A honeytoken is a security mechanism designed to detect unauthorized access by planting fictitious data or files within a system. One common example of a honeytoken in threat detection is a fake database record containing unique, identifiable information that alerts administrators when accessed. This technique helps organizations identify insider threats or external attackers by tracking interactions with the decoy data. Honeytokens can also take the form of fake credentials, such as bogus login usernames and passwords, which trigger alerts if used. These decoy credentials are monitored closely, allowing security teams to pinpoint suspicious behavior and potential breaches. Using honeytokens improves threat detection capabilities by providing early warnings and minimizing false positives in security monitoring systems.
Table of Comparison
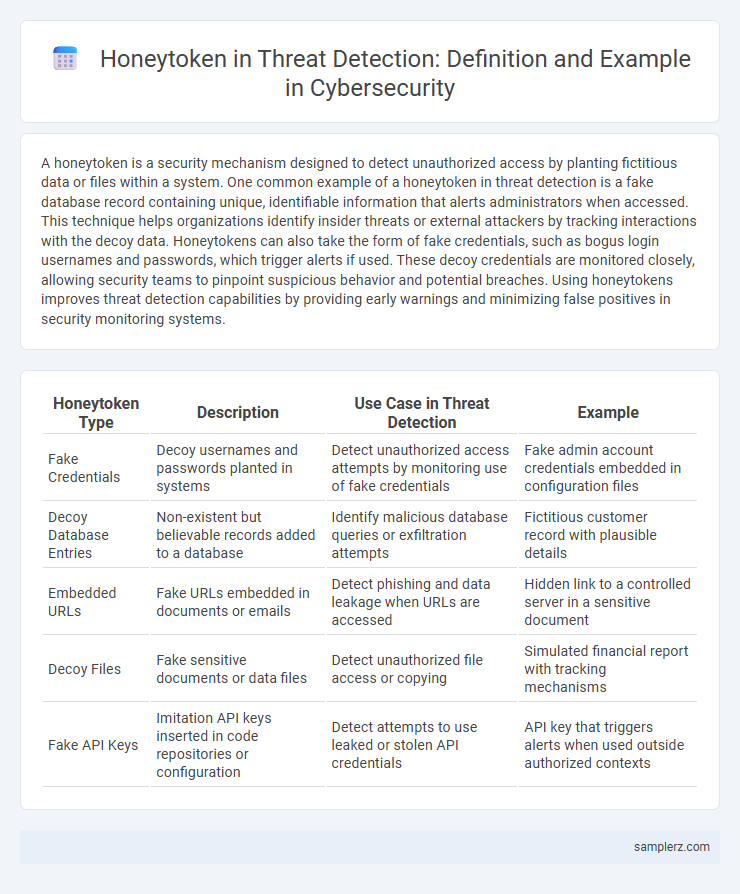
| Honeytoken Type | Description | Use Case in Threat Detection | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fake Credentials | Decoy usernames and passwords planted in systems | Detect unauthorized access attempts by monitoring use of fake credentials | Fake admin account credentials embedded in configuration files |
| Decoy Database Entries | Non-existent but believable records added to a database | Identify malicious database queries or exfiltration attempts | Fictitious customer record with plausible details |
| Embedded URLs | Fake URLs embedded in documents or emails | Detect phishing and data leakage when URLs are accessed | Hidden link to a controlled server in a sensitive document |
| Decoy Files | Fake sensitive documents or data files | Detect unauthorized file access or copying | Simulated financial report with tracking mechanisms |
| Fake API Keys | Imitation API keys inserted in code repositories or configuration | Detect attempts to use leaked or stolen API credentials | API key that triggers alerts when used outside authorized contexts |
Introduction to Honeytokens in Threat Detection
Honeytokens function as deceptive digital assets designed to lure cyber attackers by mimicking sensitive data such as fake credentials, documents, or database entries. When accessed or used, these planted tokens trigger alerts, enabling security teams to identify unauthorized activity and potential breaches early. Implementing honeytokens enhances threat detection by providing proactive, low-cost indicators of compromise within an organization's security infrastructure.
Common Types of Honeytokens Used in Security
Common types of honeytokens used in security include fake credentials, such as bogus usernames and passwords, which trigger alerts when accessed by unauthorized users. Decoy documents embedded with tracking code serve as another effective honeytoken, enabling organizations to detect data exfiltration attempts. Additionally, metadata-based honeytokens like unique email addresses or API keys can identify unauthorized usage and provide insight into potential security breaches.
Email Honeytokens: Luring Phishers and Intruders
Email honeytokens serve as decoy credentials embedded within emails to identify unauthorized access and phishing attempts by tracking illicit use or access patterns. These carefully crafted tokens generate alerts when accessed, enabling security teams to pinpoint compromised accounts or insider threats early. Deploying email honeytokens enhances threat detection by turning phishing campaigns into actionable intelligence sources that reveal attacker tactics and infrastructure.
Database Honeytokens: Detecting Insider Threats
Database honeytokens are strategically deployed fake records designed to alert security teams when accessed, signaling potential insider threats or unauthorized data exfiltration. These unique identifiers blend seamlessly within sensitive databases, triggering real-time alerts upon any interaction, thereby enhancing threat detection capabilities. Effective use of database honeytokens helps organizations monitor and respond swiftly to breaches originating from within authorized personnel.
File-Based Honeytokens for Network Monitoring
File-based honeytokens serve as decoy files strategically placed within network environments to detect unauthorized access or lateral movement by attackers. These files, embedded with unique identifiers or metadata, trigger alerts when accessed or copied, enabling security teams to identify breach attempts quickly. Effective deployment of file-based honeytokens enhances early threat detection and supports incident response by providing valuable forensic data on attacker behavior.
Credential Honeytokens in Active Directory Environments
Credential honeytokens in Active Directory environments function as fake user accounts or credentials deliberately planted to detect unauthorized access attempts. These honeytokens trigger alerts when attackers attempt to use the bogus credentials, revealing compromised accounts or insider threats. Monitoring access patterns to these credentials enhances early threat detection and limits lateral movement within enterprise networks.
Cloud Storage Honeytokens for Unauthorized Access Detection
Cloud storage honeytokens are decoy files or credentials strategically placed to detect unauthorized access within cloud environments. When an attacker interacts with these honeytokens, it triggers security alerts, enabling rapid identification of breach attempts. This proactive measure enhances threat detection by providing real-time insights into malicious activity targeting cloud storage resources.
API Key Honeytokens: Securing Application Interfaces
API Key honeytokens act as decoy credentials embedded within application code or configuration files to detect unauthorized access attempts to APIs. When these fake API keys are used, they trigger alerts signaling potential breaches or insider threats targeting application interfaces. Implementing API Key honeytokens enhances threat detection by providing early warnings of malicious activity without impacting legitimate users.
Tracking Attackers with Embedded Document Honeytokens
Embedded document honeytokens act as deceptive files seeded with unique identifiers, enabling security teams to track unauthorized access and movement within a network. When attackers open or exfiltrate these embedded honeytokens, alerts are triggered, providing real-time intelligence on their tactics and location. This method enhances threat detection by revealing attacker behavior without exposing genuine sensitive data.
Case Studies: Successful Threat Detection with Honeytokens
Honeytokens, such as fake database entries or bogus API keys, have proven effective in identifying unauthorized access in corporate environments; one case study involved a financial firm detecting insider threats after an employee accessed a honeytoken-laced document. In another instance, a healthcare provider deployed honeytoken email addresses that triggered alerts when targeted by phishing campaigns, enabling swift incident response. These examples demonstrate honeytokens' value in proactively uncovering malicious activity by creating deliberate, traceable traps within IT infrastructures.
example of honeytoken in threat detection Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com