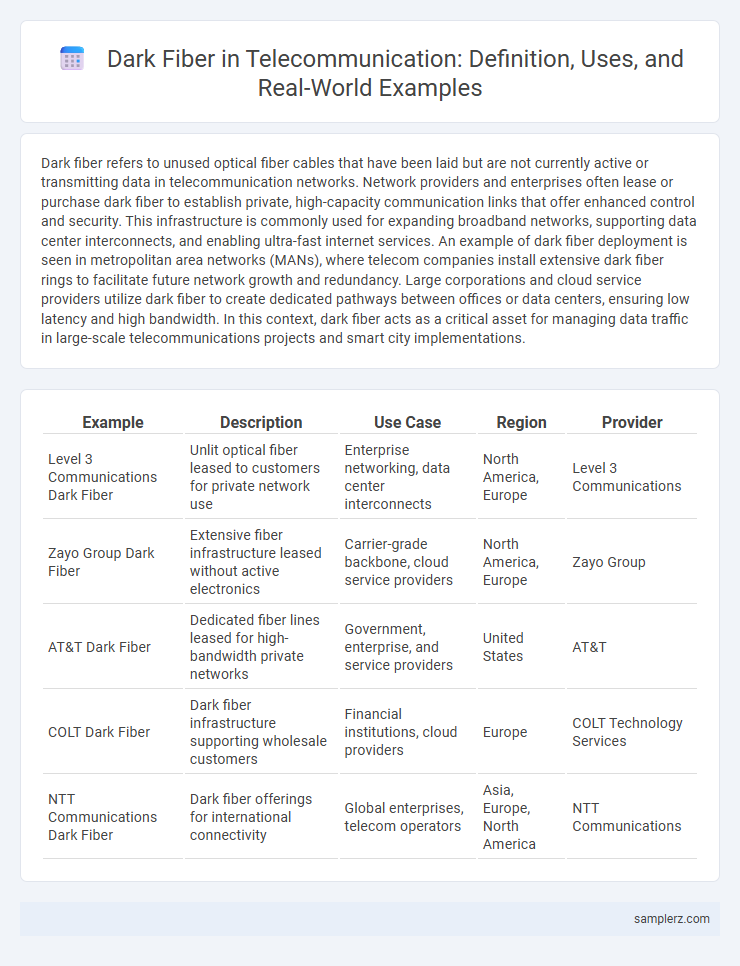
| Example | Description | Use Case | Region | Provider |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 3 Communications Dark Fiber | Unlit optical fiber leased to customers for private network use | Enterprise networking, data center interconnects | North America, Europe | Level 3 Communications |
| Zayo Group Dark Fiber | Extensive fiber infrastructure leased without active electronics | Carrier-grade backbone, cloud service providers | North America, Europe | Zayo Group |
| AT&T Dark Fiber | Dedicated fiber lines leased for high-bandwidth private networks | Government, enterprise, and service providers | United States | AT&T |
| COLT Dark Fiber | Dark fiber infrastructure supporting wholesale customers | Financial institutions, cloud providers | Europe | COLT Technology Services |
| NTT Communications Dark Fiber | Dark fiber offerings for international connectivity | Global enterprises, telecom operators | Asia, Europe, North America | NTT Communications |
Understanding Dark Fiber in Modern Telecommunications
Dark fiber refers to unused optical fiber cables installed in telecommunications networks, offering vast potential for high-capacity data transmission without signal interference. Major telecom providers and enterprises lease dark fiber to customize network infrastructure, enabling enhanced scalability and security in data communication. This technology supports the backbone of modern telecommunications by facilitating faster internet speeds, low latency, and flexible bandwidth management for cloud services and large-scale network operations.
Key Use Cases of Dark Fiber Networks
Dark fiber networks serve critical use cases such as enabling high-capacity data transmission for large enterprises, supporting metro area network expansion, and providing dedicated infrastructure for research and educational institutions. Telecom operators leverage dark fiber to offer scalable bandwidth solutions without the need for extensive network upgrades. Financial services firms utilize dark fiber for ultra-low latency connections essential for high-frequency trading and secure data exchanges.
Real-World Examples of Dark Fiber Deployments
Level 3 Communications operates extensive dark fiber networks across North America, enabling high-capacity, low-latency data transmission for enterprise clients. Google's deployment of dark fiber in select metropolitan areas supports its vast cloud infrastructure and data center interconnects. Verizon's dark fiber infrastructure enhances backbone connectivity and facilitates scalable bandwidth solutions for telecommunications and enterprise customers.
Benefits of Utilizing Dark Fiber in Telecom
Utilizing dark fiber in telecommunications significantly enhances network scalability and bandwidth capacity by providing dedicated, unused fiber optic infrastructure. This enables telecom providers to customize and control their data transmission with minimal latency and maximum security. Dark fiber's flexibility supports future technological advancements, ensuring long-term cost savings and improved service reliability.
Dark Fiber in Enterprise Telecommunication Solutions
Dark fiber in enterprise telecommunication solutions refers to unused optical fiber infrastructure leased or owned by businesses for private network use, enabling scalable, high-speed data transmission with enhanced security. Companies deploy dark fiber to support bandwidth-intensive applications, such as data centers, cloud services, and real-time analytics, ensuring low latency and operational control. This approach offers enterprises dedicated, high-capacity connectivity that can be customized to meet evolving technological demands without relying on traditional telecom providers.
Comparing Dark Fiber vs. Lit Fiber Services
Dark fiber refers to unused optical fiber cables available for leasing, offering greater control and scalability compared to lit fiber services, which come pre-equipped with active electronics managed by service providers. Enterprises leveraging dark fiber benefit from customizable bandwidth and enhanced security, while lit fiber services provide convenience and reduced upfront costs through managed network solutions. Evaluating dark fiber versus lit fiber hinges on factors such as network control requirements, cost considerations, and long-term scalability needs within telecommunications infrastructure.
Dark Fiber in 5G and Data Center Connectivity
Dark fiber plays a critical role in 5G infrastructure by providing high-capacity, low-latency connections essential for ultra-reliable and high-speed data transmission. Telecommunication companies leverage dark fiber networks to connect data centers, ensuring seamless integration and scalability for cloud services and edge computing applications. The use of dark fiber in 5G networks enhances network performance and supports massive IoT deployments with enhanced bandwidth capabilities.
Case Studies: Telecom Companies Leveraging Dark Fiber
Telecom companies like Verizon and CenturyLink extensively leverage dark fiber to enhance network capacity and reduce latency in metropolitan areas, driving high-speed data transmission for enterprise clients. Case studies reveal that dark fiber deployments enable unprecedented scalability and control, allowing providers to customize and upgrade infrastructure without the constraints of leased lines. This strategic utilization of dark fiber plays a crucial role in supporting 5G rollout and expanding broadband access in underserved regions.
Challenges and Considerations with Dark Fiber Usage
Dark fiber in telecommunication presents challenges including high initial installation costs, complex network management, and the need for specialized technical expertise. Considerations also involve future scalability, interoperability with existing infrastructure, and ensuring robust security measures to protect data transmission. Operators must evaluate these factors carefully to maximize the benefits of dark fiber deployment in enhancing network capacity and flexibility.
Future Trends of Dark Fiber in Global Telecom Expansion
Dark fiber networks are increasingly pivotal in global telecom expansion, enabling ultra-high-speed connectivity and scalable infrastructure for 5G and beyond. Telecom providers are investing in dark fiber to support burgeoning data demands, edge computing, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications, driving enhanced network efficiency and reduced latency. The growing adoption of dark fiber facilitates cost-effective network upgrades, positioning it as a key enabler in the future of global digital transformation.
example of dark fiber in telecommunication Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com