In the automotive industry, a spider refers to a lightweight structural framework that supports various vehicle components such as the suspension, engine mounts, or drivetrain systems. Universal spiders are designed to fit a wide range of vehicle models and types, enhancing their adaptability and ease of replacement. These components are typically made from durable materials like aluminum or steel to ensure strength and longevity under dynamic driving conditions. Universal spiders play a critical role in the drivetrain assembly, especially in CV (constant velocity) joints and drive shafts where they help transmit torque smoothly while accommodating angular movement. They contribute to vehicle stability by absorbing shocks and vibrations, thus improving ride quality and overall performance. Manufacturers optimize spider designs to balance weight reduction with structural integrity, supporting fuel efficiency and safety standards.
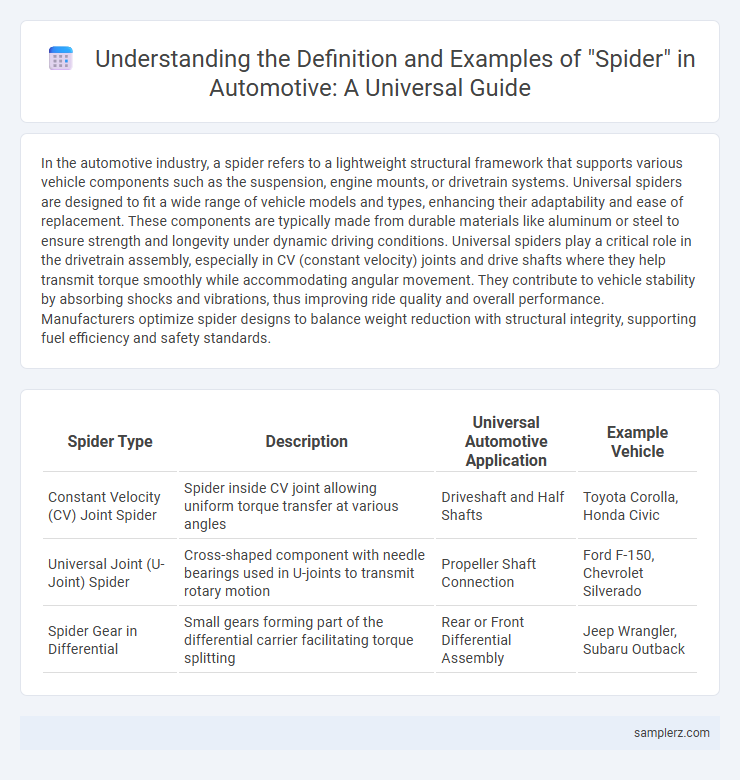
Table of Comparison
| Spider Type | Description | Universal Automotive Application | Example Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant Velocity (CV) Joint Spider | Spider inside CV joint allowing uniform torque transfer at various angles | Driveshaft and Half Shafts | Toyota Corolla, Honda Civic |
| Universal Joint (U-Joint) Spider | Cross-shaped component with needle bearings used in U-joints to transmit rotary motion | Propeller Shaft Connection | Ford F-150, Chevrolet Silverado |
| Spider Gear in Differential | Small gears forming part of the differential carrier facilitating torque splitting | Rear or Front Differential Assembly | Jeep Wrangler, Subaru Outback |
Introduction to Spider Mechanisms in the Automotive Industry
Spider mechanisms in the automotive industry refer to universal joint components that transmit torque between shafts while allowing angular misalignment. These spider joints consist of a central cross-shaped member fitted with needle bearings, enabling smooth rotation and flexibility in drivetrain systems. Their application in drive shafts and steering columns ensures enhanced vehicle performance and durability under varying motion conditions.
The Role of Spider Couplings in Universal Joints
Spider couplings play a crucial role in universal joints by transmitting torque while accommodating misalignment between connected shafts in automotive drivetrains. These couplings consist of a cross-shaped element with needle bearings at each arm, ensuring smooth rotational movement and reducing wear in vehicle drive shafts. Their ability to maintain efficient power transfer and absorb vibration significantly enhances the durability and performance of automotive steering and drivetrain systems.
How Spider Components Enhance Drivetrain Performance
Spider gears in a universal joint play a crucial role in maintaining smooth power transfer between the driveshaft and differential. These precision-engineered components reduce vibrations and accommodate angular misalignments, which enhances drivetrain efficiency and longevity. Optimized spider gear designs contribute to improved torque distribution and overall vehicle handling in high-performance automotive applications.
Common Types of Spider Assemblies in Automotive Applications
Spider assemblies in automotive drivelines typically include tripod and ball-type spider joints, essential for transmitting torque between the drive shaft and wheels while allowing angular movement. Tripod spider joints offer smooth rotation and axial movement, commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles to accommodate suspension travel. Ball-type spider joints provide high durability and flexibility, frequently employed in rear-wheel-drive and four-wheel-drive systems for enhanced performance under varying load conditions.
Step-by-Step Example: Spider in a Universal Joint
A spider in a universal joint, also known as a cross or yoke, is a critical component that facilitates rotational movement between two shafts at varying angles. This four-armed component fits inside the yokes, allowing torque transmission while accommodating angular misalignment, reducing vibration and wear. By enabling smooth power transfer in drive shafts, the spider ensures enhanced vehicle drivability and longevity of the drivetrain assembly.
Key Materials Used for Automotive Spider Components
Automotive spider components commonly utilize high-strength steel alloys and aluminum composites to ensure lightweight durability and resistance to wear. Advanced polymer materials, such as reinforced nylon and phenolic resins, enhance thermal stability and reduce friction in spider gears. Precision manufacturing of these materials contributes to improved drivetrain efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
Maintenance Tips for Spider Universal Joints
Spider universal joints in automotive drivetrains require regular lubrication to prevent wear and ensure smooth operation. Inspecting these joints for signs of rust, cracks, or excessive play can help identify potential failures before they lead to drivetrain damage. Applying high-quality grease and replacing worn spiders promptly extends the lifespan of universal joints and maintains vehicle performance.
Signs of Wear and Failure in Spider Assemblies
Spider assemblies in automotive universal joints exhibit signs of wear such as excessive play, rust, and visible cracks. Increased vibration during driving and unusual noises when turning are indicative of spider failure. Timely inspection of needle bearings and lubrication condition is crucial to prevent complete joint breakdown.
Innovations in Spider Design for Modern Vehicles
Universal's innovative spider designs integrate lightweight carbon-fiber materials and adaptive suspension technology, significantly enhancing vehicle agility and stability. Advanced engineering enables these spiders to optimize load distribution and reduce vibrations, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and ride comfort. These developments mark a substantial leap forward in automotive performance and safety standards.
Choosing the Right Spider for Your Universal Joint System
Selecting the right spider for your universal joint system ensures optimal performance and durability, with options like forged steel or billet aluminum spiders providing varying levels of strength and corrosion resistance. High-quality spiders feature precision-machined bearings and grease fittings, crucial for maintaining smooth rotational movement under heavy automotive loads. Matching spider size and material to your vehicle's torque requirements and operating conditions enhances drivetrain longevity and reduces wear in demanding environments.
example of spider in universal Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com