An air gap is a cybersecurity measure where a computer or network is physically isolated from unsecured networks, such as the internet, to prevent unauthorized access. This method ensures that sensitive data remains protected by eliminating any direct digital connection that hackers could exploit. Organizations handling classified information often use air-gapped systems to store and process critical data safely. In data security, air gaps are commonly employed in environments requiring the highest level of protection, such as government agencies and financial institutions. These systems operate without network interfaces or USB ports, minimizing the risk of data breaches through external devices or remote access. Air-gapped networks also support secure backups by isolating copies of data from potential malware or cyberattacks affecting connected networks.
Table of Comparison
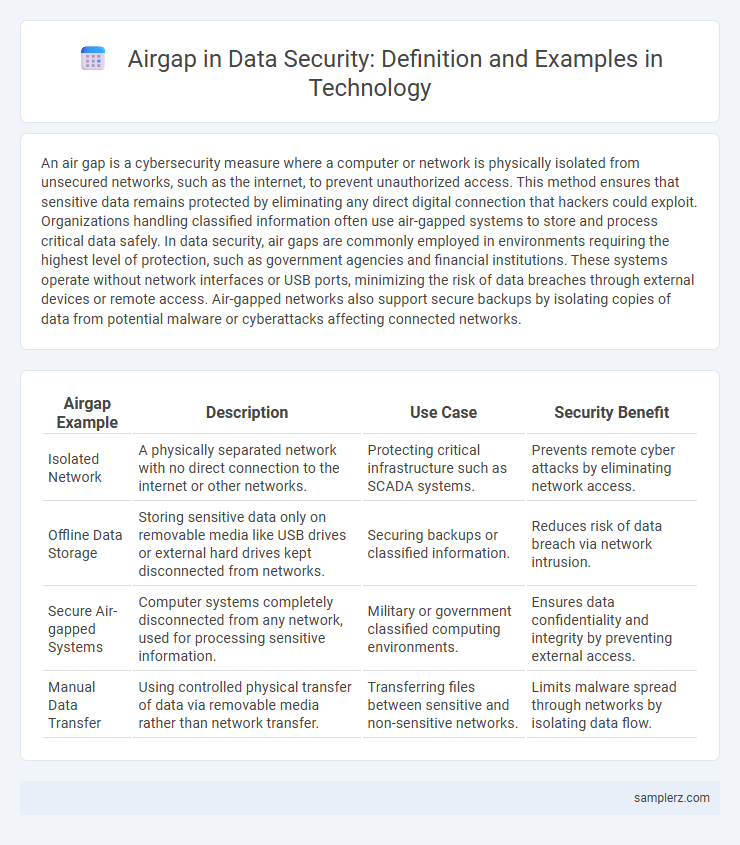
| Airgap Example | Description | Use Case | Security Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isolated Network | A physically separated network with no direct connection to the internet or other networks. | Protecting critical infrastructure such as SCADA systems. | Prevents remote cyber attacks by eliminating network access. |
| Offline Data Storage | Storing sensitive data only on removable media like USB drives or external hard drives kept disconnected from networks. | Securing backups or classified information. | Reduces risk of data breach via network intrusion. |
| Secure Air-gapped Systems | Computer systems completely disconnected from any network, used for processing sensitive information. | Military or government classified computing environments. | Ensures data confidentiality and integrity by preventing external access. |
| Manual Data Transfer | Using controlled physical transfer of data via removable media rather than network transfer. | Transferring files between sensitive and non-sensitive networks. | Limits malware spread through networks by isolating data flow. |
Understanding Airgap: Defining the Concept in Data Security
Airgap in data security refers to the physical isolation of a computer or network from unsecured external connections, ensuring no direct or wireless communication links exist between the secure system and outside networks. This method is critical in protecting highly sensitive data from cyber threats by eliminating potential entry points for hackers and malware. Used extensively in government, defense, and critical infrastructure sectors, airgapped systems provide a robust security layer by preventing unauthorized access and data exfiltration.
How Airgap Enhances Data Protection
Airgap enhances data protection by physically isolating critical systems from unsecured networks, preventing unauthorized access and cyberattacks. This isolation creates a barrier that stops malware propagation and unauthorized data transfers, ensuring sensitive information remains secure. Organizations handling classified or proprietary data leverage airgapped environments to maintain the highest level of data integrity and confidentiality.
Physical vs. Logical Airgap: Key Differences
Physical airgaps in data security involve completely isolating a system by ensuring no physical connection to unsecured networks, such as removing wired or wireless connections, while logical airgaps use software-based methods like firewalls and access controls to create virtual separation within connected systems. Physical airgaps provide a higher level of security against remote threats by preventing any network communication, whereas logical airgaps offer flexibility but rely on software integrity and configurations that might be vulnerable to sophisticated cyberattacks. Industries handling classified or sensitive data, such as military and critical infrastructure, often employ physical airgaps to guarantee absolute isolation from external networks, contrasting with enterprises that implement logical airgaps for operational efficiency combined with controlled security measures.
Real-World Applications of Airgap in Enterprises
Airgapped networks are widely implemented in enterprises to protect sensitive data by physically isolating critical systems from unsecured networks, preventing unauthorized access and cyber threats. Financial institutions often use airgaps to secure transaction processing systems, ensuring that confidential financial records remain inaccessible from the internet. Government agencies employ airgapped environments to safeguard classified information, maintaining strict separation between classified networks and external communication infrastructures.
Airgap Solutions for Critical Infrastructure
Airgap solutions for critical infrastructure isolate sensitive systems by physically disconnecting them from unsecured networks, effectively preventing cyber threats and unauthorized access. These implementations are prevalent in power grids, nuclear facilities, and water treatment plants where data integrity and operational continuity are paramount. Advanced airgap technologies integrate encrypted data transfer protocols via removable media and hardware firewalls to ensure secure offline environments.
Case Study: Airgapped Networks in Financial Institutions
Financial institutions implement airgapped networks to enhance data security by isolating critical systems from external internet connections, effectively preventing cyberattacks and unauthorized data access. A prominent case study involves a major bank that deployed airgapped environments for transaction processing, ensuring sensitive financial data remains protected from ransomware and malware threats. This strategic separation of networks demonstrates robust defense mechanisms essential for compliance with regulatory standards and risk mitigation in the finance sector.
Using Airgap for Secure Backup and Disaster Recovery
Using airgap technology for secure backup ensures critical data remains physically isolated from network connections, preventing unauthorized access and cyberattacks. This method involves storing backup copies on devices disconnected from the main system, which significantly reduces ransomware and malware risks during disaster recovery. Airgapped backups provide a reliable fail-safe, enabling organizations to restore data swiftly and maintain business continuity after system breaches or failures.
Airgap Implementation: Best Practices and Considerations
Airgap implementation in data security involves physically isolating critical systems from unsecured networks to prevent cyber threats and data breaches. Best practices include ensuring strict physical controls, regularly auditing the isolated environment, and maintaining updated, offline security protocols. Considerations should focus on balancing security with operational efficiency by carefully planning data transfer procedures and minimizing human error.
Limitations and Challenges of Airgap in Cybersecurity
Airgaps in cybersecurity create physical isolation between secure networks and external systems, reducing exposure to remote cyber threats. However, limitations include difficulty managing updates and patching without risking human error or introducing malware via removable media. Challenges also arise from insider threats, data exfiltration through electromagnetic emissions, and limited scalability in dynamic, cloud-integrated environments.
Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Airgap in Data Security
The future of airgap technology in data security centers on integrating AI-driven anomaly detection to enhance threat identification within isolated networks. Quantum encryption methods are poised to complement airgaps by securing data transfers in critical infrastructure systems. Emerging trends indicate that hybrid architectures combining airgaps with blockchain verification will set new standards for protecting sensitive information against sophisticated cyberattacks.
example of airgap in data security Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com