Blockchain technology revolutionizes traditional ledger systems by providing a decentralized and immutable record of transactions. Each block in a blockchain contains a unique cryptographic hash, timestamp, and transaction data, ensuring transparency and security. The ledger operates on a distributed network, eliminating the need for a central authority and reducing the risk of fraud. In practical applications, blockchain ledgers are integral to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, where they track ownership and movement of digital assets. Enterprises utilize blockchain ledgers for supply chain management, enhancing traceability and accountability of goods from origin to consumer. The technology's data structure supports consensus mechanisms, enabling multiple parties to validate and record entries collectively on the blockchain ledger.
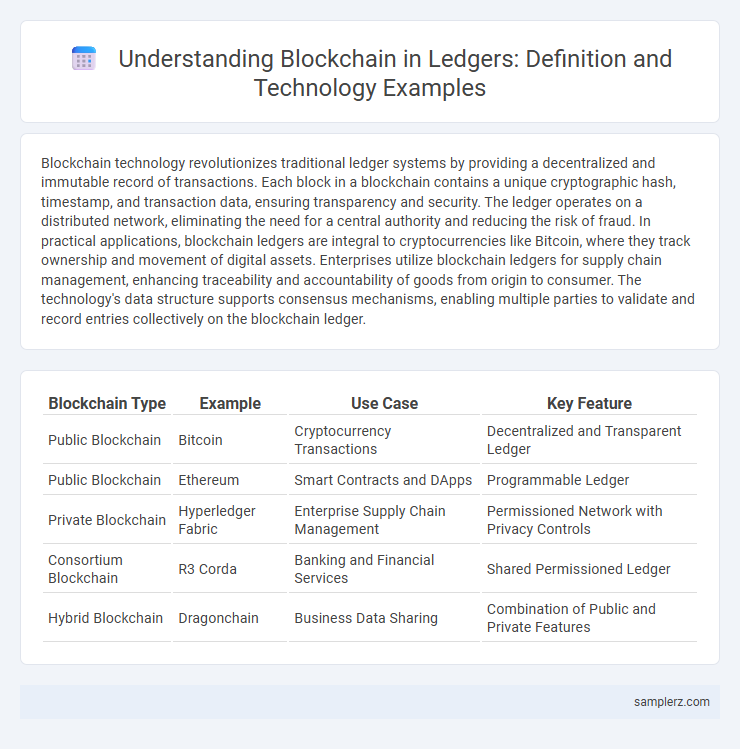
Table of Comparison
| Blockchain Type | Example | Use Case | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Blockchain | Bitcoin | Cryptocurrency Transactions | Decentralized and Transparent Ledger |
| Public Blockchain | Ethereum | Smart Contracts and DApps | Programmable Ledger |
| Private Blockchain | Hyperledger Fabric | Enterprise Supply Chain Management | Permissioned Network with Privacy Controls |
| Consortium Blockchain | R3 Corda | Banking and Financial Services | Shared Permissioned Ledger |
| Hybrid Blockchain | Dragonchain | Business Data Sharing | Combination of Public and Private Features |
Introduction to Blockchain in Ledger Technology
Blockchain serves as a decentralized and immutable ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency and security. In ledger technology, blockchain enables the creation of tamper-proof digital records by grouping transactions into blocks linked through cryptographic hashes. This innovation revolutionizes industries such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare by providing a reliable and transparent system for data management.
How Blockchain Transforms Traditional Ledgers
Blockchain transforms traditional ledgers by enabling decentralized and immutable record-keeping, which eliminates the need for a central authority and reduces fraud risk. Each transaction is cryptographically secured and linked in a chain, ensuring transparency and traceability across participants. Industries like finance and supply chain leverage blockchain to improve data integrity, enhance trust, and streamline reconciliation processes.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain-Based Ledgers
Supply chain management platforms like IBM Food Trust use blockchain ledgers to provide transparent tracking of food products from farm to table. Financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase employ blockchain-based ledgers to enable secure, efficient cross-border payment settlements. Land registry systems in countries like Sweden leverage blockchain technology to create immutable, tamper-proof records for property ownership verification.
Cryptocurrency Ledger Systems: Bitcoin and Ethereum
Bitcoin and Ethereum exemplify blockchain's role in cryptocurrency ledger systems by providing decentralized, immutable records of transactions. Bitcoin's blockchain operates through proof-of-work consensus, ensuring secure and transparent peer-to-peer bitcoin transfers. Ethereum extends this functionality with smart contracts, enabling programmable transactions and decentralized applications on its ledger.
Blockchain in Banking and Financial Record-Keeping
Blockchain technology in banking and financial record-keeping enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof ledger management by utilizing decentralized consensus mechanisms. Banks leverage blockchain to streamline cross-border payments, reduce fraud, and enhance auditability through immutable transaction records. This innovation significantly improves operational efficiency and regulatory compliance in financial institutions.
Supply Chain Management Ledgers Powered by Blockchain
Supply chain management ledgers powered by blockchain enhance transparency and traceability by recording every transaction in a decentralized and immutable manner. Companies like IBM and Maersk utilize blockchain to track shipments, verify provenance, and reduce fraud across global supply networks. This technology streamlines operations, improves data accuracy, and ensures real-time visibility of goods from origin to delivery.
Smart Contracts and Automated Ledger Entries
Smart contracts on blockchain enable automated execution of agreements without intermediaries, enhancing transaction efficiency and security. Automated ledger entries record every transaction immutably, ensuring transparent and tamper-proof financial data management. Enterprises use this technology to streamline processes, reduce costs, and maintain real-time audit trails.
Blockchain for Transparent Auditing and Compliance
Blockchain technology enables transparent auditing and compliance by creating an immutable ledger where every transaction is securely recorded and time-stamped. This tamper-proof digital ledger facilitates real-time verification of financial and operational data, enhancing regulatory adherence and reducing fraud risks. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain leverage blockchain to ensure accountability and streamline audit processes through decentralized transparency.
Decentralized Identity Management Ledgers
Decentralized Identity Management Ledgers leverage blockchain technology to provide secure, tamper-proof storage of digital identities, enabling users to control their personal data without relying on centralized authorities. Platforms like Sovrin and uPort utilize distributed ledgers to verify identity credentials, enhancing privacy and reducing identity fraud risks. These systems employ cryptographic proofs to ensure identity authenticity while fostering interoperability across multiple services and applications.
Future Trends in Blockchain-Driven Ledger Solutions
Blockchain-driven ledger solutions are evolving with advancements such as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and enterprise-grade permissioned blockchains that enhance transaction transparency and security. Integration of artificial intelligence and smart contract automation is poised to optimize ledger operations, reducing fraud and operational costs in industries like finance and supply chain management. Emerging trends also highlight the rise of cross-chain interoperability protocols, enabling seamless data transfer across multiple blockchain networks, which will significantly boost scalability and adoption.
example of blockchain in ledger Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com