Dark fiber refers to unused optical fiber cables that are installed but not currently active for data transmission. In backbone networks, these dark fibers provide a cost-effective and scalable infrastructure for expanding capacity without laying new cables. Companies lease or purchase dark fiber to establish private, high-speed connections between data centers and network hubs. An example of dark fiber in a backbone network is the extensive fiber optic infrastructure developed by major telecommunications companies like Level 3 Communications. Their network includes thousands of miles of dark fiber, enabling clients to light these fibers for ultra-fast, dedicated bandwidth tailored to specific enterprise needs. This approach enhances network flexibility, reduces latency, and supports high-volume data transfer across metropolitan and long-haul routes.
Table of Comparison
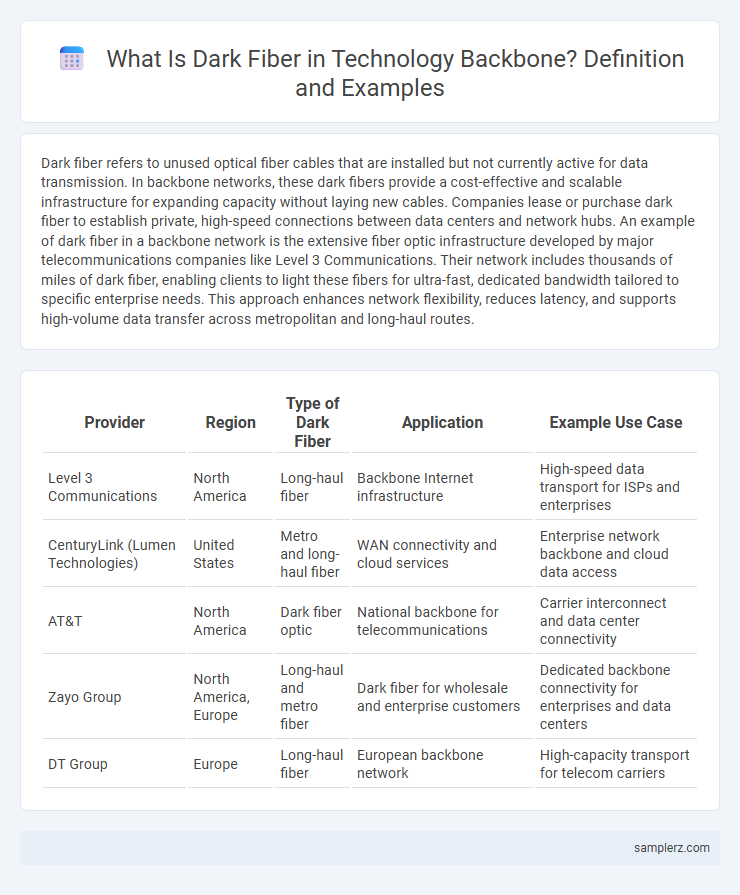
| Provider | Region | Type of Dark Fiber | Application | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 3 Communications | North America | Long-haul fiber | Backbone Internet infrastructure | High-speed data transport for ISPs and enterprises |
| CenturyLink (Lumen Technologies) | United States | Metro and long-haul fiber | WAN connectivity and cloud services | Enterprise network backbone and cloud data access |
| AT&T | North America | Dark fiber optic | National backbone for telecommunications | Carrier interconnect and data center connectivity |
| Zayo Group | North America, Europe | Long-haul and metro fiber | Dark fiber for wholesale and enterprise customers | Dedicated backbone connectivity for enterprises and data centers |
| DT Group | Europe | Long-haul fiber | European backbone network | High-capacity transport for telecom carriers |
Understanding Dark Fiber in Backbone Networks
Dark fiber refers to unused optical fiber cables that form an essential part of backbone networks, providing vast potential bandwidth for high-speed data transmission. Telecommunications companies or large enterprises lease or purchase dark fiber to build customizable, scalable networks that support increasing traffic and future technological demands. Leveraging dark fiber enables control over network architecture, reduces latency, and enhances security by avoiding shared infrastructure with third-party providers.
Key Benefits of Using Dark Fiber for Backbone Infrastructure
Dark fiber in backbone infrastructure offers unparalleled bandwidth capacity, enabling businesses to scale their network performance without the limitations of leased lines. The dedicated nature of dark fiber ensures enhanced security and low latency, critical for data-intensive applications and real-time communications. Additionally, leveraging dark fiber reduces long-term operational costs by eliminating recurring leasing fees and providing greater control over network configurations.
Real-World Examples of Dark Fiber Backbone Deployments
Dark fiber backbone deployments include Google's private fiber network connecting data centers across the United States, enabling ultra-low latency and high-capacity data transfer. Level 3 Communications operates an extensive dark fiber backbone that supports global IP transit services, enhancing network reliability and scalability. Facebook's use of dark fiber in its backbone infrastructure improves bandwidth efficiency and supports rapid data exchange between its international data centers.
Major Telecom Providers Leveraging Dark Fiber Backbones
Major telecom providers such as AT&T, Verizon, and CenturyLink leverage dark fiber backbones to enhance network capacity and reliability. These companies utilize dark fiber infrastructure to support high-speed data transmission, enabling scalable bandwidth for expanding 5G networks and cloud services. By deploying dark fiber, providers achieve greater control over their network architecture, reducing dependence on leased lines and lowering operational costs.
Private Enterprises Using Dark Fiber for Backbone Connectivity
Private enterprises increasingly utilize dark fiber for backbone connectivity to achieve enhanced control, security, and scalability in their network infrastructure. By leasing or owning dark fiber, companies can customize bandwidth capacity, reduce latency, and support high-volume data transmission critical for cloud computing, data centers, and real-time applications. Major technology firms and financial institutions leverage dark fiber networks to maintain competitive advantages and ensure reliable, high-speed communications across multiple sites.
Municipal Networks Employing Dark Fiber in Their Backbone
Municipal networks frequently utilize dark fiber in their backbone infrastructure to enhance bandwidth capacity and reduce latency for public services. Cities like Chattanooga, Tennessee, have successfully deployed dark fiber backbones to provide high-speed connectivity, enabling smart city applications and economic development. Leveraging dark fiber allows these municipal networks to maintain control over their broadband infrastructure while supporting extensive data transmission needs.
Educational and Research Institutions with Dark Fiber Backbones
Educational and research institutions often deploy dark fiber backbones to ensure high-speed, low-latency connectivity essential for data-intensive projects and collaboration. For example, the Internet2 network in the United States connects universities and research centers using dark fiber, enabling terabit-level data transfers and advanced networking capabilities. This infrastructure supports large-scale scientific research, cloud computing, and real-time data sharing among academic communities worldwide.
Upgrading Legacy Backbones with Dark Fiber Solutions
Upgrading legacy network backbones with dark fiber solutions significantly enhances bandwidth capacity and reduces latency for enterprise data centers and internet service providers. Deploying dark fiber enables organizations to leverage unused optical fibers for scalable, high-speed connectivity tailored to evolving network demands. This approach ensures cost-effective infrastructure modernization, supporting next-generation applications like 5G, cloud computing, and IoT without the need for extensive physical fiber installation.
Dark Fiber Backbone in Data Center Interconnects
Dark fiber backbone in data center interconnects provides dedicated, high-capacity optical fibers that enable secure, low-latency communication between geographically dispersed data centers. These unused fibers offer scalable bandwidth to support massive data transfers and enhance network resilience without relying on third-party carriers. Enterprises leverage dark fiber backbones to achieve maximum control over their data traffic and future-proof infrastructure for growing cloud and edge computing demands.
Future Trends in Dark Fiber Backbone Implementations
Future trends in dark fiber backbone implementations highlight increased adoption of AI-driven network management for real-time optimization and predictive maintenance. Integration of quantum-safe encryption protocols is becoming essential to ensure data security in next-generation backbones. Expansion of 5G and edge computing relies heavily on scalable dark fiber infrastructure to support ultra-low latency and high bandwidth demands.
example of darkfiber in backbone Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com