A container in application deployment is a lightweight, standalone, and executable software package that includes everything needed to run an application, such as code, runtime, system tools, and libraries. Docker is one of the most popular containerization platforms widely used to create, deploy, and manage containers. Kubernetes serves as an orchestration system to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, making it an integral technology in modern cloud environments. Containers enable consistent environments across development, testing, and production, enhancing portability and reducing conflicts between different system dependencies. They isolate applications from the underlying infrastructure by packaging the application and its dependencies into a single unit. This encapsulation ensures that containers run reliably on any system that supports containerization, improving scalability and resource efficiency in microservices architectures.
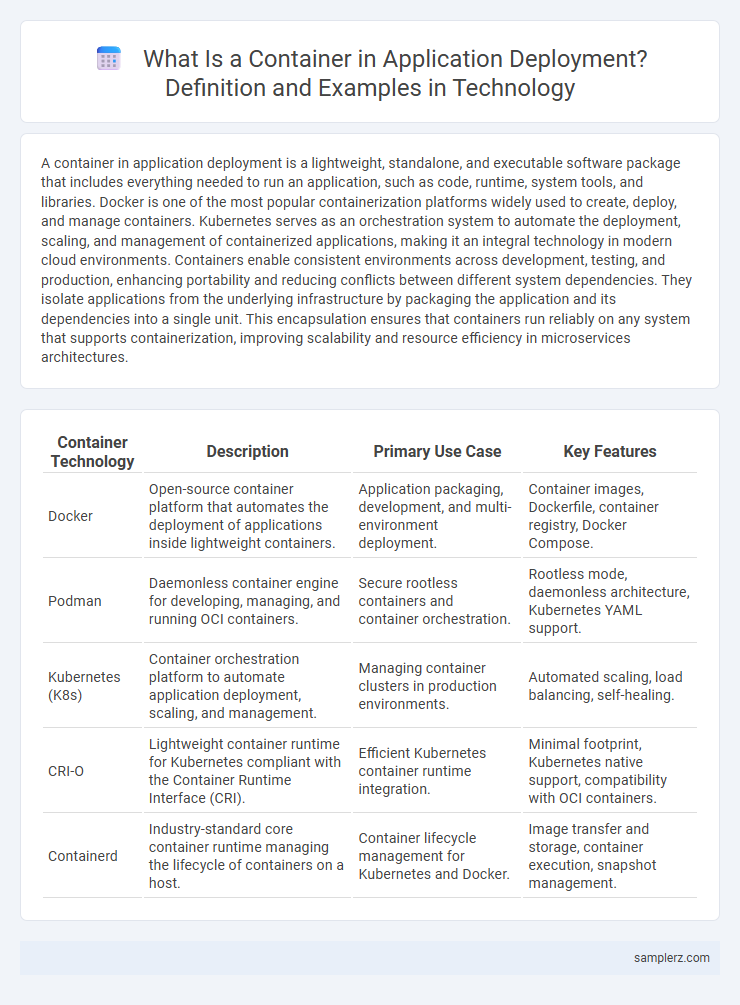
Table of Comparison
| Container Technology | Description | Primary Use Case | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Docker | Open-source container platform that automates the deployment of applications inside lightweight containers. | Application packaging, development, and multi-environment deployment. | Container images, Dockerfile, container registry, Docker Compose. |
| Podman | Daemonless container engine for developing, managing, and running OCI containers. | Secure rootless containers and container orchestration. | Rootless mode, daemonless architecture, Kubernetes YAML support. |
| Kubernetes (K8s) | Container orchestration platform to automate application deployment, scaling, and management. | Managing container clusters in production environments. | Automated scaling, load balancing, self-healing. |
| CRI-O | Lightweight container runtime for Kubernetes compliant with the Container Runtime Interface (CRI). | Efficient Kubernetes container runtime integration. | Minimal footprint, Kubernetes native support, compatibility with OCI containers. |
| Containerd | Industry-standard core container runtime managing the lifecycle of containers on a host. | Container lifecycle management for Kubernetes and Docker. | Image transfer and storage, container execution, snapshot management. |
Introduction to Containers in Application Deployment
Containers, such as Docker, revolutionize application deployment by packaging software with its dependencies into isolated units. These lightweight, portable containers ensure consistent environments across development, testing, and production stages. Kubernetes further optimizes container orchestration, enabling scalable and efficient management of containerized applications.
Key Benefits of Using Containers
Containers, such as Docker, offer lightweight and consistent environments that simplify application deployment across various platforms. They enhance scalability by enabling rapid instance replication and isolation, ensuring optimal resource utilization. Key benefits include faster startup times, improved portability, and streamlined DevOps workflows, which significantly reduce development-to-production cycles.
Popular Container Platforms for Deployment
Docker remains the leading container platform for application deployment, enabling consistent environments across development and production. Kubernetes offers robust orchestration capabilities, managing containerized applications at scale with automated deployment, scaling, and maintenance. Other notable platforms include OpenShift and Amazon ECS, which integrate container management with cloud infrastructure for streamlined DevOps workflows.
Docker: The Leading Container Solution
Docker revolutionizes application deployment by packaging software and its dependencies into portable containers, ensuring consistent environments across development, testing, and production stages. Its lightweight architecture optimizes resource utilization compared to traditional virtual machines, accelerating deployment cycles and scalability. As the leading container solution, Docker integrates seamlessly with orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, enhancing automation and management of complex application infrastructures.
Examples of Containerized Applications
Docker and Kubernetes are prominent examples of container technologies used in application deployment, enabling scalable and portable software environments. Applications like Nginx web servers, Redis databases, and Node.js microservices are commonly containerized for efficient resource utilization and rapid scaling. Containerized applications enhance continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, improving overall development lifecycle agility.
Container Orchestration with Kubernetes
Kubernetes is a leading container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It efficiently schedules containers across clusters, ensuring high availability and resource optimization. Kubernetes supports features like self-healing, load balancing, and automated rollouts, making it essential for modern application deployment.
Microservices Deployment Using Containers
Docker is a prime example of a container technology used in microservices deployment, enabling developers to package applications and their dependencies into isolated, lightweight containers. Kubernetes orchestrates these Docker containers, managing scaling, load balancing, and automated rollouts in microservices architectures. This container-based approach accelerates development cycles, enhances portability, and ensures consistent environments across development, testing, and production stages.
Real-World Use Cases of Container Deployment
Docker containers streamline application deployment by packaging software and its dependencies into isolated environments, enabling consistent performance across development, testing, and production. Kubernetes orchestrates container clusters in large-scale environments, managing load balancing, scaling, and self-healing for microservices architectures. Companies like Spotify utilize container deployment to accelerate continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, enhancing feature rollout speed while maintaining system stability.
Security Considerations in Containerized Environments
Docker containers encapsulate applications and their dependencies, enhancing deployment consistency while introducing unique security challenges such as container escape and image vulnerabilities. Implementing runtime security tools like Aqua Security or Twistlock can monitor container activity and enforce policies to prevent unauthorized access or privilege escalation. Regular scanning of container images for known vulnerabilities and adhering to the principle of least privilege in container configurations significantly reduce attack surfaces in containerized environments.
Future Trends in Container-Based Application Deployment
Kubernetes continues to dominate container orchestration, enabling scalable and efficient deployment of microservices across cloud environments. Emerging trends highlight the integration of AI-powered automation to optimize resource allocation and security in containerized applications. Serverless container platforms like AWS Fargate are gaining traction, reducing infrastructure management complexity while enhancing deployment agility.
example of container in application deployment Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com