A jackshaft in an automotive drivetrain is a secondary shaft used to transfer power between the engine and the wheels, often found in vehicles with complex drivetrains. It acts as an intermediary component that can alter torque and speed, enhancing the overall performance and efficiency of the transmission system. Jackshafts are typically connected to the engine crankshaft via a belt or chain and then transmit power to other drivetrain components. In electric vehicles, a jackshaft can play a crucial role in managing power distribution between the electric motor and the wheels. It allows for better control of torque and can help in optimizing energy use by adjusting rotational speeds. By integrating a jackshaft, automotive engineers improve drivetrain flexibility and durability while maintaining smooth power delivery.
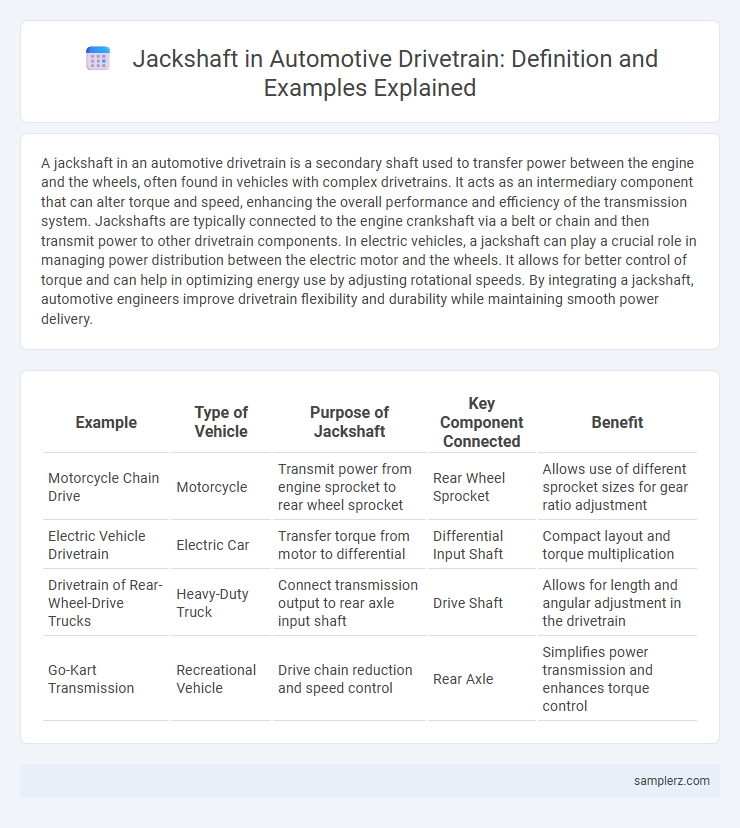
Table of Comparison
| Example | Type of Vehicle | Purpose of Jackshaft | Key Component Connected | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motorcycle Chain Drive | Motorcycle | Transmit power from engine sprocket to rear wheel sprocket | Rear Wheel Sprocket | Allows use of different sprocket sizes for gear ratio adjustment |
| Electric Vehicle Drivetrain | Electric Car | Transfer torque from motor to differential | Differential Input Shaft | Compact layout and torque multiplication |
| Drivetrain of Rear-Wheel-Drive Trucks | Heavy-Duty Truck | Connect transmission output to rear axle input shaft | Drive Shaft | Allows for length and angular adjustment in the drivetrain |
| Go-Kart Transmission | Recreational Vehicle | Drive chain reduction and speed control | Rear Axle | Simplifies power transmission and enhances torque control |
Introduction to Jackshafts in Automotive Drivetrains
A jackshaft in automotive drivetrains serves as an intermediary shaft that transmits power between the engine or transmission and the drive axle, enhancing torque distribution and allowing for more flexible drivetrain layouts. Commonly found in rear-wheel-drive and four-wheel-drive vehicles, jackshafts enable gear ratio adjustments and facilitate the connection of multiple drive components while maintaining alignment and reducing mechanical stress. Their integration improves drivetrain efficiency, supports heavy-duty applications, and accommodates complex vehicle architectures such as all-wheel-drive systems.
Function and Importance of Jackshafts
Jackshafts in automotive drivetrains serve as intermediate shafts that transfer rotational power from the engine or transmission to other drivetrain components, enabling smoother power distribution and speed adjustments. They play a crucial role in optimizing torque delivery, especially in vehicles with complex drivetrain layouts such as four-wheel drives or heavy-duty trucks. By absorbing and redirecting mechanical loads, jackshafts enhance drivetrain efficiency, reduce wear on primary components, and contribute to overall vehicle performance and reliability.
Common Applications of Jackshafts in Vehicles
Jackshafts in vehicle drivetrains are commonly used to transfer power between the engine and the driven components when space constraints prevent direct coupling. They frequently appear in heavy-duty trucks to bridge the power output from the transmission to the rear differential or secondary drive axles. In off-road vehicles and agricultural machinery, jackshafts enable flexible power distribution to auxiliary systems such as PTOs and hydraulic pumps, improving drivetrain efficiency and serviceability.
Example: Jackshaft in Classic Rear-Wheel-Drive Cars
A jackshaft in classic rear-wheel-drive cars serves as an intermediate shaft connecting the transmission output to the drive shaft, allowing for optimal power transfer and alignment in the drivetrain. This component helps accommodate engine placement and chassis design by facilitating torque delivery through the propeller shaft to the rear differential. Its use in vehicles such as the vintage Ford Mustang or Chevrolet Camaro enhances drivetrain efficiency and durability in rear-wheel-drive configurations.
Example: Motorcycle Drivetrains Using Jackshafts
Motorcycle drivetrains often incorporate jackshafts to optimize power transmission between the engine and rear wheel, especially in models with complex frame geometries or unique suspension setups. The jackshaft serves as an intermediate shaft, redirecting torque from the crankshaft to the final drive chain or shaft, improving alignment and reducing stress on drivetrain components. Examples include sport-touring motorcycles where jackshafts enable smoother power delivery and enhanced reliability in confined spaces.
Jackshafts in Commercial Truck Transmissions
Jackshafts in commercial truck transmissions serve as intermediate shafts that transfer power between the engine and the drive axle, optimizing torque distribution for heavy-duty hauling. These components are engineered to withstand high torque loads and ensure smooth power delivery, enhancing transmission efficiency and vehicle performance. The use of durable materials and precision gearing in jackshafts contributes to improved drivetrain reliability and reduced maintenance costs in commercial trucks.
Performance Upgrades: Aftermarket Jackshaft Solutions
Aftermarket jackshaft solutions enhance drivetrain performance by increasing torque transmission and optimizing power distribution in high-performance vehicles. These upgraded jackshafts often feature lightweight materials such as aluminum or chromoly steel, reducing rotational mass and improving acceleration response. Performance-focused designs also allow for custom gear ratios, enabling finer tuning of drivetrain efficiency and overall vehicle speed.
Jackshafts in All-Wheel-Drive and Four-Wheel-Drive Systems
Jackshafts in all-wheel-drive (AWD) and four-wheel-drive (4WD) systems serve as critical components that transfer power from the transmission to the front or rear differentials. They enable precise torque distribution and accommodate the varying rotational speeds of wheels during off-road or dynamic driving conditions. High-performance AWD and 4WD vehicles often use reinforced jackshafts made from alloy steel to withstand increased drivetrain loads and improve durability.
Maintenance Tips for Jackshaft Components
Regular inspection of jackshaft components, including bearings and seals, prevents premature wear and ensures smooth drivetrain operation. Lubricate the jackshaft periodically with manufacturer-recommended grease to reduce friction and avoid overheating. Tighten mounting bolts and check alignment to maintain optimal power transfer and extend the lifespan of the drivetrain system.
Future Trends of Jackshafts in Automotive Engineering
Jackshafts in automotive drivetrains are evolving with advancements in electric and hybrid vehicle technologies, enhancing torque distribution and efficiency. Integration of lightweight materials and optimized gear ratios will improve fuel economy and reduce emissions. Future jackshafts will also support smarter drivetrain systems, enabling adaptive power delivery for improved performance and durability.
example of jackshaft in drivetrain Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com