A notable example of a botnet used in cyberattacks is the Mirai botnet, which emerged in 2016. Mirai primarily targeted Internet of Things (IoT) devices by exploiting default login credentials, leading to one of the largest distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks in history. This botnet harnessed hundreds of thousands of compromised devices to overwhelm websites and online services, causing significant disruptions. Another prominent case involves the Emotet botnet, initially designed as a banking Trojan but later evolved into a modular botnet used for distributing malware and ransomware. Emotet infected millions of computers worldwide by leveraging email phishing campaigns and malicious attachments. The control infrastructure of the Emotet botnet allowed cybercriminals to orchestrate large-scale cyberattacks, stealing sensitive financial data and personal information.
Table of Comparison
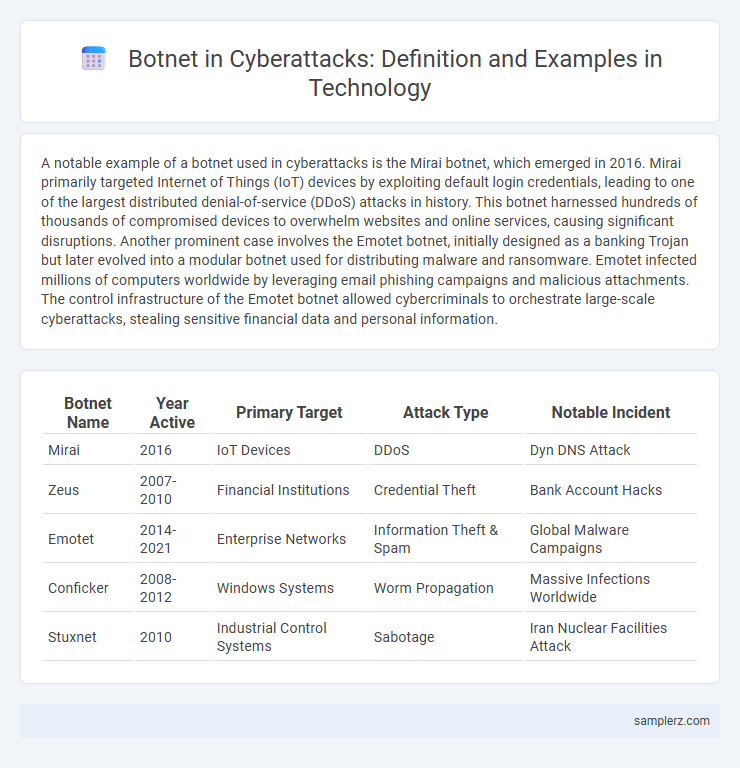
| Botnet Name | Year Active | Primary Target | Attack Type | Notable Incident |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mirai | 2016 | IoT Devices | DDoS | Dyn DNS Attack |
| Zeus | 2007-2010 | Financial Institutions | Credential Theft | Bank Account Hacks |
| Emotet | 2014-2021 | Enterprise Networks | Information Theft & Spam | Global Malware Campaigns |
| Conficker | 2008-2012 | Windows Systems | Worm Propagation | Massive Infections Worldwide |
| Stuxnet | 2010 | Industrial Control Systems | Sabotage | Iran Nuclear Facilities Attack |
Notorious Botnet Attacks in Cybersecurity History
The Mirai botnet, infamous for launching massive Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks in 2016, exploited insecure Internet of Things (IoT) devices to disrupt major websites like Twitter, Netflix, and Reddit. Another notorious example is the Zeus botnet, which targeted financial institutions by stealing sensitive banking credentials through sophisticated malware. Conficker, a worm-based botnet from 2008, infected millions of Windows computers worldwide, demonstrating the scale and persistence of cyber threats in cybersecurity history.
The Mirai Botnet: Disrupting the Internet of Things
The Mirai Botnet represents a significant cyberattack targeting Internet of Things (IoT) devices by co-opting thousands of unsecured smart gadgets to perform massive distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Exploiting default credentials on routers, cameras, and DVRs, Mirai overwhelmed key internet infrastructure, including major DNS providers, disrupting service for millions of users worldwide. Its architecture demonstrated the vulnerabilities inherent in IoT ecosystems, emphasizing the critical need for improved device security and firmware updates.
Emotet: The Banking Trojan Turned Botnet
Emotet, originally a banking Trojan designed to steal financial information, has evolved into a sophisticated botnet used for large-scale cyberattacks. This malware spreads through malicious email attachments and employs modular payloads to deliver ransomware, steal data, and distribute additional malware. Emotet's infrastructure enables attackers to control thousands of infected devices globally, amplifying the scale and impact of coordinated cyber threats.
The Avalanche Botnet Network: Global Malware Distribution
The Avalanche Botnet Network operated as a notorious cybercriminal infrastructure responsible for distributing malware globally, infecting millions of computers across more than 180 countries. It enabled cyberattacks such as banking fraud, ransomware campaigns, and phishing schemes by controlling vast numbers of compromised devices in a highly coordinated manner. Law enforcement agencies dismantled Avalanche in a landmark operation, disrupting one of the most significant botnet networks influencing global cybersecurity threats.
Conficker Worm: A Persistent Botnet Threat
The Conficker Worm exemplifies a persistent botnet threat that infected millions of computers worldwide by exploiting Windows vulnerabilities to create a vast network of compromised devices. This malware enabled cybercriminals to execute large-scale attacks, distribute additional malware, and steal sensitive information. Its resilience and rapid propagation highlight the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures and timely patch management.
Necurs Botnet: Spamming and Ransomware Campaigns
Necurs Botnet remains one of the largest and most persistent botnets, primarily known for orchestrating extensive spamming campaigns distributing malicious emails. It facilitates ransomware attacks by delivering payloads such as Locky and GlobeImposter, causing significant financial and data losses worldwide. The botnet's resilience and ability to evade detection make it a critical threat in cybersecurity.
Zeus Botnet: Targeting Financial Institutions
Zeus Botnet is a notorious example of a cyberattack targeting financial institutions by stealing banking credentials and enabling unauthorized wire transfers. This malware operates through Trojan horse techniques, infiltrating systems via phishing emails and malicious downloads. Its sophisticated command-and-control infrastructure allows cybercriminals to execute large-scale financial fraud and data theft.
GameOver Zeus: Evolution of a Sophisticated Botnet
GameOver Zeus represents a sophisticated evolution of botnet technology, primarily targeting financial institutions and personal computers to steal sensitive information. Its decentralized peer-to-peer architecture enhances resilience against takedown efforts, using encryption to secure command-and-control communications. This botnet's advanced capabilities include stealing banking credentials and enabling distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, making it a notable threat in cybercrime.
Trik Botnet: Spreading via Social Engineering
Trik Botnet exemplifies cyberattack threats by employing sophisticated social engineering techniques to spread malware through deceptive email campaigns and malicious attachments. This botnet manipulates users into downloading harmful payloads that compromise system security and enable credential theft or unauthorized access. Its persistent use of social engineering makes Trik a significant risk for enterprise networks and individual devices alike.
Observed Real-World Impacts of Botnet-Driven Cyberattacks
Botnet-driven cyberattacks, such as those executed by the Mirai botnet, have caused massive Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks that disabled major internet services and disrupted global online access. The Emotet botnet has been observed spreading malware and stealing sensitive financial information, resulting in millions of dollars in losses for organizations worldwide. These real-world impacts demonstrate how botnets enable cybercriminals to orchestrate large-scale disruptions and cause significant economic damage.
example of botnet in cyberattack Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com