Heuristics in antivirus software refers to a technique used to detect previously unknown viruses and malware by analyzing code behavior and patterns. Antivirus programs use heuristic algorithms to identify suspicious files based on their attributes, such as unusual file size, code structure, and commands. This method allows the software to flag potential threats without relying solely on known virus definitions. Heuristic analysis focuses on behavioral patterns and code similarities to detect zero-day exploits and polymorphic malware variants. By simulating the execution of a file in a controlled environment, heuristics can monitor actions like file modification, system registry changes, or network communications. This proactive detection mechanism enhances cybersecurity by identifying threats before they are added to signature databases.
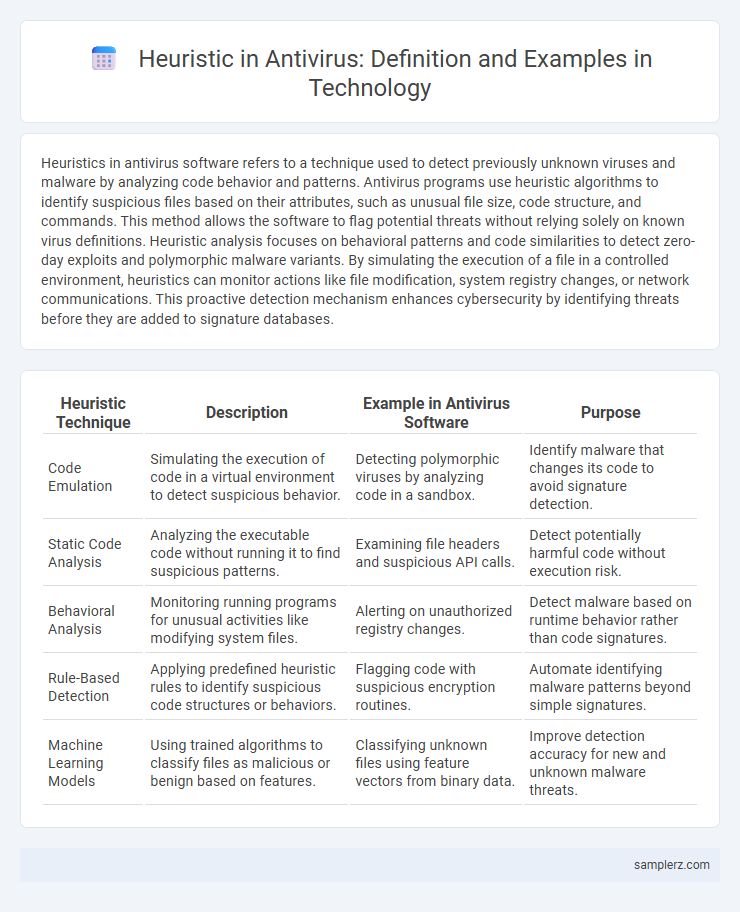
Table of Comparison
| Heuristic Technique | Description | Example in Antivirus Software | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code Emulation | Simulating the execution of code in a virtual environment to detect suspicious behavior. | Detecting polymorphic viruses by analyzing code in a sandbox. | Identify malware that changes its code to avoid signature detection. |
| Static Code Analysis | Analyzing the executable code without running it to find suspicious patterns. | Examining file headers and suspicious API calls. | Detect potentially harmful code without execution risk. |
| Behavioral Analysis | Monitoring running programs for unusual activities like modifying system files. | Alerting on unauthorized registry changes. | Detect malware based on runtime behavior rather than code signatures. |
| Rule-Based Detection | Applying predefined heuristic rules to identify suspicious code structures or behaviors. | Flagging code with suspicious encryption routines. | Automate identifying malware patterns beyond simple signatures. |
| Machine Learning Models | Using trained algorithms to classify files as malicious or benign based on features. | Classifying unknown files using feature vectors from binary data. | Improve detection accuracy for new and unknown malware threats. |
Understanding Heuristics: The Core of Modern Antivirus
Heuristic analysis in antivirus software employs behavior-based detection methods to identify unknown malware by examining code patterns and actions that resemble malicious activity. By simulating program execution in a controlled environment, heuristics detect potential threats before signature databases are updated, enhancing proactive defense. This approach enables the identification of zero-day exploits and polymorphic viruses, providing crucial protection against emerging cyber threats.
Real-World Heuristic Detection Scenarios
Heuristic detection in antivirus software analyzes code patterns and behaviors to identify unknown malware by simulating suspicious actions, such as unexpected file modifications or unauthorized network connections. Real-world heuristic scenarios include detecting polymorphic viruses that evade signature-based detection by continually changing their code, ensuring early threat identification. This proactive approach enhances cybersecurity by preventing zero-day exploits and minimizing false negatives in threat detection.
How Antivirus Uses Heuristics to Uncover Zero-Day Threats
Antivirus software employs heuristic analysis by examining code behavior and suspicious patterns to identify zero-day threats before signature databases are updated. This technique leverages algorithms that detect anomalies and potential malware traits, such as code obfuscation or unusual system calls. By continuously analyzing unknown files in real time, heuristics enable proactive defense against emerging cyber threats.
Behavioral Analysis: A Key Heuristic Approach
Behavioral analysis in antivirus software detects malicious activity by monitoring program behavior and system changes rather than relying solely on signature databases. This heuristic approach identifies malware based on suspicious patterns such as unauthorized file modifications, unusual network traffic, or abnormal CPU usage. By analyzing runtime behavior, behavioral heuristics provide proactive protection against zero-day threats and polymorphic viruses.
Signature-Based Detection vs. Heuristic Methods
Signature-based detection identifies malware by matching known virus signatures stored in a database, providing fast and accurate recognition of previously encountered threats. Heuristic methods analyze suspicious behavior and code patterns to detect new or modified malware that lacks existing signatures, enhancing protection against zero-day exploits. Combining both approaches optimizes antivirus efficiency by balancing precise detection with proactive threat identification.
Popular Heuristic Algorithms in Leading Antivirus Solutions
Popular heuristic algorithms in leading antivirus solutions include pattern recognition, behavior monitoring, and code analysis techniques. These algorithms detect unknown malware by analyzing suspicious code snippets, unusual system behavior, and file structures that deviate from known safe baselines. Examples include Kaspersky's heuristic engine, Norton's SONAR technology, and Bitdefender's Advanced Heuristics, all effectively identifying zero-day threats through proactive scanning.
Case Study: Heuristic Identification of Polymorphic Malware
Heuristic identification in antivirus software analyzes code behavior and structure to detect polymorphic malware that frequently changes its signature to evade traditional signature-based detection methods. In a case study, heuristic algorithms successfully identified polymorphic threats by recognizing suspicious encryption routines, code obfuscation patterns, and anomalous execution flows, enabling early detection before signature updates are available. This proactive approach improves malware defense by dynamically adapting to evolving threats without relying solely on known samples.
Advantages and Limitations of Heuristic Techniques
Heuristic techniques in antivirus software enable the detection of previously unknown malware by analyzing code behavior and suspicious patterns, improving early threat identification and reducing reliance on signature databases. These methods enhance protection against zero-day attacks and polymorphic viruses but may generate false positives, leading to occasional misidentification of benign files as malicious. Performance impact on system resources and the need for continuous tuning of heuristic algorithms are key limitations that affect overall efficiency and accuracy.
False Positives: Managing Heuristic Detection in Antivirus
Heuristic detection in antivirus software uses behavior-based algorithms to identify potential threats by analyzing code patterns rather than relying solely on known virus signatures. This approach improves the discovery of new or polymorphic malware but often results in false positives, where benign files are mistakenly flagged as malicious. Effective management of false positives involves tuning heuristic sensitivity, implementing whitelist schemes, and regularly updating heuristic rules to balance detection accuracy and system performance.
The Future of Heuristics in Cybersecurity
Heuristic algorithms in antivirus software analyze behavior patterns to detect unknown malware, significantly enhancing threat identification beyond signature-based methods. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning are driving the evolution of heuristic models, enabling real-time adaptive defense against sophisticated cyberattacks. The future of heuristics in cybersecurity promises more proactive and predictive threat mitigation, reducing false positives while improving detection accuracy.
example of heuristic in antivirus Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com