A femtocell is a small, low-power cellular base station typically used to improve indoor mobile coverage. In telecommunication, companies like Verizon deploy femtocells to enhance signal strength in homes and small businesses, providing better voice and data connectivity. These devices connect to the service provider's network through broadband internet, ensuring seamless integration with existing cellular infrastructure. Femtocells support multiple mobile users simultaneously, often up to 16, by creating a personal cell tower within a limited range of about 10 meters. Entities such as AT&T and T-Mobile utilize femtocells to offload traffic from macrocell networks, thereby optimizing overall network performance. Data from femtocell usage helps service providers identify areas of weak coverage and improve customer experience by minimizing dropped calls and boosting data speeds.
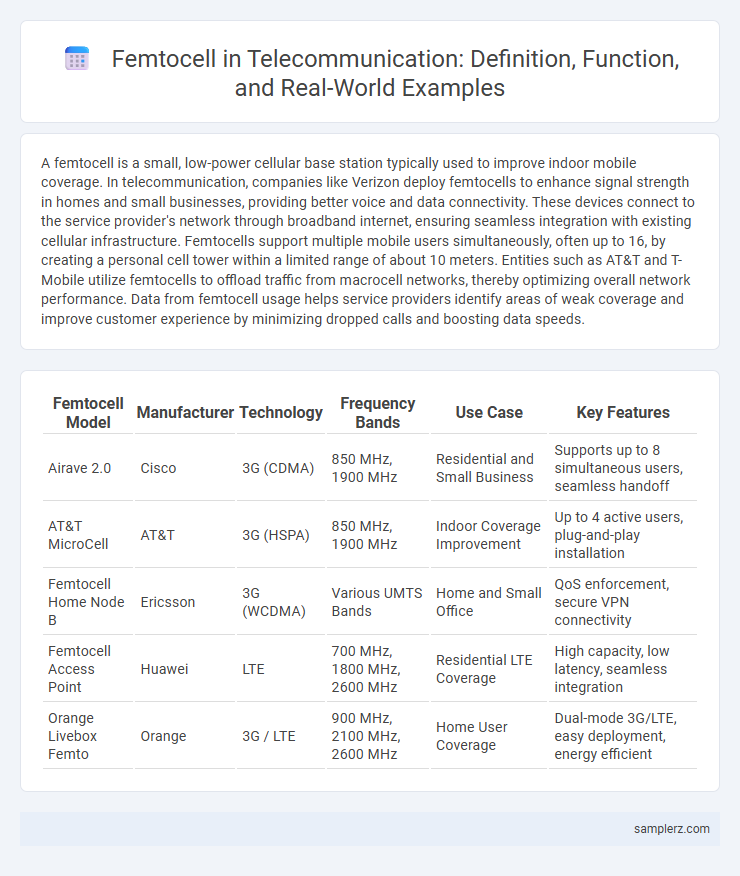
Table of Comparison
| Femtocell Model | Manufacturer | Technology | Frequency Bands | Use Case | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airave 2.0 | Cisco | 3G (CDMA) | 850 MHz, 1900 MHz | Residential and Small Business | Supports up to 8 simultaneous users, seamless handoff |
| AT&T MicroCell | AT&T | 3G (HSPA) | 850 MHz, 1900 MHz | Indoor Coverage Improvement | Up to 4 active users, plug-and-play installation |
| Femtocell Home Node B | Ericsson | 3G (WCDMA) | Various UMTS Bands | Home and Small Office | QoS enforcement, secure VPN connectivity |
| Femtocell Access Point | Huawei | LTE | 700 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2600 MHz | Residential LTE Coverage | High capacity, low latency, seamless integration |
| Orange Livebox Femto | Orange | 3G / LTE | 900 MHz, 2100 MHz, 2600 MHz | Home User Coverage | Dual-mode 3G/LTE, easy deployment, energy efficient |
Introduction to Femtocell Technology in Telecommunications
Femtocell technology in telecommunications involves small cellular base stations designed to improve indoor mobile signal quality by connecting to a user's broadband internet. These low-power femtocells enhance network capacity and coverage in homes or small offices, reducing dead zones and offloading traffic from macrocell towers. Leading telecom operators deploy femtocells to optimize spectrum efficiency and provide seamless 4G and 5G connectivity in challenging indoor environments.
Key Features of Femtocells
Femtocells in telecommunication enhance indoor cellular coverage by creating a small, low-power cellular base station connected via broadband internet. Key features include improved signal quality, reduced network congestion, seamless handover between macro and femtocell networks, and support for multiple simultaneous users. These devices optimize network capacity and energy efficiency while providing secure, localized voice and data communications.
How Femtocells Work: Technical Overview
Femtocells are small, low-power cellular base stations designed to improve indoor mobile coverage by connecting to a user's broadband internet. They operate by creating a localized 3G, 4G, or 5G signal, transmitting and receiving mobile signals to nearby devices while routing communications through internet protocols to the cellular operator's core network. This setup reduces macrocell network congestion and enhances call quality and data speeds in residential or small office environments.
Real-World Applications of Femtocells
Femtocells significantly enhance indoor cellular coverage by creating small, low-power cellular base stations that connect users to the mobile network through broadband internet. They are widely deployed in residential homes and office buildings to improve signal quality, reduce dropped calls, and offload traffic from macrocell networks. Telecommunication providers like AT&T and Vodafone leverage femtocells to boost network capacity and deliver seamless voice and data services in areas with weak macrocell signals.
Leading Femtocell Products and Manufacturers
Leading femtocell products in telecommunication include Nokia's Flexi Multiradio Micro and Cisco's Small Cell portfolio, both delivering enhanced indoor coverage and high-capacity cellular connectivity. Manufacturers like Huawei and Ericsson dominate the market with their advanced femtocell solutions, integrating seamless 4G and 5G support for residential and enterprise applications. These products optimize network performance by mitigating macrocell congestion and improving user experience through localized signal enhancement.
Femtocell Deployment in Home and Enterprise Environments
Femtocell deployment in home and enterprise environments enhances cellular coverage by creating small, low-power base stations that connect to the service provider's network via broadband. These devices improve indoor voice and data quality, reduce network congestion, and support seamless handovers between macrocell and femtocell networks. Leading telecom operators deploy femtocells to optimize network capacity, improve user experience, and enable cost-effective expansions in both residential and corporate settings.
Use Cases: Femtocell Solutions for Urban and Rural Areas
Femtocell technology enhances mobile network coverage by providing localized, low-power cellular signals in both urban and rural environments. In urban areas, femtocells address indoor signal weaknesses caused by dense building structures, boosting data speeds and call quality for users inside high-rise apartments and commercial complexes. In rural regions, femtocells extend cellular service to remote locations with limited macrocell coverage, improving connectivity for residents and supporting emergency communication needs.
Advantages of Using Femtocells in Telecom Networks
Femtocells enhance telecom networks by significantly improving indoor coverage and boosting signal strength, which leads to fewer dropped calls and better voice quality. They reduce network congestion by offloading traffic from macrocells, enhancing overall network capacity and user experience. Energy efficiency is improved as femtocells consume less power compared to traditional base stations, supporting sustainable telecom infrastructure.
Challenges and Limitations of Femtocell Adoption
Femtocell adoption in telecommunication faces challenges such as interference management with macrocell networks, leading to signal degradation and user experience issues. Security concerns arise from the increased vulnerability to cyber-attacks within private residential environments. Limited backhaul capacity and regulatory constraints further restrict widespread femtocell deployment, impacting overall network efficiency.
Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Femtocells in 5G and Beyond
Femtocells are becoming integral to 5G networks by enhancing indoor coverage and reducing network congestion through small, low-power cellular base stations. Future trends indicate their evolution towards supporting massive MIMO and AI-driven self-optimization for seamless connectivity in smart homes and IoT ecosystems. Their deployment is poised to expand in ultra-dense networks, enabling ultra-reliable low-latency communication essential for next-generation telecommunication applications.
example of femtocell in telecommunication Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com