Blockchain technology has revolutionized supply chain management by providing transparent and immutable record-keeping. For example, Walmart uses blockchain to track the provenance of food products, enhancing food safety and reducing the time required to trace contamination sources. This system records every transaction on a decentralized ledger, allowing stakeholders to verify product origins and movement with real-time data. Another example is IBM Food Trust, which employs blockchain to improve traceability across the food supply chain. The platform collects and stores data from multiple participants, including farmers, processors, and retailers, ensuring the authenticity of products and reducing fraud. By using cryptographic hashes and smart contracts, the system guarantees data integrity and automates compliance processes within supply networks.
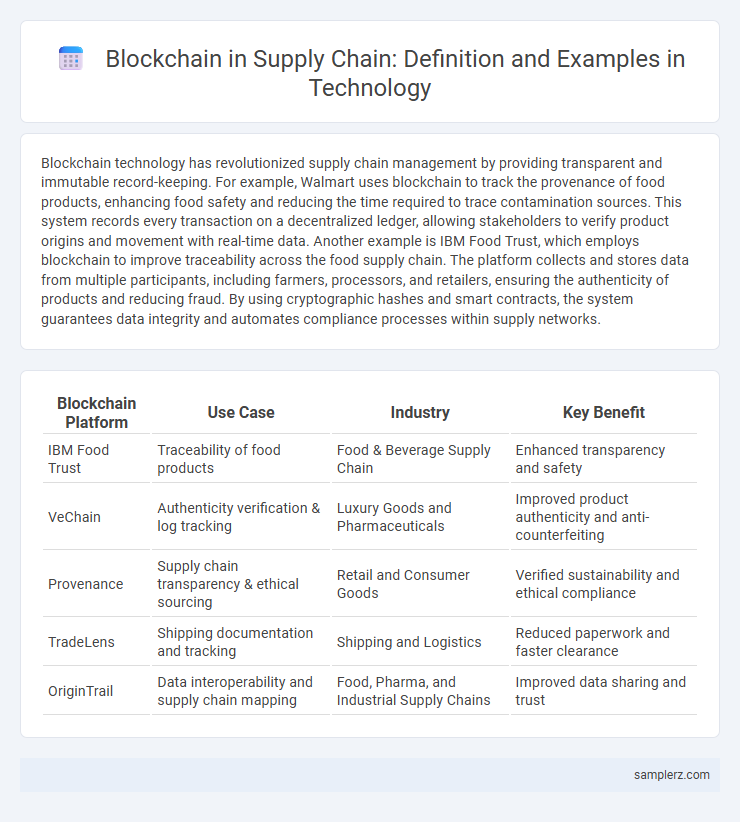
Table of Comparison
| Blockchain Platform | Use Case | Industry | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBM Food Trust | Traceability of food products | Food & Beverage Supply Chain | Enhanced transparency and safety |
| VeChain | Authenticity verification & log tracking | Luxury Goods and Pharmaceuticals | Improved product authenticity and anti-counterfeiting |
| Provenance | Supply chain transparency & ethical sourcing | Retail and Consumer Goods | Verified sustainability and ethical compliance |
| TradeLens | Shipping documentation and tracking | Shipping and Logistics | Reduced paperwork and faster clearance |
| OriginTrail | Data interoperability and supply chain mapping | Food, Pharma, and Industrial Supply Chains | Improved data sharing and trust |
Introduction to Blockchain in Supply Chain
Blockchain in supply chain technology enhances transparency by recording every transaction on an immutable digital ledger accessible to all authorized participants. This decentralized system enables real-time tracking of goods from origin to delivery, reducing fraud and errors while increasing efficiency. Major companies like Walmart and Maersk utilize blockchain platforms to optimize logistics, improve traceability, and ensure product authenticity throughout the supply chain.
Enhancing Traceability with Blockchain
Blockchain technology enhances supply chain traceability by providing an immutable ledger that records every transaction and movement of goods in real time. Companies like IBM Food Trust utilize blockchain to track food products from farm to table, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud. This transparent system enables faster recalls, improved regulatory compliance, and increased consumer trust through verified product origins.
Real-Time Inventory Management Using Blockchain
Real-time inventory management using blockchain enhances supply chain transparency by recording every transaction on a decentralized ledger accessible to all authorized parties. This technology enables automated tracking of inventory levels, shipments, and deliveries, reducing errors and preventing fraud. Companies like Walmart use blockchain to monitor product origins and ensure accurate stock updates, improving efficiency and responsiveness.
Smart Contracts for Automated Supply Chain Processes
Smart contracts streamline supply chain operations by automating transactions and enforcing contract terms without intermediaries. These blockchain-based protocols enhance transparency, reduce delays, and minimize human errors in procurement, shipment, and payments. Industry leaders like IBM and Maersk implement smart contracts to optimize traceability and efficiency across global supply networks.
Blockchain in Food Safety and Provenance
Blockchain enhances food safety and provenance by providing an immutable ledger that tracks the origin, processing, and distribution of food products. Companies like IBM Food Trust use blockchain to increase transparency and reduce fraud in the supply chain, ensuring consumers receive authentic and safe products. Real-time data on temperature, handling, and shipping conditions are recorded on the blockchain, enabling rapid response to contamination outbreaks and recalls.
Counterfeit Prevention Through Blockchain Authentication
Blockchain technology enhances supply chain security by enabling immutable product authentication records that prevent counterfeit goods. Each item is assigned a unique digital identity stored on the blockchain, ensuring transparent verification at every stage from manufacturer to retailer. This decentralized ledger reduces fraud by providing tamper-proof evidence of authenticity.
Transparent Logistics Tracking with Blockchain
Transparent logistics tracking with blockchain enhances supply chain visibility by recording every transaction on an immutable ledger. This technology enables real-time tracking of goods, reducing fraud and errors while improving accountability among suppliers and carriers. Companies like IBM Food Trust demonstrate how blockchain ensures provenance and authenticity in complex supply networks.
Blockchain for Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency by providing immutable records that verify sustainable practices and ensure ethical sourcing of materials. By enabling real-time tracking and authentic provenance, it reduces fraud and supports compliance with environmental regulations. Companies leveraging blockchain demonstrate commitment to corporate social responsibility while improving stakeholder trust and operational efficiency.
Streamlining Payments and Settlements in Supply Chain
Blockchain technology revolutionizes supply chain payments by enabling secure, transparent, and instantaneous transactions between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. Smart contracts automate payment settlements, reducing errors and minimizing delays typically caused by intermediaries. Companies leveraging blockchain experience enhanced financial efficiency, improved cash flow visibility, and increased trust among supply chain partners.
Case Studies: Successful Blockchain Implementations in Supply Chain
Walmart utilizes blockchain to enhance traceability and reduce contamination risks in its food supply chain, leading to faster recalls and increased consumer safety. Maersk and IBM's TradeLens platform integrates blockchain to streamline global shipping logistics, improving transparency and reducing fraud. De Beers employs blockchain to verify the origin of diamonds, ensuring ethical sourcing and preventing the circulation of conflict gems.
example of blockchain in supply chain Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com