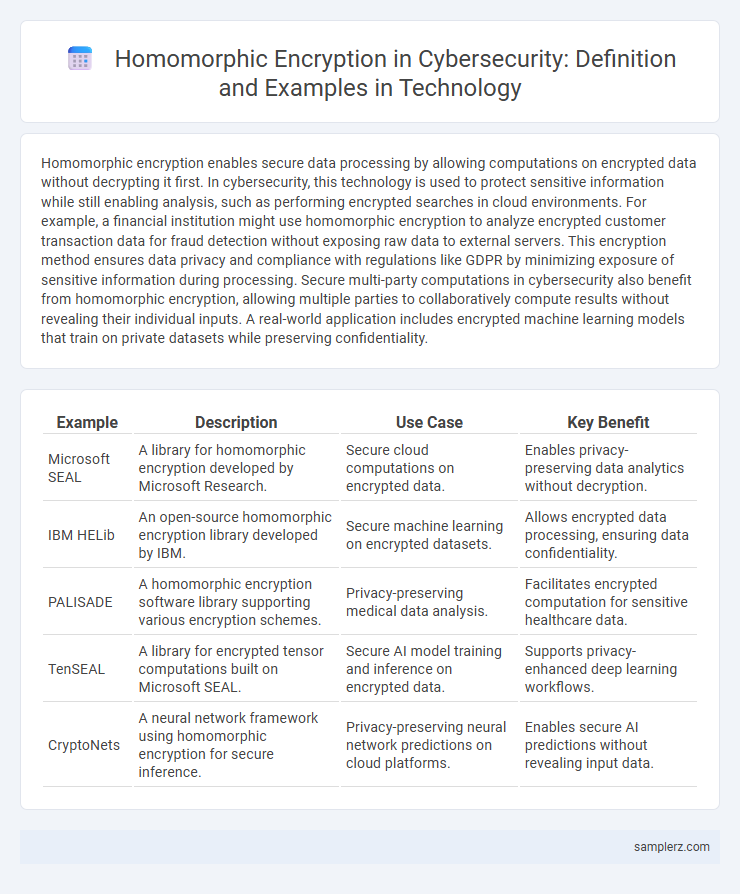
Homomorphic encryption enables secure data processing by allowing computations on encrypted data without decrypting it first. In cybersecurity, this technology is used to protect sensitive information while still enabling analysis, such as performing encrypted searches in cloud environments. For example, a financial institution might use homomorphic encryption to analyze encrypted customer transaction data for fraud detection without exposing raw data to external servers. This encryption method ensures data privacy and compliance with regulations like GDPR by minimizing exposure of sensitive information during processing. Secure multi-party computations in cybersecurity also benefit from homomorphic encryption, allowing multiple parties to collaboratively compute results without revealing their individual inputs. A real-world application includes encrypted machine learning models that train on private datasets while preserving confidentiality.
Table of Comparison
| Example | Description | Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft SEAL | A library for homomorphic encryption developed by Microsoft Research. | Secure cloud computations on encrypted data. | Enables privacy-preserving data analytics without decryption. |
| IBM HELib | An open-source homomorphic encryption library developed by IBM. | Secure machine learning on encrypted datasets. | Allows encrypted data processing, ensuring data confidentiality. |
| PALISADE | A homomorphic encryption software library supporting various encryption schemes. | Privacy-preserving medical data analysis. | Facilitates encrypted computation for sensitive healthcare data. |
| TenSEAL | A library for encrypted tensor computations built on Microsoft SEAL. | Secure AI model training and inference on encrypted data. | Supports privacy-enhanced deep learning workflows. |
| CryptoNets | A neural network framework using homomorphic encryption for secure inference. | Privacy-preserving neural network predictions on cloud platforms. | Enables secure AI predictions without revealing input data. |
Introduction to Homomorphic Encryption in Cybersecurity
Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, ensuring data privacy during processing. In cybersecurity, this technology allows secure data analysis and threat detection in encrypted environments, minimizing exposure to attacks. Practical applications include secure multi-party computations and privacy-preserving cloud services, where sensitive information remains protected throughout processing.
Key Advantages of Homomorphic Encryption for Data Protection
Homomorphic encryption enables performing computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, significantly enhancing data confidentiality in cybersecurity. This technology allows secure data sharing and processing in cloud environments, reducing exposure to breaches while maintaining privacy. Key advantages include preserving data integrity, supporting compliance with regulations like GDPR, and enabling secure multi-party computations.
Secure Cloud Computing: Homomorphic Encryption in Action
Homomorphic encryption enables secure cloud computing by allowing encrypted data to be processed without decryption, preserving data confidentiality throughout computation. Companies like IBM and Microsoft leverage this technology to perform encrypted data analytics and machine learning on cloud platforms, ensuring user privacy. This approach mitigates risks of data breaches and enhances compliance with stringent data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Financial Services: Protecting Transactions with Homomorphic Encryption
Financial services leverage homomorphic encryption to secure sensitive transaction data by enabling computations on encrypted information without exposing raw data. This technology enhances fraud detection and risk assessment while maintaining customer privacy during real-time processing. By allowing encrypted data analysis, financial institutions reduce the risk of data breaches and comply with strict regulatory requirements.
Healthcare Data Security Using Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption enables secure processing of sensitive healthcare data by allowing computations on encrypted medical records without exposing patient information. This technology ensures privacy compliance while facilitating advanced analytics for diagnosis and treatment planning. Hospitals and research institutions leverage homomorphic encryption to protect Electronic Health Records (EHRs) against data breaches during cloud-based analysis.
Encrypted Search: Real-World Applications in Cybersecurity
Encrypted search leveraging homomorphic encryption enables cybersecurity systems to perform queries on encrypted data without decrypting it, preserving data confidentiality during threat analysis. Real-world applications include secure email filtering, where spam detection algorithms analyze encrypted messages without exposing sensitive content. This technology significantly enhances privacy-preserving data mining in intrusion detection systems by allowing encrypted pattern recognition and anomaly detection.
Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning with Homomorphic Encryption
Privacy-preserving machine learning leverages homomorphic encryption to enable data analysis on encrypted datasets without exposing sensitive information. This cryptographic technique allows models to train and infer on ciphertext, ensuring that raw data remains confidential even in untrusted environments. Applications in cybersecurity include secure threat detection and anomaly identification while maintaining stringent privacy standards.
Challenges and Limitations of Homomorphic Encryption in Practice
Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without decryption, enhancing data privacy in cybersecurity. However, significant challenges include high computational overhead and latency, which hinder real-time processing and scalability. Limited support for complex operations and increased ciphertext size further restrict its practical deployment in large-scale cybersecurity applications.
Homomorphic Encryption in Compliance and Regulatory Environments
Homomorphic encryption enables secure data processing in compliance and regulatory environments by allowing computations on encrypted data without exposing sensitive information. Financial institutions utilize this technology to perform risk assessments and fraud detection while adhering to GDPR and HIPAA regulations. This approach reduces data breach risks and ensures that organizations maintain strict data privacy standards during analysis.
Future Trends of Homomorphic Encryption in Cyber Defense
Homomorphic encryption enables secure data processing on encrypted information without decryption, revolutionizing cybersecurity by protecting sensitive data during analysis. Future trends include the integration of quantum-resistant algorithms to enhance encryption robustness against emerging quantum threats. Increased adoption of cloud-based homomorphic encryption solutions will drive real-time, privacy-preserving threat detection and response in cyber defense systems.
example of homomorphic encryption in cybersecurity Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com