Steganography in cybersecurity involves concealing sensitive information within digital files such as images, audio, or video to prevent unauthorized access. One common example is embedding secret messages within the least significant bits of an image file, making the data invisible to the naked eye but recoverable with specialized software. This method enhances data confidentiality by hiding information in everyday digital content rather than encrypting it outright. Another example of steganography in cybersecurity is its use in malware communication, where hidden codes are embedded within seemingly harmless files to evade detection by security systems. Cybercriminal groups often exploit steganography to transmit commands or exfiltrate data, making it difficult for traditional antivirus tools to identify malicious activity. This technique leverages the subtle manipulation of digital file structures, emphasizing the need for advanced detection solutions in modern cybersecurity frameworks.
Table of Comparison
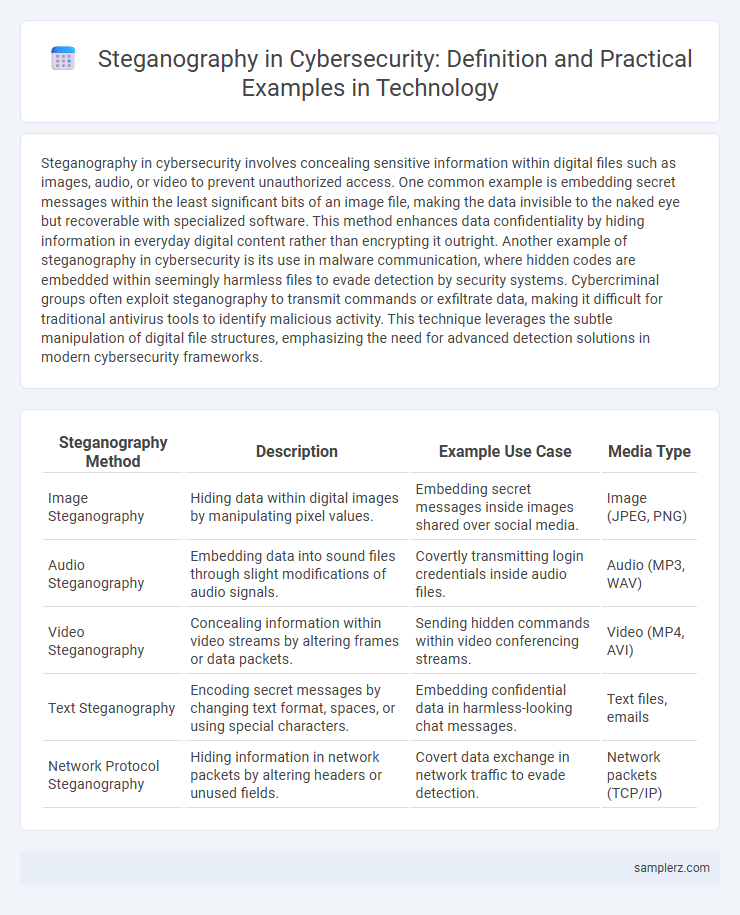
| Steganography Method | Description | Example Use Case | Media Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Steganography | Hiding data within digital images by manipulating pixel values. | Embedding secret messages inside images shared over social media. | Image (JPEG, PNG) |
| Audio Steganography | Embedding data into sound files through slight modifications of audio signals. | Covertly transmitting login credentials inside audio files. | Audio (MP3, WAV) |
| Video Steganography | Concealing information within video streams by altering frames or data packets. | Sending hidden commands within video conferencing streams. | Video (MP4, AVI) |
| Text Steganography | Encoding secret messages by changing text format, spaces, or using special characters. | Embedding confidential data in harmless-looking chat messages. | Text files, emails |
| Network Protocol Steganography | Hiding information in network packets by altering headers or unused fields. | Covert data exchange in network traffic to evade detection. | Network packets (TCP/IP) |
Real-World Steganography Techniques in Cybersecurity
Real-world steganography techniques in cybersecurity often involve embedding malicious code within image files or audio clips to evade detection by security systems. Cybercriminals use methods like Least Significant Bit (LSB) modification to hide sensitive data in innocuous media, making traditional antivirus scans less effective. Advanced steganographic tools enable covert communication channels, complicating threat intelligence and incident response efforts.
Common Digital File Formats Used for Steganography
Common digital file formats used for steganography in cybersecurity include images such as PNG, BMP, and JPEG, which offer extensive pixel data for embedding hidden messages without noticeable alteration. Audio files like WAV and MP3 are also frequently exploited due to their high data capacity and minimal perceptible changes when modified. Video formats including MP4 and AVI provide large containers for concealed information, leveraging both audio and visual channels to enhance data hiding efficiency.
Steganography in Malware: Concealing Malicious Code
Steganography in malware involves embedding malicious code within harmless-looking files such as images, audio, or video to evade detection by traditional security tools. Cybercriminals exploit this technique to secretly deliver payloads or command-and-control instructions without raising suspicion. Advanced malware campaigns use steganographic methods to maintain persistence and enhance stealth in compromised systems.
Case Studies: Steganography Attacks in Recent Cyber Incidents
Recent cyber incidents have revealed steganography as a covert method for malware delivery and data exfiltration, with case studies highlighting the use of image files to hide malicious code. Notably, the 2020 Maze ransomware attack employed steganographic techniques to conceal command-and-control instructions within seemingly innocuous PNG images. These examples underscore the evolving complexity of cyber threats, emphasizing the need for advanced detection methods to identify steganographic payloads in cybersecurity defense strategies.
Steganography vs. Cryptography: Key Differences in Practice
Steganography embeds secret messages within digital files like images or audio, making the presence of information undetectable, whereas cryptography encrypts data to render it unreadable without a decryption key. In cybersecurity, steganography provides covert communication by hiding the existence of messages, contrasting with cryptography's focus on securing visible data through complex algorithms. Both techniques complement each other, with steganography offering concealment and cryptography providing robust data protection against unauthorized access.
Social Media Steganography: Hiding Data in Plain Sight
Social media steganography involves embedding hidden data within images, videos, or audio files shared on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok, enabling covert communication or data exfiltration. Cybersecurity experts identify and analyze these concealed payloads using advanced detection algorithms and machine learning models tailored to spot anomalies in digital media metadata and pixel alterations. This technique poses significant risks for data leakage, unauthorized information exchange, and cyber espionage, requiring continuous development of robust steganalysis tools to safeguard user privacy and network security.
Steganography Tools and Software Used by Cybercriminals
Cybercriminals frequently utilize steganography tools like OpenStego, Steghide, and SilentEye to embed malicious code or sensitive data within seemingly innocuous digital files, evading detection by traditional security systems. These software applications support various file formats such as images, audio, and video, allowing covert communication and data exfiltration in cyber espionage and malware campaigns. By leveraging advanced algorithms for data hiding, steganography tools enhance the stealth capabilities of cyber attacks, complicating forensic investigations and threat mitigation efforts.
Steganographic Methods for Exfiltrating Sensitive Information
Steganographic methods for exfiltrating sensitive information in cybersecurity often involve embedding hidden data within digital images, audio files, or video streams to avoid detection by traditional security systems. Techniques such as Least Significant Bit (LSB) manipulation and spread spectrum encoding enable covert communication by altering file properties without noticeable changes to the user. These methods exploit the large data capacity of multimedia files, allowing cyber attackers to discreetly transfer confidential information across networks.
Detection and Prevention of Steganography in Cybersecurity
Steganography in cybersecurity involves hiding malicious data within innocuous files like images or audio to evade detection. Detection techniques utilize statistical analysis, machine learning algorithms, and signature-based methods to identify abnormalities in file structures or data patterns. Preventive measures include implementing robust data validation, deploying network monitoring tools, and employing encryption methods to reduce the risk of covert data exfiltration.
Future Trends: Steganography’s Evolving Role in Cyber Threats
Emerging trends in steganography reveal increasingly sophisticated methods for embedding malicious code within seemingly innocuous files, such as images and videos, complicating detection in cybersecurity defenses. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning enable attackers to automate and enhance steganographic techniques, creating dynamic, adaptive payloads that evade traditional signature-based detection systems. Future cybersecurity strategies must integrate advanced behavioral analysis and quantum-resistant encryption to counter the evolving landscape of steganographic cyber threats.
example of steganography in cybersecurity Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com