Toe-in alignment refers to the adjustment of a vehicle's wheels so that the front edges point slightly toward each other. This setup is common in front-wheel-drive cars to enhance stability and improve tire wear. Typical toe-in values range from 0.05 to 0.15 degrees, depending on the vehicle specifications and manufacturer recommendations. Correct toe-in alignment reduces uneven tire wear and ensures precise steering response, improving overall vehicle handling. Technicians use alignment machines to measure the wheel angles relative to the vehicle's centerline and adjust the tie rods accordingly. Proper toe-in settings contribute to safety and fuel efficiency by minimizing rolling resistance during motion.
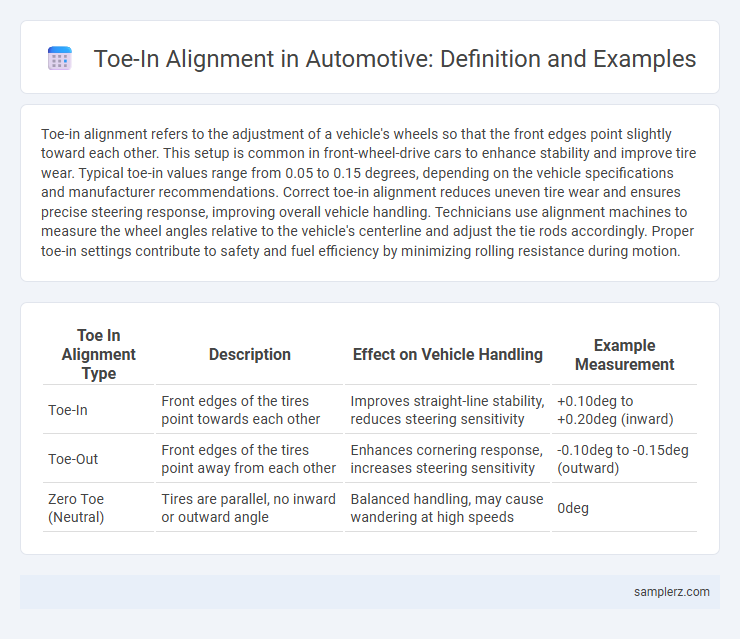
Table of Comparison
| Toe In Alignment Type | Description | Effect on Vehicle Handling | Example Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toe-In | Front edges of the tires point towards each other | Improves straight-line stability, reduces steering sensitivity | +0.10deg to +0.20deg (inward) |
| Toe-Out | Front edges of the tires point away from each other | Enhances cornering response, increases steering sensitivity | -0.10deg to -0.15deg (outward) |
| Zero Toe (Neutral) | Tires are parallel, no inward or outward angle | Balanced handling, may cause wandering at high speeds | 0deg |
Understanding Toe-In Alignment in Automotive Suspension
Toe-in alignment refers to the slight inward angle of a vehicle's front wheels when viewed from above, typically measured in fractions of an inch or degrees. Correct toe-in settings improve tire contact with the road, enhancing steering stability and reducing tire wear in automotive suspension systems. For example, a common specification might be 0.1 degrees toe-in, ensuring optimal handling and safety in passenger cars.
Key Functions of Toe-In for Vehicle Handling
Toe-in alignment enhances vehicle stability by ensuring the front wheels point slightly inward, improving straight-line tracking and reducing tire wear. This adjustment optimizes steering response and contributes to balanced cornering performance. Proper toe-in settings prevent excessive understeer and promote safer handling during high-speed maneuvers.
How Toe-In Affects Tire Wear and Performance
Toe-in alignment, where the front edges of the tires point slightly inward, enhances straight-line stability and improves cornering response. Excessive toe-in causes inner tire tread to wear prematurely due to increased friction, reducing tire lifespan and fuel efficiency. Precise toe-in settings optimize tire contact with the road, balancing performance and tire longevity in automotive suspension tuning.
Common Signs Indicating Improper Toe-In
Uneven tire wear, especially excessive wear on the inner or outer edges, commonly indicates improper toe-in alignment in vehicles. Steering wheel vibration or pulling to one side during driving are also key symptoms of incorrect toe settings. Poor handling and reduced fuel efficiency often accompany these alignment issues, highlighting the importance of regular toe-in adjustments.
Step-by-Step Example of Measuring Toe-In Alignment
To measure toe-in alignment, start by positioning the vehicle on a level surface and ensuring the steering wheel is centered. Use a tape measure to record the distance between the front edges of the front tires and again at the rear edges, then calculate the difference to determine the toe-in measurement. Proper toe-in alignment, typically ranging from 0.05 to 0.15 inches, ensures optimal tire wear and improved vehicle handling.
Real-World Examples of Toe-In Adjustments
Toe-in alignment refers to the front edges of the tires being closer together than the rear edges, commonly set between 0.05 to 0.15 degrees inward for passenger cars. A real-world example includes improving stability on high-performance vehicles like the Subaru WRX, which uses a slight toe-in to enhance cornering grip and reduce understeer. Precise toe-in adjustments significantly impact tire wear patterns and handling characteristics, proving critical in racing and daily driving scenarios.
Comparing Toe-In vs. Toe-Out: Practical Differences
Toe-in alignment angles involve the front of the wheels pointing slightly inward, enhancing straight-line stability and reducing tire wear on the outer edges. In contrast, toe-out alignment, where the wheels point outward, improves cornering responsiveness but can lead to increased tire wear and less stability on highways. Choosing between toe-in and toe-out depends on driving style and vehicle application, with toe-in favored for highway use and toe-out often preferred in performance or racing vehicles.
Impact of Toe-In Alignment on Straight-Line Stability
Toe-in alignment, where the front edges of the tires are closer together than the rear edges, enhances straight-line stability by promoting better tire contact with the road surface during driving. This alignment reduces tire scrubbing and uneven wear, leading to improved handling and increased tire lifespan. Optimal toe-in settings prevent wandering and ensure precise steering response, critical for safety and performance in automotive systems.
Professional Tips for Achieving Optimal Toe-In
Precise toe-in alignment, typically set between 0.05 and 0.15 degrees inward per wheel, enhances tire wear and vehicle stability. Professional technicians use laser-guided alignment tools to measure and adjust toe angles accurately, ensuring optimal handling and fuel efficiency. Consistent toe-in checks during routine maintenance prevent uneven tire wear and improve steering response, critical for both performance and safety.
When and Why to Adjust Toe-In on Your Vehicle
Toe-in alignment is typically adjusted when there is uneven tire wear or unstable steering, often detected during routine maintenance or after suspension repairs. Proper toe-in settings enhance vehicle stability and improve tire longevity by ensuring the front wheels are slightly angled inward, optimizing contact with the road surface. Adjusting toe-in is crucial for preventing premature tire wear, improving handling response, and maintaining overall driving safety.
example of toe in alignment Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com