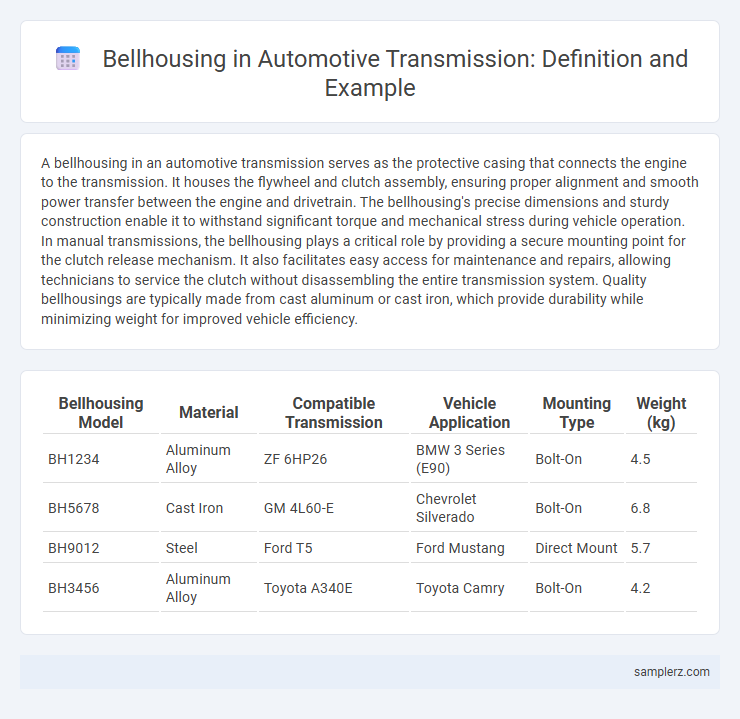
A bellhousing in an automotive transmission serves as the protective casing that connects the engine to the transmission. It houses the flywheel and clutch assembly, ensuring proper alignment and smooth power transfer between the engine and drivetrain. The bellhousing's precise dimensions and sturdy construction enable it to withstand significant torque and mechanical stress during vehicle operation. In manual transmissions, the bellhousing plays a critical role by providing a secure mounting point for the clutch release mechanism. It also facilitates easy access for maintenance and repairs, allowing technicians to service the clutch without disassembling the entire transmission system. Quality bellhousings are typically made from cast aluminum or cast iron, which provide durability while minimizing weight for improved vehicle efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Bellhousing Model | Material | Compatible Transmission | Vehicle Application | Mounting Type | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BH1234 | Aluminum Alloy | ZF 6HP26 | BMW 3 Series (E90) | Bolt-On | 4.5 |
| BH5678 | Cast Iron | GM 4L60-E | Chevrolet Silverado | Bolt-On | 6.8 |
| BH9012 | Steel | Ford T5 | Ford Mustang | Direct Mount | 5.7 |
| BH3456 | Aluminum Alloy | Toyota A340E | Toyota Camry | Bolt-On | 4.2 |
Understanding the Bellhousing in Automotive Transmissions
The bellhousing in automotive transmissions serves as a protective cover that encases the clutch and flywheel, connecting the engine to the transmission system. Made from durable materials like aluminum or cast iron, it ensures precise alignment between the crankshaft and input shaft, crucial for optimal power transfer and transmission efficiency. Proper maintenance of the bellhousing prevents contamination and mechanical wear, contributing to the longevity and performance of the vehicle's drivetrain.
Key Functions of a Bellhousing
The bellhousing serves as a critical component in automotive transmissions by securely enclosing the flywheel and clutch assembly, protecting them from debris and external damage. It provides precise alignment between the engine and transmission, ensuring smooth power transfer and minimizing wear on internal components. Additionally, the bellhousing supports the starter motor mounting, facilitating reliable engine ignition.
Common Materials Used for Bellhousing Construction
Bellhousings in automotive transmissions are commonly constructed from cast aluminum and cast iron due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratios and thermal conductivity. Aluminum alloys provide lightweight durability, reducing overall vehicle weight and enhancing fuel efficiency, while cast iron offers superior rigidity and vibration damping for heavy-duty applications. These materials ensure reliable protection of the transmission system while maintaining optimal performance under various operating conditions.
Typical Bellhousing Locations in Vehicles
Typical bellhousing locations in vehicles are positioned between the engine block and the transmission, serving as a critical connection point that houses the clutch assembly or torque converter. In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the bellhousing is usually mounted directly behind the engine, linking it to the longitudinal transmission. Front-wheel-drive cars often use a transverse bellhousing integrated into the transmission casing to accommodate compact engine layouts and efficient power transfer.
Popular Bellhousing Designs in Modern Cars
Popular bellhousing designs in modern cars include the cast aluminum and stamped steel variants, each optimized for strength and weight reduction in transmission systems. Cast aluminum bellhousings offer superior heat dissipation and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles and turbocharged engines. Stamped steel bellhousings remain prevalent in mass-market vehicles due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing, providing reliable transmission-to-engine connection with adequate durability.
Compatibility of Bellhousing with Different Engines
Bellhousings serve as critical interface components connecting transmissions to various engine models, requiring precise alignment and bolt pattern compatibility to ensure optimal drivetrain performance. Compatibility depends on factors such as engine make, model, and block design, with aftermarket and OEM bellhousings often tailored for specific engines like V8s or inline-fours. Using a bellhousing matched to the engine guarantees proper fitment, prevents misalignment issues, and supports efficient power transfer within automotive transmission systems.
Signs of Bellhousing Wear or Damage
Signs of bellhousing wear or damage in automotive transmissions include visible cracks, warping, and excessive corrosion around the mounting surface. Unusual vibrations or noises during gear shifts can also indicate bellhousing misalignment or structural compromise. Frequent inspection for these issues ensures timely repair, preventing further transmission damage.
Bellhousing Example: Manual vs. Automatic Transmission
A bellhousing is a crucial component that connects the engine to the transmission, housing the clutch in manual transmissions and the torque converter in automatic transmissions. In manual transmission bellhousings, the design accommodates a clutch assembly and often features a provision for the starter motor near the flywheel. Automatic transmission bellhousings are typically designed to encase the torque converter and have reinforced mounting points to handle the increased rotational forces and thermal loads.
Upgrading Your Transmission Bellhousing: What to Consider
Upgrading your transmission bellhousing involves selecting a compatible material, such as aluminum for weight reduction or steel for durability, that matches your vehicle's power output and driving conditions. Ensure precise fitment to maintain proper alignment between the engine and transmission, which prevents premature wear and improves overall drivetrain performance. Consider heat dissipation properties and aftermarket options designed for specific transmission models like Tremec or T56 to enhance both reliability and cooling efficiency.
Maintenance Tips for Bellhousing Longevity
Regular inspection of the bellhousing for cracks, corrosion, and loose bolts ensures optimal performance and prevents transmission misalignment. Applying appropriate lubrication to the bellhousing's input shaft and pilot bearing reduces wear and facilitates smooth clutch operation. Keeping the bellhousing clean from debris and promptly addressing oil leaks extends the lifespan of transmission components.
example of bellhousing in transmission Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com