A tuple in programming is a data structure that stores a fixed number of elements, often of different types, in a specific order. Commonly used in languages like Python, tuples are immutable, meaning their contents cannot be changed once created. For example, a tuple in Python can be defined as (42, "OpenAI", 3.14), combining an integer, a string, and a floating-point number. Tuples provide efficient grouping of related data without the overhead of objects or lists. They are useful in scenarios requiring heterogeneous data storage and quick access with indexing. Programming languages such as Scala and Haskell also support tuples, enabling multiple values to be returned from functions consistently and safely.
Table of Comparison
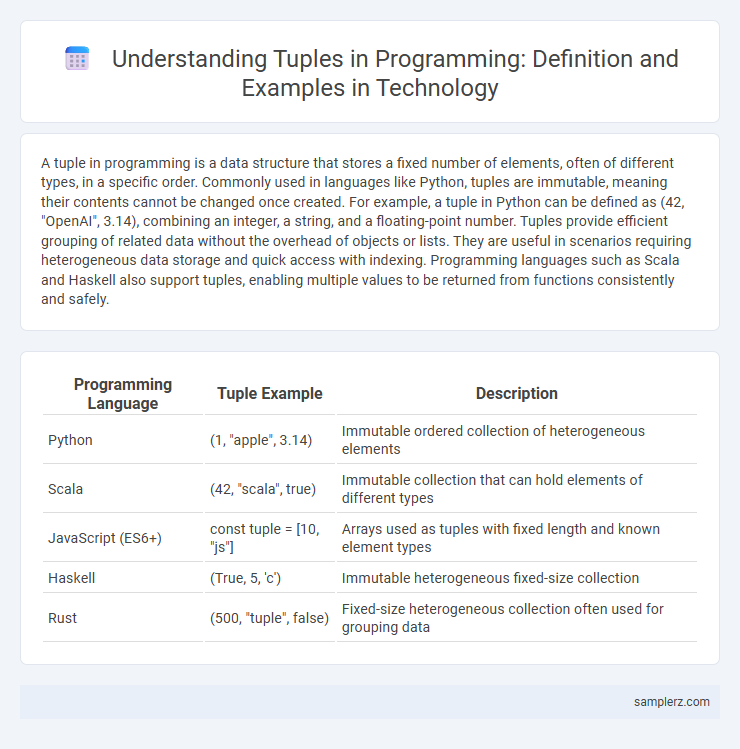
| Programming Language | Tuple Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Python | (1, "apple", 3.14) | Immutable ordered collection of heterogeneous elements |
| Scala | (42, "scala", true) | Immutable collection that can hold elements of different types |
| JavaScript (ES6+) | const tuple = [10, "js"] | Arrays used as tuples with fixed length and known element types |
| Haskell | (True, 5, 'c') | Immutable heterogeneous fixed-size collection |
| Rust | (500, "tuple", false) | Fixed-size heterogeneous collection often used for grouping data |
Introduction to Tuples in Programming
Tuples in programming are immutable collections used to group multiple elements into a single compound data structure, commonly seen in languages like Python, Swift, and Scala. A tuple example in Python is (1, "apple", True), which holds an integer, a string, and a boolean together without allowing modification after creation. This fixed-size, ordered grouping enhances code readability and efficiency by enabling multiple return values from functions or packing related but heterogeneous data effortlessly.
Key Characteristics of Tuples
Tuples in programming languages are immutable ordered collections that can hold multiple data types, making them ideal for fixed sets of related values. They provide fast access due to indexed positions and ensure data integrity by preventing modification after creation. Commonly used in languages like Python and Scala, tuples enable efficient data grouping without the overhead of mutable structures.
Tuple Syntax Across Programming Languages
Tuples are ordered collections of elements commonly used in programming languages like Python, Swift, and Scala, with syntax varying across these languages. In Python, tuples are defined using parentheses and commas, such as `(1, 'apple', True)`, while Swift uses parentheses without explicit type definitions, e.g., `(42, "hello")`, and Scala denotes tuples with `TupleN` types or parentheses like `(1, "Scala")`. Understanding these syntactic differences assists developers in leveraging tuples efficiently for immutable data grouping and pattern matching.
Common Examples of Tuples in Python
Tuples in Python are immutable sequences often used to store heterogeneous data, such as coordinates (e.g., (x, y) = (10, 20)) or RGB color values (e.g., (255, 0, 0)). Common examples include returning multiple values from functions like divmod(10, 3) which yields the tuple (3, 1). Python tuples are frequently used for grouping fixed sets of items, enhancing data integrity and readability in code.
Tuple Usage in JavaScript
Tuples in JavaScript are typically represented using arrays to store a fixed-size sequence of elements with different types, such as `[string, number]` for a pair containing a name and an age. Utilizing tuples helps enforce type safety and clarity when working with structured data, especially in TypeScript where tuples are explicitly supported. Common use cases include function return values and parameter grouping, improving code readability and reducing errors during development.
Implementing Tuples in C#
Tuples in C# are implemented using the System.ValueTuple structure, allowing multiple values to be grouped into a single object without creating a separate class. For example, a tuple can be declared as (int, string) person = (1, "Alice"), enabling efficient data handling and return of multiple values from methods. C# 7.0 and later versions provide syntactic support with named elements, enhancing code readability and maintainability in complex applications.
Real-World Applications of Tuples
Tuples are widely used in programming languages like Python and Scala to efficiently store immutable sequences of heterogeneous data, such as geographic coordinates (latitude, longitude) in mapping applications or RGB color values in graphics programming. Their fixed-size, ordered nature enables quick access and prevents accidental modifications, making tuples ideal for managing database records or configuring function parameters. Real-world applications often leverage tuples for compact data representation and improved performance in scenarios like sensor data processing and API response parsing.
Tuple Immutability: Pros and Cons
Tuples in programming languages like Python offer immutability, meaning their elements cannot be altered after creation, providing data integrity and thread safety advantages. This immutability ensures fixed-size and fixed-content collections ideal for use as dictionary keys or constant data sets. However, the inability to modify tuples limits flexibility, requiring creation of new tuples for data updates, which may impact performance in scenarios demanding frequent changes.
Differences Between Tuples and Lists
Tuples in programming are immutable sequences used to store fixed collections of heterogeneous data, differing from lists which are mutable and allow dynamic modification. Unlike lists, tuples offer faster performance and can be used as dictionary keys due to their hashable property. Commonly, languages like Python distinguish tuples with parentheses (e.g., (1, 'apple', 3.5)) while lists use brackets, emphasizing their distinct use cases in data organization and integrity.
Best Practices for Using Tuples in Code
Tuples in programming languages like Python are immutable sequences that efficiently store multiple related values, such as coordinates (x, y) or database records. Best practices for using tuples include leveraging their immutability to ensure data integrity, using them as dictionary keys, and prioritizing readability by clearly documenting the elements contained within each tuple. Avoid excessive tuple nesting and prefer namedtuples or data classes when code clarity and element access by name become important.
example of tuple in programming language Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com