A stub in an axle refers to the short, projecting shaft at the end of an axle assembly where the wheel hub is mounted. It serves as a crucial entity in the automotive drivetrain, transferring rotational force from the axle to the wheel. Data from automotive manufacturers indicate that stub axles are typically constructed from high-strength steel to withstand torsional stresses. The design of the stub axle varies depending on the vehicle type and axle configuration. In passenger vehicles, the stub axle often integrates with the wheel bearing and brake components. Engineering data highlights that precise machining of the stub axle's dimensions is essential to ensure proper wheel alignment and safe vehicle operation.
Table of Comparison
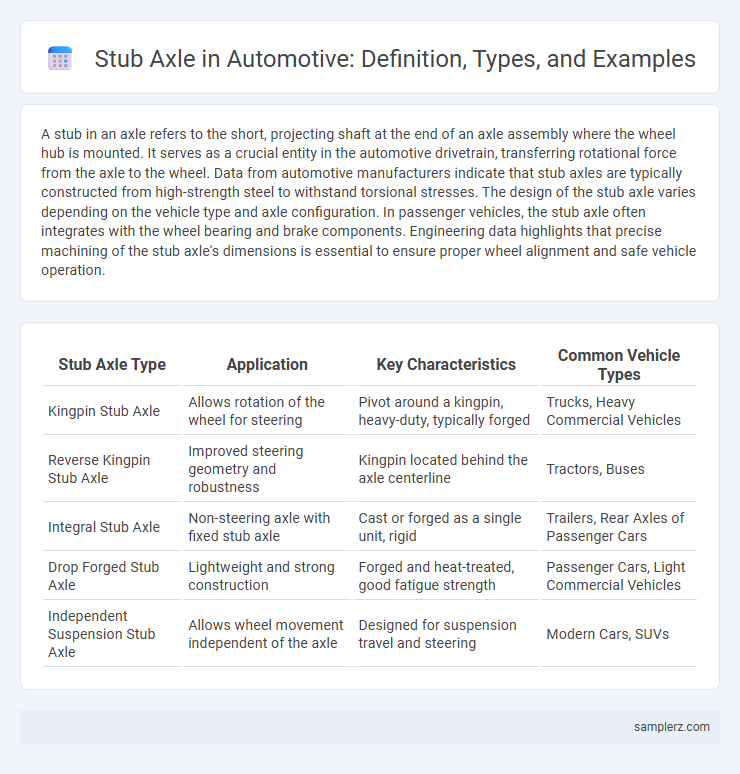
| Stub Axle Type | Application | Key Characteristics | Common Vehicle Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kingpin Stub Axle | Allows rotation of the wheel for steering | Pivot around a kingpin, heavy-duty, typically forged | Trucks, Heavy Commercial Vehicles |
| Reverse Kingpin Stub Axle | Improved steering geometry and robustness | Kingpin located behind the axle centerline | Tractors, Buses |
| Integral Stub Axle | Non-steering axle with fixed stub axle | Cast or forged as a single unit, rigid | Trailers, Rear Axles of Passenger Cars |
| Drop Forged Stub Axle | Lightweight and strong construction | Forged and heat-treated, good fatigue strength | Passenger Cars, Light Commercial Vehicles |
| Independent Suspension Stub Axle | Allows wheel movement independent of the axle | Designed for suspension travel and steering | Modern Cars, SUVs |
Introduction to Stub Axles in Automotive Engineering
Stub axles are crucial components in automotive engineering, connecting the wheel hub to the suspension system and allowing for controlled wheel rotation and steering. Typically made from forged steel or cast iron, stub axles must withstand significant stresses from vehicle weight, road conditions, and braking forces. Their design and material selection directly impact vehicle stability, handling performance, and overall safety.
Key Functions of Stub Axles in Vehicle Design
Stub axles serve as crucial components connecting the wheel hubs to the suspension system, enabling smooth rotation and supporting vehicle loads. They help maintain proper wheel alignment, ensuring stability and safe handling during steering maneuvers. By transmitting braking forces and accommodating differential movement, stub axles enhance overall vehicle performance and safety.
Common Types of Stub Axles Used in Automobiles
Common types of stub axles used in automobiles include the Elliot, Lamoine, and reverse Elliot designs, each offering distinct mounting and load distribution features. The Elliot stub axle is characterized by its cast iron construction with a forged hub, commonly found in heavy-duty vehicles. Lamoine stub axles, typically used in light vehicles, provide improved steering geometry, while reverse Elliot axles enable easier assembly and maintenance in front-wheel-drive automobiles.
Example of Stub Axle: Elliot Type Explained
The Elliot type stub axle is a common example used in automotive front suspension systems, featuring a robust cast or forged steel construction designed to handle high load stresses. It integrates a pivot point for easy steering motion and typically includes a spindle for mounting the wheel hub. The design enhances vehicle stability and steering precision, making it suitable for heavy-duty trucks and passenger cars.
Example of Stub Axle: Lamoine and Reverse Lamoine Stub Axles
Lamoine and Reverse Lamoine stub axles are commonly used in automotive front suspension systems, providing crucial support and pivot points for the vehicle's steering mechanism. The Lamoine stub axle features an outward placement of the spindle, optimizing wheel alignment and load distribution, while the Reverse Lamoine places the spindle inward, enhancing stability in heavy-duty applications. Both designs improve vehicle handling and durability by ensuring efficient load transfer from the wheel to the suspension components.
Example of Stub Axle: Reverse Elliot Stub Axle
The Reverse Elliot Stub Axle is a common example of a stub axle used in automotive front suspension systems, particularly in light commercial vehicles and vintage cars. It features a forged steel construction designed to support wheel hubs while allowing for steering articulation. This type of stub axle improves wheel alignment and load distribution, enhancing vehicle stability and handling performance.
Material Selection for Automotive Stub Axles
Automotive stub axles require high-strength materials such as forged steel or alloy steel to withstand dynamic loads and enhance durability. Selection criteria prioritize fatigue resistance, tensile strength, and toughness to ensure safety and performance in suspension systems. Optimizing material properties directly contributes to the longevity and reliability of stub axles in various driving conditions.
Stub Axle vs Full-Floating Axle: Key Differences
A stub axle is a crucial component that supports the wheel and connects it to the suspension system, primarily used in semi-floating axle configurations, while a full-floating axle features a separate hub that carries the vehicle's weight independently of the axle shaft. The key differences between a stub axle and a full-floating axle include load distribution, with the stub axle bearing both the weight and driving torque, whereas the full-floating axle only transmits torque, enhancing durability and ease of maintenance. In automotive applications, full-floating axles are preferred for heavy-duty vehicles due to their superior strength and reliability, while stub axles are common in lighter vehicles for cost efficiency and simpler design.
Impact of Stub Axle Design on Vehicle Handling and Safety
The stub axle design directly influences vehicle handling by affecting wheel alignment, suspension geometry, and steering precision. An optimized stub axle enhances load distribution and reduces vibrations, improving overall ride stability and safety. Poorly designed stub axles can lead to uneven tire wear, compromised braking performance, and increased risk of axle failure under dynamic driving conditions.
Maintenance and Failure Symptoms of Stub Axles in Cars
Stub axles in cars require regular maintenance such as lubrication and inspection for cracks or corrosion to ensure optimal performance and safety. Common failure symptoms include uneven tire wear, abnormal noise during steering, and vibrations felt in the steering wheel. Timely replacement of worn or damaged stub axles prevents further damage to suspension components and maintains vehicle stability.
example of stub in axle Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com